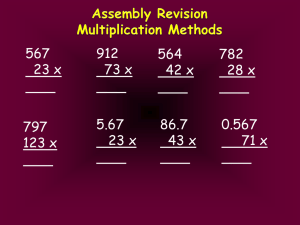
Significant Figures
... Converting One Unit to Another • Read. Identify the known and unknown. • Plan. Identify the principles or equations needed to solve the problem. • Set up. Use dimensional analysis to solve the problem, canceling all units except the unit needed in the answer. • Calculate the answer and round for sig ...
... Converting One Unit to Another • Read. Identify the known and unknown. • Plan. Identify the principles or equations needed to solve the problem. • Set up. Use dimensional analysis to solve the problem, canceling all units except the unit needed in the answer. • Calculate the answer and round for sig ...
Miss Sutherland - Ordering fractions
... Here’s an easier example, with just 2 fractions to start us off. ...
... Here’s an easier example, with just 2 fractions to start us off. ...
PAL Chapter 04 - usd352prealgebra8
... will find extra examples for each lesson in the Student Edition of your textbook. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to www.pre-alg.com/extra_examples. ...
... will find extra examples for each lesson in the Student Edition of your textbook. When you finish exploring, exit the browser program to return to this presentation. If you experience difficulty connecting to the Web site, manually launch your Web browser and go to www.pre-alg.com/extra_examples. ...
Full text
... satisfies Benford’s law (base B) if the probability of a first digit base B of d is logB (1 + 1/d), or more generally the probability that the significand1 is at most s is logB (s). Benford’s law has applications in disciplines ranging from accounting (where it is used to detect fraud) to zoology an ...
... satisfies Benford’s law (base B) if the probability of a first digit base B of d is logB (1 + 1/d), or more generally the probability that the significand1 is at most s is logB (s). Benford’s law has applications in disciplines ranging from accounting (where it is used to detect fraud) to zoology an ...
Ordering fractions
... This means that we check to see which numbers are in the 6 times table, and the 9 times table. We need a number that appears in both lists. ...
... This means that we check to see which numbers are in the 6 times table, and the 9 times table. We need a number that appears in both lists. ...
Slide 1
... This means that we check to see which numbers are in the 6 times table, and the 9 times table. We need a number that appears in both lists. ...
... This means that we check to see which numbers are in the 6 times table, and the 9 times table. We need a number that appears in both lists. ...
A2-Level Maths: Core 3 for Edexcel
... An algebraic fraction is called an improper fraction when the numerator is a polynomial of degree greater than, or equal to, the degree of the denominator. ...
... An algebraic fraction is called an improper fraction when the numerator is a polynomial of degree greater than, or equal to, the degree of the denominator. ...