
Galaxies
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
Active Galactic Nuclei: are they important?
... •Active Galactic Nuclei are fantastic subject for somebody who likes to apply GR •They consist of a massive black hole surrounded by plentiful material flowing in and out •This material emits radiation so we can trace what is happening close to a black hole ...
... •Active Galactic Nuclei are fantastic subject for somebody who likes to apply GR •They consist of a massive black hole surrounded by plentiful material flowing in and out •This material emits radiation so we can trace what is happening close to a black hole ...
click here - CAPSTONE 2011
... is it from the Sun and where does that place it with respect to the orbits of the major planets. (Find the values for the planets in the appendices to the text book.) 2. What is the angular diameter of a star identical to the Sun, at a distance of 1pc from Earth? 10pc? 100pc? To use the skinny trian ...
... is it from the Sun and where does that place it with respect to the orbits of the major planets. (Find the values for the planets in the appendices to the text book.) 2. What is the angular diameter of a star identical to the Sun, at a distance of 1pc from Earth? 10pc? 100pc? To use the skinny trian ...
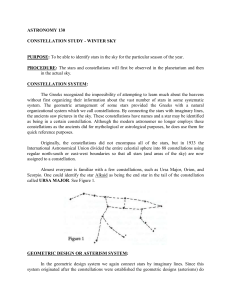
ASTRONOMY 130
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
... It is easier to locate a celestial object if some prominent constellation or asterism can be found and used as a reference point. Ursa Major (the Big Dipper) serves as a good reference point for the north circumpolar constellations. Locate the Big Dipper. Begin with the star at the tip of the handle ...
Chapter 09 - The Independent School
... Example: Star Radii Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. ...
... Example: Star Radii Polaris has just about the same spectral type (and thus surface temperature) as our sun, but it is 10,000 times brighter than our sun. ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... A Comparison of the Nearest and Brightest Stars • The nearest stars to the Sun are thought to represent the true distribution of stars in the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy. • To truly understand the Galaxy, these stars must be studied. ...
... A Comparison of the Nearest and Brightest Stars • The nearest stars to the Sun are thought to represent the true distribution of stars in the disk of the Milky Way Galaxy. • To truly understand the Galaxy, these stars must be studied. ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... well as its history and its rise from a little known occurrence to a headline-grabbing phenomenon. It looked at whether its occurrence can be accurately predicted, and the possibly of its power being ...
... well as its history and its rise from a little known occurrence to a headline-grabbing phenomenon. It looked at whether its occurrence can be accurately predicted, and the possibly of its power being ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... the first planetary nebula discovered in a globular cluster – Pease 1 (K 648) – as well as 112 variable stars, 9 known pulsars discovered to date. Slide 29: Globular cluster NGC 1846 is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy 160,000 LY away in the southern constellation Doradus. The population ...
... the first planetary nebula discovered in a globular cluster – Pease 1 (K 648) – as well as 112 variable stars, 9 known pulsars discovered to date. Slide 29: Globular cluster NGC 1846 is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud galaxy 160,000 LY away in the southern constellation Doradus. The population ...
Exploring Stars - Discovery Education
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
... 1. Talk about the life of a star. A good way to introduce this topic is to show Exploring Stars. After watching the program, talk about the different types of stars found in the universe. What are stars? What are they made of? How is a red star different from a blue star? Discuss and review the life ...
Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date
... been dedicatedto study this common-envelope stage, but the many questions related to this process are yet to be answered. If one binary survives the common-envelope, the binary will emerge asa white dwarfaccompanied by low-mass main sequence star in close orbit, or often referred as the post commone ...
... been dedicatedto study this common-envelope stage, but the many questions related to this process are yet to be answered. If one binary survives the common-envelope, the binary will emerge asa white dwarfaccompanied by low-mass main sequence star in close orbit, or often referred as the post commone ...
Chapter 12 Quiz, Nov. 28, 2012, Astro 162, Section 4 12-1
... 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars formed in the spiral arms explode as supernovae before they emerge from the arms. Therefore, these stars are not found between the arms of spiral galaxies. 12-33. Describe the Sun’s motion through ...
... 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars formed in the spiral arms explode as supernovae before they emerge from the arms. Therefore, these stars are not found between the arms of spiral galaxies. 12-33. Describe the Sun’s motion through ...
Binocular Sky Newsletter
... In October, we are able to look out of the plane of the Galaxy during the evening. This makes more globular clusters and galaxies available for observation. Very well placed this month are M81 (Bode's Nebula) and M82 (The Cigar Galaxy), both of which are easy in a 50mm binocular. These can be used a ...
... In October, we are able to look out of the plane of the Galaxy during the evening. This makes more globular clusters and galaxies available for observation. Very well placed this month are M81 (Bode's Nebula) and M82 (The Cigar Galaxy), both of which are easy in a 50mm binocular. These can be used a ...
The difficulty of forming large disk galaxies with small bulges
... What is mode of quenching in this picture ? Mergers ? ...
... What is mode of quenching in this picture ? Mergers ? ...
THE METER STICK MODEL OF THE SOLAR SYSTEM
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
... 5. Ask the students to predict how long it would take to run or walk 63,360 inches. 6. Explain that since an inch is so small compared to the total distance being measured, it is hard to imagine how far 63,360 inches is. For this reason, it is difficult to predict how long it would take to run that ...
The Sagittarius dwarf irregular galaxy: Metallicity and stellar
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
distant stars nearby star parallax angle The principle of geometrical
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
... Does the star Vega in Lyra appear exceptionally bright because it’s an intrinsically bright star, or simply because it’s unusually close by? What about Betelgeuse in Orion? If we didn’t know the distances to these stars, we wouldn’t know that Betelgeuse is a red giant star, with a much greater intri ...
The Sagittarius dwarf irregular galaxy: Metallicity and stellar
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
The Sagittarius dwarf irregular galaxy
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
... (Saviane et al. 2001). The new estimate, 12 + log(O/H) = 7.23 ± 0.20, is by 0.2 dex more metal-poor than found by Skillman et al. (1989b). The photometric properties of the Hii regions were investigated by Strobel et al. (1991), who detected 3 regions in their 2.0 5 square field. High-resolution, hi ...
BREATHING IN LOW MASS GALAXIES: A STUDY - N
... the fluctuations are strictly periodic, though they would be unlikely to be so in a full cosmological context. The periods of their oscillation are 292, 342, and 387 Myr, respectively. These times are characteristic of the dynamical time of the central region of constant density gas that forms after ...
... the fluctuations are strictly periodic, though they would be unlikely to be so in a full cosmological context. The periods of their oscillation are 292, 342, and 387 Myr, respectively. These times are characteristic of the dynamical time of the central region of constant density gas that forms after ...
Star Basics
... the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. One example is the luminous H II region surrounding star cluster M ...
... the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. One example is the luminous H II region surrounding star cluster M ...
Transcript - Chandra X
... The southern hemisphere constellation Tucana is the location of the neighboring Small Magellanic Cloud Galaxy (SMC) – a member of the Local Group of galaxies along with the MWG, LMC and Andromeda. The SMC contains huge star formation regions. Slide 36: Polaris is a spectral type F7I supergiant star. ...
... The southern hemisphere constellation Tucana is the location of the neighboring Small Magellanic Cloud Galaxy (SMC) – a member of the Local Group of galaxies along with the MWG, LMC and Andromeda. The SMC contains huge star formation regions. Slide 36: Polaris is a spectral type F7I supergiant star. ...
Antlia, the Machine Pneumatique
... Alpha Antliae is an easy star to spot with NGC 3175, one of the most outstanding the naked eye in the far north-west of the spindles in appearance, is situated in the constellation. It displays a lovely warm far eastern part of Antlia, 1.3 degrees from orange colour – spectral type K4. This Hydra. T ...
... Alpha Antliae is an easy star to spot with NGC 3175, one of the most outstanding the naked eye in the far north-west of the spindles in appearance, is situated in the constellation. It displays a lovely warm far eastern part of Antlia, 1.3 degrees from orange colour – spectral type K4. This Hydra. T ...
Evolution of High
... Evolutionary High-Mass Stars – II Tracks in the H-R Diagram For high-mass stars, fusion of successively heavier and heavier elements (helium, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, etc) can take place in the core. • For medium-mass stars: As the star goes through several stages of core contraction, shell burnin ...
... Evolutionary High-Mass Stars – II Tracks in the H-R Diagram For high-mass stars, fusion of successively heavier and heavier elements (helium, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, etc) can take place in the core. • For medium-mass stars: As the star goes through several stages of core contraction, shell burnin ...
What powers luminous infrared galaxies?
... rectangles in Fig. 2) all LBol /LLyc ratios in the luminous IRAS galaxies are reduced significantly, but for UGC 5101, NGC 6240, and Arp 220 still not sufficiently to fit normal starburst models. The new ISO data now suggest that observations at midand far-infrared wavelengths are required to penetr ...
... rectangles in Fig. 2) all LBol /LLyc ratios in the luminous IRAS galaxies are reduced significantly, but for UGC 5101, NGC 6240, and Arp 220 still not sufficiently to fit normal starburst models. The new ISO data now suggest that observations at midand far-infrared wavelengths are required to penetr ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.








![Session: [B5B-3] S3 : Stars, Exoplanets and Stellar Systems Date](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747311_2-a6f8878211ea1c8526dde4b9d41aac5c-300x300.png)













