Revised_Second_Level_Parent_Leaflet_Maths_1_1_1_
... Each draw 10 circles. Write a different two-digit number in each circle – but not a multiple of ten (10, 20, 30, 40…). In turn, choose one of the other player’s numbers. The other player must then say what to add to that number to make 100, e.g. choose 64, add 36. If the other player is right, she c ...
... Each draw 10 circles. Write a different two-digit number in each circle – but not a multiple of ten (10, 20, 30, 40…). In turn, choose one of the other player’s numbers. The other player must then say what to add to that number to make 100, e.g. choose 64, add 36. If the other player is right, she c ...
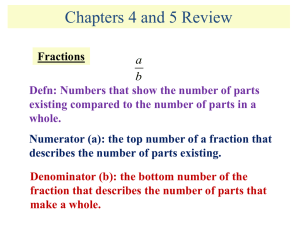
1.02 Fractions Fact Sheet
... To subtract fractions, the fractions must have the same denominator. Subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same. For example: 4/6 - 1/6 = 3/6 If the denominators are not the same, you must make them the same or find common denominators. The easiest way tot do this is to look at the h ...
... To subtract fractions, the fractions must have the same denominator. Subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same. For example: 4/6 - 1/6 = 3/6 If the denominators are not the same, you must make them the same or find common denominators. The easiest way tot do this is to look at the h ...
York-6_SOLReview11-12 - pams
... Find the value of numerical expressions, using order of operations, mental mathematics, and appropriate tools. Exponents are limited to positive values. ...
... Find the value of numerical expressions, using order of operations, mental mathematics, and appropriate tools. Exponents are limited to positive values. ...
Document
... Do you have what it takes to join us and help solve this mystery? We’ll lead you through a review of fractions and you might even learn something new. Then we’ll ask you some questions and if you can answer them all by the end of this class period, we’ll give you a copy of our notes with all of the ...
... Do you have what it takes to join us and help solve this mystery? We’ll lead you through a review of fractions and you might even learn something new. Then we’ll ask you some questions and if you can answer them all by the end of this class period, we’ll give you a copy of our notes with all of the ...