significant
... Digits that are always significant: 1. Non-zero digits. 2. Zeroes between two significant digits. 3. All final zeroes to the right of a decimal point. Digits that are never significant: 4. Leading zeroes to the right of a decimal point. (0.002 cm has only one significant ...
... Digits that are always significant: 1. Non-zero digits. 2. Zeroes between two significant digits. 3. All final zeroes to the right of a decimal point. Digits that are never significant: 4. Leading zeroes to the right of a decimal point. (0.002 cm has only one significant ...
Rational Numbers Notes
... Day 1 (Lesson 2.1 Part I) Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers Lesson Focus: We begin our unit learning about rational numbers and learn to reduce fractions, compare and order fractions, express fractions with a common denominator and convert fractions into decimal form. What are Rational Numbers ...
... Day 1 (Lesson 2.1 Part I) Comparing and Ordering Rational Numbers Lesson Focus: We begin our unit learning about rational numbers and learn to reduce fractions, compare and order fractions, express fractions with a common denominator and convert fractions into decimal form. What are Rational Numbers ...
ppt
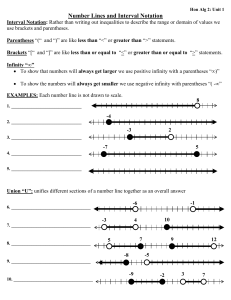
... • Order Property for Real Numbers indicates how to use inequality signs. If a and b are real numbers, a < b means a is to the left of b on a number line. a > b means a is to the right of b on a number line. • Absolute value of a number is the distance of that number away from 0. a 0, since distan ...
... • Order Property for Real Numbers indicates how to use inequality signs. If a and b are real numbers, a < b means a is to the left of b on a number line. a > b means a is to the right of b on a number line. • Absolute value of a number is the distance of that number away from 0. a 0, since distan ...
LP.092514
... The Integers are sometimes called signed numbers. Z stands for the set of Integers. Z = {…, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}. The set of Integers have both Positive and Negative Whole Numbers. The Rationals are symbolized by Q. The Integers is a subset of Q. All fractions with an Integer for ...
... The Integers are sometimes called signed numbers. Z stands for the set of Integers. Z = {…, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}. The set of Integers have both Positive and Negative Whole Numbers. The Rationals are symbolized by Q. The Integers is a subset of Q. All fractions with an Integer for ...
Scope and Sequence - year 9 - mathsyear7-12
... They comprehend that irrational numbers have an infinite non-terminating decimal form. They specify decimal rational approximations for square roots of primes, rational numbers that are not perfect squares, the golden ratio φ , and simple fractions of π correct to a required decimal place accuracy. ...
... They comprehend that irrational numbers have an infinite non-terminating decimal form. They specify decimal rational approximations for square roots of primes, rational numbers that are not perfect squares, the golden ratio φ , and simple fractions of π correct to a required decimal place accuracy. ...
Chapter 1
... two integers. Includes all numbers whose decimal forms are either terminating decimals (4, 2.5) or repeating decimals (0.33…). ...
... two integers. Includes all numbers whose decimal forms are either terminating decimals (4, 2.5) or repeating decimals (0.33…). ...
Lecture14 Logic Circuits
... Positive and Negative Binary Numbers This can be used in subtraction operation. To subtract number B from A we add two’s complement of B to A Example: Compute A-B=25-11 using binary adders 1) Find binary representations A=011001, B=001011 2) Find two’s complement of B -B=110101 3) Add A+(-B) using ...
... Positive and Negative Binary Numbers This can be used in subtraction operation. To subtract number B from A we add two’s complement of B to A Example: Compute A-B=25-11 using binary adders 1) Find binary representations A=011001, B=001011 2) Find two’s complement of B -B=110101 3) Add A+(-B) using ...