Foundations of Geometry
... All of the points of a which lie upon the same side of O, when taken together, are called the half-ray emanating from O. Hence, each point of a straight line divides it into two half-rays. Making use of the notation of theorem 5, we say: The points A, A′ lie in the plane α upon one and the same side ...
... All of the points of a which lie upon the same side of O, when taken together, are called the half-ray emanating from O. Hence, each point of a straight line divides it into two half-rays. Making use of the notation of theorem 5, we say: The points A, A′ lie in the plane α upon one and the same side ...
Section 9.3 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
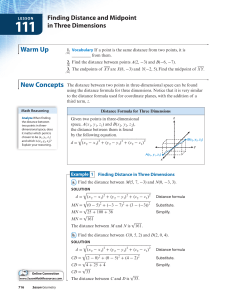
... When two planes intersect, we call the angle between the planes a dihedral angle. Figure 9.41 shows three dihedral angles and their measures. A dihedral angle is measured by measuring the angle whose sides lie in the planes and are perpendicular to the line of intersection of the two planes. Parts a ...
... When two planes intersect, we call the angle between the planes a dihedral angle. Figure 9.41 shows three dihedral angles and their measures. A dihedral angle is measured by measuring the angle whose sides lie in the planes and are perpendicular to the line of intersection of the two planes. Parts a ...
Chapter 1
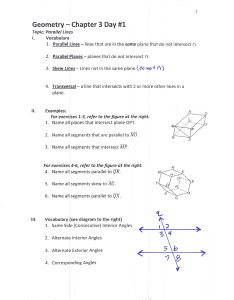
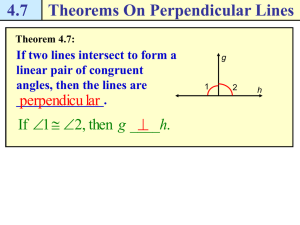
... Postulate 3: Through any two points there can be exactly one line. Postulate 4: Through any three noncollinear points there can be exactly one plane. Postulate 5: If two points lie in a plane, then the line they lie on is in the same plane. Postulate 6: Where two planes intersect, their intersection ...
... Postulate 3: Through any two points there can be exactly one line. Postulate 4: Through any three noncollinear points there can be exactly one plane. Postulate 5: If two points lie in a plane, then the line they lie on is in the same plane. Postulate 6: Where two planes intersect, their intersection ...
Geometry and Measurement of Plane Figures Activity Set 3 Trainer
... angle A geometric figure composed of two rays or line segments that share the same endpoint, called a vertex. area The number of square units in a region. circle The set of all points in a plane that are the same distance from a fixed point (the center of the circle). circumference The perimeter of ...
... angle A geometric figure composed of two rays or line segments that share the same endpoint, called a vertex. area The number of square units in a region. circle The set of all points in a plane that are the same distance from a fixed point (the center of the circle). circumference The perimeter of ...
Subject Geometry Academic Grade 10 Unit # 2 Pacing 8
... Prove two triangles congruent using the SAS Theorem Prove two Triangles congruent using the ASA Theorem Prove two triangles congruent using the AAS Theorem Prove two triangles congruent using the HL Theorem Generate formal constructions of regular polygons inscribed in a circle with paper folding, g ...
... Prove two triangles congruent using the SAS Theorem Prove two Triangles congruent using the ASA Theorem Prove two triangles congruent using the AAS Theorem Prove two triangles congruent using the HL Theorem Generate formal constructions of regular polygons inscribed in a circle with paper folding, g ...