Chapter 3 GAUSS` LAW
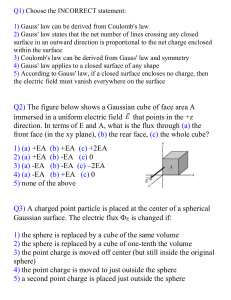
... net flux out is zero. However, this does not mean that there is not electric field. Actually one has flux flowing inward in some locations and outwards at others, such that the net total is zero as seen in Figure 5. ...
... net flux out is zero. However, this does not mean that there is not electric field. Actually one has flux flowing inward in some locations and outwards at others, such that the net total is zero as seen in Figure 5. ...
The Mediums for Light are Hiding in Plain Sight
... The propagation of light remains one of the enduring mysteries of science. Unlike every other known kind of wave, it travels at a constant speed through empty space without a medium of propagation. What supports its travel in empty space? Why is its speed so constant? And why is it so very fast? Eve ...
... The propagation of light remains one of the enduring mysteries of science. Unlike every other known kind of wave, it travels at a constant speed through empty space without a medium of propagation. What supports its travel in empty space? Why is its speed so constant? And why is it so very fast? Eve ...
Theory of Nanometric Optical Tweezers
... The proposed nanometric optical tweezers rely on the strongly enhanced electric field at a sharply pointed metal tip under laser illumination. The near field close to the tip mainly consists of evanescent components which decay rapidly with distance from the tip. The utilization of the metal tip for ...
... The proposed nanometric optical tweezers rely on the strongly enhanced electric field at a sharply pointed metal tip under laser illumination. The near field close to the tip mainly consists of evanescent components which decay rapidly with distance from the tip. The utilization of the metal tip for ...
Dielectric
A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization. Because of dielectric polarization, positive charges are displaced toward the field and negative charges shift in the opposite direction. This creates an internal electric field that reduces the overall field within the dielectric itself. If a dielectric is composed of weakly bonded molecules, those molecules not only become polarized, but also reorient so that their symmetry axes align to the field.The study of dielectric properties concerns storage and dissipation of electric and magnetic energy in materials. Dielectrics are important for explaining various phenomena in electronics, optics, and solid-state physics.