Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of beta brings us to NGC 5915 and 5916. The western most galaxy NGC 5915 is the brighter, a face-on barred spiral that ...
... North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of beta brings us to NGC 5915 and 5916. The western most galaxy NGC 5915 is the brighter, a face-on barred spiral that ...
argo and other tidal structures around the milky way
... Sun, between 220◦ < l < 300◦ comprises the presumed center of the Monoceros system. Two main overdensities can be seen in this system: CMa and Argo. We have found that Argo has 2-3 times more stars than CMa. ...
... Sun, between 220◦ < l < 300◦ comprises the presumed center of the Monoceros system. Two main overdensities can be seen in this system: CMa and Argo. We have found that Argo has 2-3 times more stars than CMa. ...
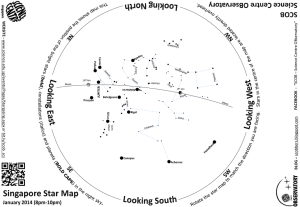
Star Map - Science Centre
... Located towards the South East of Orion’s belt is the brightest star in the sky, Sirius (scorching), belonging to the constellation Canis Major. Its brightness causes it to twinkle more than other stars as its light passes through our atmosphere. ...
... Located towards the South East of Orion’s belt is the brightest star in the sky, Sirius (scorching), belonging to the constellation Canis Major. Its brightness causes it to twinkle more than other stars as its light passes through our atmosphere. ...
Molecular Cooling Rates (Neufeld, Lepp and Melnick 1995)
... • How quickly is the outflowing material accelerated? • How does the envelope composition (dust and gas) relate to the photospheric abundances (C-rich or O-rich)? • What roles do photochemistry and shock chemistry play in the circumstellar envelopes of evolved stars? • What is the thermal structure ...
... • How quickly is the outflowing material accelerated? • How does the envelope composition (dust and gas) relate to the photospheric abundances (C-rich or O-rich)? • What roles do photochemistry and shock chemistry play in the circumstellar envelopes of evolved stars? • What is the thermal structure ...
on the mass distribution of stars in the solar neighbourhood
... radius of 10 pc the effects of observational selection against K and M dwarfs become rather strong. For this reason the authors are inclined to think that the results concerning this heliocentric sphere appear as realistic, i.e. the fraction of low-mass stars (under half solar mass) is about 50% and ...
... radius of 10 pc the effects of observational selection against K and M dwarfs become rather strong. For this reason the authors are inclined to think that the results concerning this heliocentric sphere appear as realistic, i.e. the fraction of low-mass stars (under half solar mass) is about 50% and ...
ted_2012_power_of_design
... Okay, this one’s big, as in the biggest engineering project in California history. Crucial to the success of replacing the east span of the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge was the ability to communicate to the general public how the world’s largest self-anchored suspension bridge would reshape the ...
... Okay, this one’s big, as in the biggest engineering project in California history. Crucial to the success of replacing the east span of the San Francisco–Oakland Bay Bridge was the ability to communicate to the general public how the world’s largest self-anchored suspension bridge would reshape the ...
A dozen new galaxies caught in the act: Gas stripping and extended
... radial velocity distribution of Coma cluster member galaxies. Our findings suggest that the most of the parent galaxies were recently captured by the Coma cluster potential and are now infalling toward the cluster center with their disk gas being stripped off and producing the observed Hα clouds. Su ...
... radial velocity distribution of Coma cluster member galaxies. Our findings suggest that the most of the parent galaxies were recently captured by the Coma cluster potential and are now infalling toward the cluster center with their disk gas being stripped off and producing the observed Hα clouds. Su ...
PHYS3380_110215_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... zone that is in thermal equilibrium and undergoes little or no mixing. •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously ...
... zone that is in thermal equilibrium and undergoes little or no mixing. •In stars of less than about 10 solar masses, the outer envelope of the star contains a region where partial ionization of hydrogen and helium raises the heat capacity. The relatively low temperature in this region simultaneously ...
The Strikingly Uniform, Highly Turbulent Interstellar Medium of the
... hosted by otherwise normal galaxies are likely to be at a key stage of their evolution –when feedback from the AGN may have started quenching star formation–, just about to become regular quasars and decay into dead elliptical galaxies (Sanders et al. 1988). W2246-0526 is the most extreme of these r ...
... hosted by otherwise normal galaxies are likely to be at a key stage of their evolution –when feedback from the AGN may have started quenching star formation–, just about to become regular quasars and decay into dead elliptical galaxies (Sanders et al. 1988). W2246-0526 is the most extreme of these r ...
Lecture18
... “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White Dwarfs tiny (size of Earth), Supergiants larger than the entire solar system! Thursday, November 4, 2010 ...
... “Luminosity class” used to distinguish a red main sequence (e.g. M5V) from a red supergiant (M5I). Sizes of stars vary tremendously: White Dwarfs tiny (size of Earth), Supergiants larger than the entire solar system! Thursday, November 4, 2010 ...
Stars - cayugascience
... With less gravity and lower pressures than other stars, the nuclear reactions in the core of low mass stars happen at a relatively slow rate. The stars therefore exist a long time, shining weakly as small red stars called red dwarfs (Figure 8.5). Like the light from a flashlight whose batteries are ...
... With less gravity and lower pressures than other stars, the nuclear reactions in the core of low mass stars happen at a relatively slow rate. The stars therefore exist a long time, shining weakly as small red stars called red dwarfs (Figure 8.5). Like the light from a flashlight whose batteries are ...
The Official Magazine of the University Of St Andrews Astronomical Society 1
... The vast majority of exoplanets found have been large gas giants, close to their parent star, with orbital periods of only a few days. Our gas giants, however, are orders of magnitude more distant from the sun than typical exoplanets are from their stars. Why is our Solar system so different to – wh ...
... The vast majority of exoplanets found have been large gas giants, close to their parent star, with orbital periods of only a few days. Our gas giants, however, are orders of magnitude more distant from the sun than typical exoplanets are from their stars. Why is our Solar system so different to – wh ...
Galaxies and Stars
... A) main sequence star with a temperature of approximately 4,000ºC and a luminosity of 100 B) main sequence star with a temperature of approximately 6,000ºC and a luminosity of 1 C) white dwarf star with a temperature of approximately 10,000ºC and a luminosity of ...
... A) main sequence star with a temperature of approximately 4,000ºC and a luminosity of 100 B) main sequence star with a temperature of approximately 6,000ºC and a luminosity of 1 C) white dwarf star with a temperature of approximately 10,000ºC and a luminosity of ...
Activities
... continuous cycle in the number of sunspots, which are the most visible tracer of the magnetic fields that cause all forms of solar activity. The solar cycle seems to be linked to changes in the Sun’s global magnetic field. At one solar activity maximum, the magnetic field is aligned so that a compas ...
... continuous cycle in the number of sunspots, which are the most visible tracer of the magnetic fields that cause all forms of solar activity. The solar cycle seems to be linked to changes in the Sun’s global magnetic field. At one solar activity maximum, the magnetic field is aligned so that a compas ...
Red Dwarf Stars: Ages, Rotation, Magnetic
... starspot modulations) continues to expand, as does the inventory of archival XUV observations. Recently, the photometric properties of several hundred dM stars from the Kepler database are being analyzed to determine the rotation rates, starspot areal coverage/distributions and stellar flare rates. ...
... starspot modulations) continues to expand, as does the inventory of archival XUV observations. Recently, the photometric properties of several hundred dM stars from the Kepler database are being analyzed to determine the rotation rates, starspot areal coverage/distributions and stellar flare rates. ...
The HIRES science case
... solve some of the issues, others remain puzzling and may hint to more fundamental problems in our understanding. For example, the migration timescale appears to be quite short, so why have not all the planets "fallen" into their star? Why is it that Jupiter appears not to have migrated significantl ...
... solve some of the issues, others remain puzzling and may hint to more fundamental problems in our understanding. For example, the migration timescale appears to be quite short, so why have not all the planets "fallen" into their star? Why is it that Jupiter appears not to have migrated significantl ...
Dark Matter In The 21st Century
... The WIMP-paradigm for dark matter has held up to much scrutiny, but what WIMPs actually are remains to be discovered ...
... The WIMP-paradigm for dark matter has held up to much scrutiny, but what WIMPs actually are remains to be discovered ...
Video Lesson Information Astronomy: Observations & Theories Astronomy 1
... Lesson 8 - The Family of Stars To determine how bright a star actually is, we need to know how far away it is. This lesson illustrates how to find distance to nearby stars and how to plot them on an H–R diagram. It also shows why binary stars are important for the study of stars and their mass–lumi ...
... Lesson 8 - The Family of Stars To determine how bright a star actually is, we need to know how far away it is. This lesson illustrates how to find distance to nearby stars and how to plot them on an H–R diagram. It also shows why binary stars are important for the study of stars and their mass–lumi ...
Document
... • We can measure the temperature of a star relatively easily by its spectral type or color. If the distance is known, then we can measure its luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is ...
... • We can measure the temperature of a star relatively easily by its spectral type or color. If the distance is known, then we can measure its luminosity, and then compute its radius. Note, however, that the radius measured this way is not very accurate, owing to the uncertainty in the distance. • Is ...
7 November 2012 X-ray Astrophysics
... at one particular colour, sharply peaked to form an emission line, usually superimposed on the underlying continuum emission. Similarly absorption lines at very specific colours indicate where particular energies of light have been absorbed from the general continuum emission by particular atoms an ...
... at one particular colour, sharply peaked to form an emission line, usually superimposed on the underlying continuum emission. Similarly absorption lines at very specific colours indicate where particular energies of light have been absorbed from the general continuum emission by particular atoms an ...
01_test_bank
... C) Nearly every atom from which we are made once (before the solar system formed) was inside of a star. D) Nearly every atom from which we are made was once inside our star, the Sun. E) Sagan thought that all of us have the potential to be movie (or TV) stars like he was. Answer: C 13) Which of the ...
... C) Nearly every atom from which we are made once (before the solar system formed) was inside of a star. D) Nearly every atom from which we are made was once inside our star, the Sun. E) Sagan thought that all of us have the potential to be movie (or TV) stars like he was. Answer: C 13) Which of the ...
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field Project Overview
... The velocity you calculated for this star is much less than the speed of light, so we could have found a decent approximation to the answer using z = v/c. But, if you use the approximation equation to calculate the recession velocity based on the spectral shift from the spectrum of a distant galaxy ...
... The velocity you calculated for this star is much less than the speed of light, so we could have found a decent approximation to the answer using z = v/c. But, if you use the approximation equation to calculate the recession velocity based on the spectral shift from the spectrum of a distant galaxy ...
Jura et al. 2004 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... We show in Table 1 that the inferred lower bounds to MP B range from 0.004 M⊕ to 0.06 M⊕ . The summed mass of the KBOs in the Solar System is uncertain and is currently estimated to be between 0.02 M⊕ and 0.1 M⊕ (Bernstein et al. 2003; Luu & Jewitt 2002). Typical analogs of the Kuiper Belt may have ...
... We show in Table 1 that the inferred lower bounds to MP B range from 0.004 M⊕ to 0.06 M⊕ . The summed mass of the KBOs in the Solar System is uncertain and is currently estimated to be between 0.02 M⊕ and 0.1 M⊕ (Bernstein et al. 2003; Luu & Jewitt 2002). Typical analogs of the Kuiper Belt may have ...
Document
... Supernova The amount of energy released is so great, that most of the elements heavier than Fe are instantly created ...
... Supernova The amount of energy released is so great, that most of the elements heavier than Fe are instantly created ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.