PPT - Carnegie Mellon School of Computer Science
... A Natural Intuition Intuitively, what does it mean to find a bijection between a set A and ? It means to list the elements of A in some order so that if you read down the list, every element will get read. ...
... A Natural Intuition Intuitively, what does it mean to find a bijection between a set A and ? It means to list the elements of A in some order so that if you read down the list, every element will get read. ...
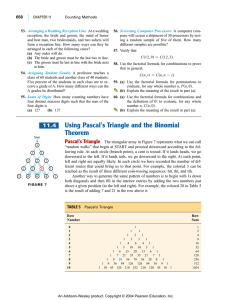
UNIT 11.4: Pascal`s Triangle
... “random walks” that begin at START and proceed downward according to the following rule. At each circle (branch point), a coin is tossed. If it lands heads, we go downward to the left. If it lands tails, we go downward to the right. At each point, left and right are equally likely. In each circle we ...
... “random walks” that begin at START and proceed downward according to the following rule. At each circle (branch point), a coin is tossed. If it lands heads, we go downward to the left. If it lands tails, we go downward to the right. At each point, left and right are equally likely. In each circle we ...
Fraction Tips
... Add the numerators of the two fractions Place that sum over the common denominator. If this fraction is improper (numerator larger than or equal to the denominator) then convert it to a mixed number Add the integer portions of the two mixed numbers If adding the fractional parts created a mixed numb ...
... Add the numerators of the two fractions Place that sum over the common denominator. If this fraction is improper (numerator larger than or equal to the denominator) then convert it to a mixed number Add the integer portions of the two mixed numbers If adding the fractional parts created a mixed numb ...
sig figs - USD305.com
... It is always equal to 1 When multiplying by a conversion factor, the numerical value is changed, but the actual size of the quantity remains the same ...
... It is always equal to 1 When multiplying by a conversion factor, the numerical value is changed, but the actual size of the quantity remains the same ...
2-DSP Fundamentals
... When defining a system in term of its coefficients, the finite precision affect the behavior of the system itself. Though there is a grid of possible locations where system’s poles can be placed. This grid depends first of the word-length and second of the structure adopted to implement of the syste ...
... When defining a system in term of its coefficients, the finite precision affect the behavior of the system itself. Though there is a grid of possible locations where system’s poles can be placed. This grid depends first of the word-length and second of the structure adopted to implement of the syste ...