Review Chapter 3 Part 1
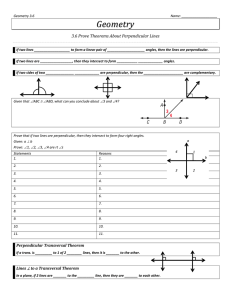
... 5. List a 3 pairs of pair of vertical angles; ____________, ______________, and _________________. 6. List 2 sets of a linear pair; _______________________ and ______________________. Think of each segment in the diagram of a rectangular box as a part of a line. Which line(s) or plane(s) contain poi ...
... 5. List a 3 pairs of pair of vertical angles; ____________, ______________, and _________________. 6. List 2 sets of a linear pair; _______________________ and ______________________. Think of each segment in the diagram of a rectangular box as a part of a line. Which line(s) or plane(s) contain poi ...
CCGPS Geometry Unit 1 ParentLetter
... Endpoint: The point at each end of a line segment or at the beginning of a ray. Image: The result of a transformation. Intersection: The point at which two or more lines intersect or cross. Isometry: a distance preserving map of a geometric figure to another location using a reflection, rota ...
... Endpoint: The point at each end of a line segment or at the beginning of a ray. Image: The result of a transformation. Intersection: The point at which two or more lines intersect or cross. Isometry: a distance preserving map of a geometric figure to another location using a reflection, rota ...
Chapter 3
... Remark: In an algebraic context equivalence classes are often called cosets. For example, lines and planes in Euclidean geometry (affine subspaces) are cosets of the underlying linear algebra, the equivalence relation on the vectors being that their difference belongs to the true subspace (line or p ...
... Remark: In an algebraic context equivalence classes are often called cosets. For example, lines and planes in Euclidean geometry (affine subspaces) are cosets of the underlying linear algebra, the equivalence relation on the vectors being that their difference belongs to the true subspace (line or p ...