OPTICAL PROPERTIES of Nanomaterials
... In cases where n < 1, the velocity which one needs to consider (instead of the 'phase velocity') is the 'group velocity (vg)' (or in still other cases the 'signal velocity' (vs)), which will be less than 'c'. [i.e. causality will not be violated!]. In negative refractive index materials (or typi ...
... In cases where n < 1, the velocity which one needs to consider (instead of the 'phase velocity') is the 'group velocity (vg)' (or in still other cases the 'signal velocity' (vs)), which will be less than 'c'. [i.e. causality will not be violated!]. In negative refractive index materials (or typi ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... where the first integral is evaluated over the body volume and the second over the surface. The quantity Q computed according to (5) is exactly the same as in the conventional theory. However, my calculations show that the volume contribution, q (V) ∝ Im(με ). I argue that in passive media, the sec ...
... where the first integral is evaluated over the body volume and the second over the surface. The quantity Q computed according to (5) is exactly the same as in the conventional theory. However, my calculations show that the volume contribution, q (V) ∝ Im(με ). I argue that in passive media, the sec ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... nanoparticles using unstructured (gradientless) light. Intuitively, one might expect that when a uniform light beam impinges on a polarizable body, the translational force acting on the body should always push it towards the direction of propagation. Notably, several groups demonstrated theoreticall ...
... nanoparticles using unstructured (gradientless) light. Intuitively, one might expect that when a uniform light beam impinges on a polarizable body, the translational force acting on the body should always push it towards the direction of propagation. Notably, several groups demonstrated theoreticall ...
Optical Tractor Beam with Chiral Light
... of isotropic media whose electromagnetic response depends on the handedness of its structural unities [28], and is characterized by a magneto-electric coupling that breaks the degeneracy between two circularly polarized plane waves so that the refractive index increases for one circular polarization ...
... of isotropic media whose electromagnetic response depends on the handedness of its structural unities [28], and is characterized by a magneto-electric coupling that breaks the degeneracy between two circularly polarized plane waves so that the refractive index increases for one circular polarization ...
PDF Version - Physics (APS)
... are much smaller than the relevant wavelength, incident light will see only an average response and a reduced effective permittivity. More complex structures, such as tiny metallic resonators, can produce more exotic effects, including negative refractive indices. Provided that the structure remains ...
... are much smaller than the relevant wavelength, incident light will see only an average response and a reduced effective permittivity. More complex structures, such as tiny metallic resonators, can produce more exotic effects, including negative refractive indices. Provided that the structure remains ...
Intra-European Fellowships (IEF)
... Here, we have discovered a special effect relating to the magnetism of one of such perovskite-oxides; lanthanummanganese-oxide. This material consists of stackings of LaMnO3 unit cells, quite comparable to stacking blocks of LEGO. In this case, the individual building blocks are only 0.4 nanometer ...
... Here, we have discovered a special effect relating to the magnetism of one of such perovskite-oxides; lanthanummanganese-oxide. This material consists of stackings of LaMnO3 unit cells, quite comparable to stacking blocks of LEGO. In this case, the individual building blocks are only 0.4 nanometer ...
3D Electromagnetic Field Simulation in Microwave Ovens: a Tool to
... Abstract: In microwave heating applications, the energy is introduced directly into the volume of the material and as consequence the quality of the process is highly dependent on the uniformity of the electromagnetic field distribution along it. That is, the non uniformity of the heating is a poten ...
... Abstract: In microwave heating applications, the energy is introduced directly into the volume of the material and as consequence the quality of the process is highly dependent on the uniformity of the electromagnetic field distribution along it. That is, the non uniformity of the heating is a poten ...
electromagnetic waves - Effingham County Schools
... These are the highest-energy electromagnetic waves and can penetrate through several centimeters of lead. Gamma rays are produced by processes that occur in atomic nuclei. Both X-rays and gamma rays are used in a technique called radiation therapy to kill diseased cells in the human body. ...
... These are the highest-energy electromagnetic waves and can penetrate through several centimeters of lead. Gamma rays are produced by processes that occur in atomic nuclei. Both X-rays and gamma rays are used in a technique called radiation therapy to kill diseased cells in the human body. ...
electromagnetic waves - Effingham County Schools
... These are the highest-energy electromagnetic waves and can penetrate through several centimeters of lead. Gamma rays are produced by processes that occur in atomic nuclei. Both X-rays and gamma rays are used in a technique called radiation therapy to kill diseased cells in the human body. ...
... These are the highest-energy electromagnetic waves and can penetrate through several centimeters of lead. Gamma rays are produced by processes that occur in atomic nuclei. Both X-rays and gamma rays are used in a technique called radiation therapy to kill diseased cells in the human body. ...
Frequency Dependence of Polarization: When a dielectric is placed
... capacitors. Note the very high value of mica, which is one of the reasons it was used in early ceramic disk capacitors. Nonlinear Dielectrics Nonlinear dielectrics have permanent dipoles that interact to give a polarization in the absence of an applied electric field. These materials are the ferroel ...
... capacitors. Note the very high value of mica, which is one of the reasons it was used in early ceramic disk capacitors. Nonlinear Dielectrics Nonlinear dielectrics have permanent dipoles that interact to give a polarization in the absence of an applied electric field. These materials are the ferroel ...
Negative Refraction and Left-handed electromagnetism in
... Furthermore these materials are highly absorptive, and unlikely to be scaled to three dimensions or to smaller sizes suitable for applications at optical frequencies 1, 6. ...
... Furthermore these materials are highly absorptive, and unlikely to be scaled to three dimensions or to smaller sizes suitable for applications at optical frequencies 1, 6. ...
CRYSTALLINE MATERIALS
... are two different directions of propagation through the crystal, depending on the direction of propagation Optic axes: directions in the crystal along which the velocities of the two orthogonally polarized waves are the same ...
... are two different directions of propagation through the crystal, depending on the direction of propagation Optic axes: directions in the crystal along which the velocities of the two orthogonally polarized waves are the same ...
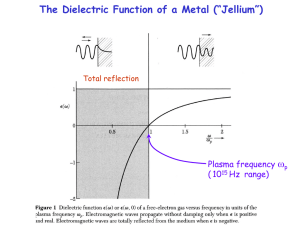
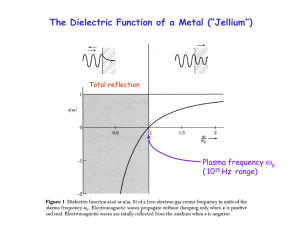
Plasmonics
... follow the field until they have compensated it. An example is the image charge, which exactly cancels the field of any external charge. This is also true for an electromagnetic wave, where electrons respond to the changing external field. As a result, the electromagnetic wave cannot enter a metal a ...
... follow the field until they have compensated it. An example is the image charge, which exactly cancels the field of any external charge. This is also true for an electromagnetic wave, where electrons respond to the changing external field. As a result, the electromagnetic wave cannot enter a metal a ...
Lecture 30/31
... Most metamaterials with negative refractive index have been made for microwaves (below left). Such devices are interesting for making an airplane invisible to radar (wavelength 3 cm) . ...
... Most metamaterials with negative refractive index have been made for microwaves (below left). Such devices are interesting for making an airplane invisible to radar (wavelength 3 cm) . ...
Fang
... o I started to talk about mechanical properties but he stopped me and wanted me to talk about magnetic properties first, so I said iron is ferromagnetic but copper is not. It seemed like he just ...
... o I started to talk about mechanical properties but he stopped me and wanted me to talk about magnetic properties first, so I said iron is ferromagnetic but copper is not. It seemed like he just ...
resonant material processing using (ultra-)short
... antinodes. The emerging structures have dimensions which are in the order of the wavelength of the laser making them considerably smaller than the actual beam diameter. The goal is now to find these resonance conditions for a variety of materials and to reliably adjust them. In order to achieve that ...
... antinodes. The emerging structures have dimensions which are in the order of the wavelength of the laser making them considerably smaller than the actual beam diameter. The goal is now to find these resonance conditions for a variety of materials and to reliably adjust them. In order to achieve that ...
Introduction to Magnetic Neutron Diffraction and Magnetic Structures
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
... The determination of magnetic structures of crystalline materials using neutron diffraction is one of the major specific applications of the use of neutrons for studying the properties of condensed matter. The knowledge of the magnetic ordering in materials provides important clues for understanding ...
Magnetism and Matter
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
... Magnetic field or magnetic flux density B will form at some point in space when an external free current loop is switched on or magnetic material is placed at that location. A charge, q moving with velocity, v generates a field, B in a perpendicular direction of its velocity vector. By Lorentz force ...
lattice of dielectric particles with double negative response
... sometimes called double negative (DNG) media or Veselago media, have been intensively studied. Some important practical applications, for example in antenna techniques, require isotropic effective permittivity and permeability. Unfortunately, most of the known designs are strongly anisotropic. This ...
... sometimes called double negative (DNG) media or Veselago media, have been intensively studied. Some important practical applications, for example in antenna techniques, require isotropic effective permittivity and permeability. Unfortunately, most of the known designs are strongly anisotropic. This ...
Faculty Mentor: Dr. Robert Ryan Project Supervisor: Dr. George
... ferromagnetic materials) to create multiferroic composite materials. In multiferroic composite materials, indirect coupling between electric and magnetic energies is created through mechanical strain. An electric field is first applied to piezoelectric material, which are bonded onto magnetostrictiv ...
... ferromagnetic materials) to create multiferroic composite materials. In multiferroic composite materials, indirect coupling between electric and magnetic energies is created through mechanical strain. An electric field is first applied to piezoelectric material, which are bonded onto magnetostrictiv ...
Abstract
... Spin phenomena in two dimensional materials Jaroslav Fabian, University of Regensburg Two dimensional materials, such as graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, or black phosphorous, offer immense opportunities for electronics and spintronics [1]. Being ultimately thin these materials could make ...
... Spin phenomena in two dimensional materials Jaroslav Fabian, University of Regensburg Two dimensional materials, such as graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, or black phosphorous, offer immense opportunities for electronics and spintronics [1]. Being ultimately thin these materials could make ...
17.1 The Nature of the Electromagnetic Waves
... • When a charged particle changes its motion, its magnetic field changes • The changing magnetic field causes the electric field to change • When one field vibrates, so does the other • **The two fields constantly causes each other to change and this produces an Electromagnetic wave** ...
... • When a charged particle changes its motion, its magnetic field changes • The changing magnetic field causes the electric field to change • When one field vibrates, so does the other • **The two fields constantly causes each other to change and this produces an Electromagnetic wave** ...
Slide 1
... Metals, plastics, ceramics, glass and fibres are some of the main categories for materials. If we look around, everything we see is made from a material, sometimes more than one .... ...
... Metals, plastics, ceramics, glass and fibres are some of the main categories for materials. If we look around, everything we see is made from a material, sometimes more than one .... ...
Metamaterial

Metamaterials are materials engineered to have properties that have not yet been found in nature. They are made from assemblies of multiple elements fashioned from conventional materials such as metals or plastics. The materials are usually arranged in repeating patterns, often at microscopic or smaller scales that are smaller than the wavelengths of the phenomena they influence. Metamaterials derive their properties not from the properties of the base materials, but from their designed structure. Their precise shape, geometry, size, orientation and arrangement gives them their properties.Appropriately designed metamaterials can affect waves of electromagnetic radiation or sound in a manner not observed in bulk materials. Those that exhibit a negative index of refraction for particular wavelengths have attracted significant research. These materials are known as negative index metamaterials.Potential applications of metamaterials are diverse and include remote aerospace applications, sensor detection and infrastructure monitoring, smart solar power management, crowd control, radomes, high-frequency battlefield communication and lenses for high-gain antennas, improving ultrasonic sensors, and even shielding structures from earthquakes. Metamaterials offer the potential to create superlenses. Such a lens could allow imaging below the diffraction limit that is the minimum resolution that can be achieved by a given wavelength. A form of 'invisibility' was demonstrated using gradient-index materials. Acoustic and seismic metamaterials are also research areas.Metamaterial research is interdisciplinary and involves such fields as electrical engineering, electromagnetics, classical optics, solid state physics, microwave and antennae engineering, optoelectronics, material sciences, nanoscience and semiconductor engineering.