April 18
... Second kind: Initial conditions: S(p,0)=0 for all p1, S(p,p)=1 for all p0. Recurrence: S(p,k) = kS(p-1,k)+S(p-1,k-1) if 0
... Second kind: Initial conditions: S(p,0)=0 for all p1, S(p,p)=1 for all p0. Recurrence: S(p,k) = kS(p-1,k)+S(p-1,k-1) if 0
Connecticut Curriculum Design Unit Planning Organizer Grade 7
... • front-end estimation with adjusting (using the highest place value and estimating from the front end making adjustments to the estimate by taking into account the remaining amounts), • clustering around an average (when the values are close together an average value is selected and multiplied by t ...
... • front-end estimation with adjusting (using the highest place value and estimating from the front end making adjustments to the estimate by taking into account the remaining amounts), • clustering around an average (when the values are close together an average value is selected and multiplied by t ...
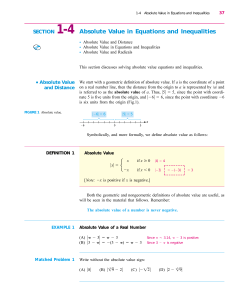
Lesson_1-4_Absolute_Value 09-10
... Assessment: Checkpoint Quiz pg. 35 Top LEQ Answer: A number line can be used to graph integers. Once they are graphed the numbers are automatically in order from least to greatest going left to right. Opposites are found by either placing a negative sign or removing a negative sign from an integ ...
... Assessment: Checkpoint Quiz pg. 35 Top LEQ Answer: A number line can be used to graph integers. Once they are graphed the numbers are automatically in order from least to greatest going left to right. Opposites are found by either placing a negative sign or removing a negative sign from an integ ...
2. 6810 Session 2 a. Follow-ups to Session 1
... 10%, you shouldn’t give 10 digits in your answer, but only a couple. In Session 1, what you really determined was upper and lower bound for such quantities. • The “intentional bug” in precision.cpp was that the #include line at the top
was left out. This statement makes available commands ...
... 10%, you shouldn’t give 10 digits in your answer, but only a couple. In Session 1, what you really determined was upper and lower bound for such quantities. • The “intentional bug” in precision.cpp was that the #include