ESA BR-170 - ESA Science
... nfrared radiation is a type of light. The term ‘light’ is usually associated with colour and brightness, but there are types of light which are invisible to the human eye: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, infrared light, microwaves and radio waves. The human eye is ‘tuned’ to detect only visib ...
... nfrared radiation is a type of light. The term ‘light’ is usually associated with colour and brightness, but there are types of light which are invisible to the human eye: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, infrared light, microwaves and radio waves. The human eye is ‘tuned’ to detect only visib ...
Missions
... This raised an unsettling question: if a first look at the infrared sky had yielded about ten new, odd, infraredbright objects, what would more detailed observations reveal? In 1969 the first catalogue of infrared-bright objects was published, including thousands of intriguing objects never seen bef ...
... This raised an unsettling question: if a first look at the infrared sky had yielded about ten new, odd, infraredbright objects, what would more detailed observations reveal? In 1969 the first catalogue of infrared-bright objects was published, including thousands of intriguing objects never seen bef ...
neutron star
... galaxies are richer in heavy elements than the Sun, with the highest abundances ever seen in the early Universe. Heavy elements that enrich mature galaxies in the local Universe were made in past generations of stars. So these young galaxies have experienced a prodigious rate of star formation and c ...
... galaxies are richer in heavy elements than the Sun, with the highest abundances ever seen in the early Universe. Heavy elements that enrich mature galaxies in the local Universe were made in past generations of stars. So these young galaxies have experienced a prodigious rate of star formation and c ...
Science with IMACS on Magellan
... of the Baade telescope. The rms image diameter averaged over the field of the collimator + f/4.3 camera is 0.15 arcsec, sharp enough to result in only 10% degradation of the best images that are expected, FWHM ∼ 0.25 arsec. The f/2.4 camera’s performance is remarkable considering the field size, wit ...
... of the Baade telescope. The rms image diameter averaged over the field of the collimator + f/4.3 camera is 0.15 arcsec, sharp enough to result in only 10% degradation of the best images that are expected, FWHM ∼ 0.25 arsec. The f/2.4 camera’s performance is remarkable considering the field size, wit ...
Massive Star Formation in the Galactic Center
... cluster. The following sections describe the stellar content in the clusters and the resultant implications for star formation in the region. They closely follow recent reviews (Figer et al. 1999a; Figer 2003, 2004), with updates, as summarized in Table 1. The three clusters are similar in many resp ...
... cluster. The following sections describe the stellar content in the clusters and the resultant implications for star formation in the region. They closely follow recent reviews (Figer et al. 1999a; Figer 2003, 2004), with updates, as summarized in Table 1. The three clusters are similar in many resp ...
3. Chapter 12
... been told that things in “outer space” never change. This conclusion was reached by astronomers who made observations using the best instruments available to them at the time. Scientific theories develop and change as we learn more. New evidence can cause scientists to rethink existing theories. Bet ...
... been told that things in “outer space” never change. This conclusion was reached by astronomers who made observations using the best instruments available to them at the time. Scientific theories develop and change as we learn more. New evidence can cause scientists to rethink existing theories. Bet ...
Astronomy Astrophysics Circumstellar emission in Be/X-ray binaries of the Magellanic
... Methods. Simultaneous U BVRI photometry and spectra in the 3500−7000 Å spectral range were obtained for 11 optical counterparts to Be/X-ray binaries in the LMC, 5 in the SMC and 12 in the Milky Way. As a measure of the amount of circumstellar emission we used the Hα equivalent width corrected for ph ...
... Methods. Simultaneous U BVRI photometry and spectra in the 3500−7000 Å spectral range were obtained for 11 optical counterparts to Be/X-ray binaries in the LMC, 5 in the SMC and 12 in the Milky Way. As a measure of the amount of circumstellar emission we used the Hα equivalent width corrected for ph ...
The empirical mass distribution of hot B subdwarfs
... to account for the existence of such objects, made of He-burning core surrounded by very thin H-rich envelope. They give quite different theoretical mass distributions for the resulting sdB stars. Detailed asteroseismic analyses, including mass estimates, of 15 pulsating hot B subdwarfs have been pu ...
... to account for the existence of such objects, made of He-burning core surrounded by very thin H-rich envelope. They give quite different theoretical mass distributions for the resulting sdB stars. Detailed asteroseismic analyses, including mass estimates, of 15 pulsating hot B subdwarfs have been pu ...
WELCOME TO THE MILKY WAY
... Globulars are generally made up of Population II stars. Population I stars are said to have a higher metallicity than Population II stars. In astronomy, all elements heavier than helium are called metals. The metallicity is a measure of the age of a star. In the early evolution of the Milky Way, the ...
... Globulars are generally made up of Population II stars. Population I stars are said to have a higher metallicity than Population II stars. In astronomy, all elements heavier than helium are called metals. The metallicity is a measure of the age of a star. In the early evolution of the Milky Way, the ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... along a narrow band that came to be called the Main Sequence. They also discovered that as one scanned the Main Sequence from one end to the other, the fundamental stellar property that changed along it was stellar mass. Mass is critically important because it determines how long stars can exist as ...
... along a narrow band that came to be called the Main Sequence. They also discovered that as one scanned the Main Sequence from one end to the other, the fundamental stellar property that changed along it was stellar mass. Mass is critically important because it determines how long stars can exist as ...
Gamma Ray Burst Afterglows and Host Galaxies
... Deaths of Massive Stars Afterglow data suggests that GRBs occur… • in galaxies with active star formation, • often in regions with a lot of gas, which is where new stars form and where the most massive stars spend their entire brief lives. However, GRBs are so rare that only a tiny fraction of massi ...
... Deaths of Massive Stars Afterglow data suggests that GRBs occur… • in galaxies with active star formation, • often in regions with a lot of gas, which is where new stars form and where the most massive stars spend their entire brief lives. However, GRBs are so rare that only a tiny fraction of massi ...
The Formation and Early Evolution of Young Massive Clusters
... dense (radius of a few pc) young stellar clusters, focusing on the role that studies of these objects in our Galaxy can play in our understanding of star and planet formation as a whole. Comparing the demographics of young massive cluster (YMC) progenitor clouds and YMCs across the Galaxy shows that ...
... dense (radius of a few pc) young stellar clusters, focusing on the role that studies of these objects in our Galaxy can play in our understanding of star and planet formation as a whole. Comparing the demographics of young massive cluster (YMC) progenitor clouds and YMCs across the Galaxy shows that ...
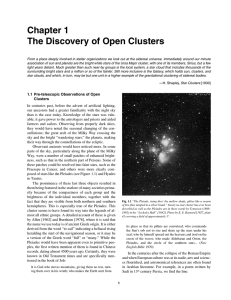
Chapter 1 The Discovery of Open Clusters - Willmann-Bell
... the massive Devil’s Tower rock formation in Wyoming was created by the Great Spirit to protect seven Indian maidens who were being pursued by bears. The maidens were subsequently placed in the sky as the Pleiades cluster. These stars were also important in the world system of the peoples of Mexico a ...
... the massive Devil’s Tower rock formation in Wyoming was created by the Great Spirit to protect seven Indian maidens who were being pursued by bears. The maidens were subsequently placed in the sky as the Pleiades cluster. These stars were also important in the world system of the peoples of Mexico a ...
The first carbon-enhanced metal-poor star found in the Sculptor
... CEMP-no stars, however, are not especially associated with binaries. Though some of them do belong to binary systems, for many of them close binaries that favor mass transfer can be excluded (e.g., Starkenburg et al. 2014). These stars are more frequent, and their carbon enhancement becomes more ext ...
... CEMP-no stars, however, are not especially associated with binaries. Though some of them do belong to binary systems, for many of them close binaries that favor mass transfer can be excluded (e.g., Starkenburg et al. 2014). These stars are more frequent, and their carbon enhancement becomes more ext ...
Formation of the First Galaxies: Theory and Simulations
... and evolution of stars. By this definition, the formation sites of the first stars, dark matter minihalos with masses 105 - 106 M⊙ , are unlikely candidates for the first galaxies, as the high energy radiation emitted by young stars and the supernovae that mark their end of life can rarify and expel ...
... and evolution of stars. By this definition, the formation sites of the first stars, dark matter minihalos with masses 105 - 106 M⊙ , are unlikely candidates for the first galaxies, as the high energy radiation emitted by young stars and the supernovae that mark their end of life can rarify and expel ...
The accretion disk paradigm for young stars
... 1968) when he found that several TTSs and related objects had strong infrared excesses up to 5µm. Mendoza, who was using Johnson’s photometric equipment at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, also confirmed the UV excess and was the first to present quasi-simultaneous UBVRIJHKLM spectral energy distri ...
... 1968) when he found that several TTSs and related objects had strong infrared excesses up to 5µm. Mendoza, who was using Johnson’s photometric equipment at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, also confirmed the UV excess and was the first to present quasi-simultaneous UBVRIJHKLM spectral energy distri ...
A SPECTROSCOPIC STUDY OF A LARGE SAMPLE OF WOLF-RAYET GALAXIES
... all galaxies in our sample show broad WR emission in the blue region of the spectrum (the blue bump) consisting of an unresolved blend of N III λ4640, C III λ4650, C IV λ4658 and He II λ4686 emission lines. Broad C IV λ5808 emission (the red bump) is detected in 30 galaxies. Additionally, weaker WR ...
... all galaxies in our sample show broad WR emission in the blue region of the spectrum (the blue bump) consisting of an unresolved blend of N III λ4640, C III λ4650, C IV λ4658 and He II λ4686 emission lines. Broad C IV λ5808 emission (the red bump) is detected in 30 galaxies. Additionally, weaker WR ...
GAS KINEMATICS ON GMC SCALES IN M51 WITH PAWS: CLOUD
... and its global patterns of star formation. In this paper we continue our study of the interacting Whirlpool galaxy M51 (D=7.6 Mpc; Ciardullo et al. 2002), which is more representative of a typical star forming galaxy than the well-studied lower mass galaxies in the Local Group. The unparalleled high ...
... and its global patterns of star formation. In this paper we continue our study of the interacting Whirlpool galaxy M51 (D=7.6 Mpc; Ciardullo et al. 2002), which is more representative of a typical star forming galaxy than the well-studied lower mass galaxies in the Local Group. The unparalleled high ...
Fluorine abundances in dwarf stars of the solar neighbourhood⋆
... Cloud and in the globular cluster ω Cen. They found that the abundance ratio of F/O declines as the oxygen abundance decreases. They therefore suggested that the observed low values of F/O exclude AGB synthesis as the dominant source of fluorine in their targeted stellar populations. In particular, ...
... Cloud and in the globular cluster ω Cen. They found that the abundance ratio of F/O declines as the oxygen abundance decreases. They therefore suggested that the observed low values of F/O exclude AGB synthesis as the dominant source of fluorine in their targeted stellar populations. In particular, ...
– 1 – 1. Galaxy Observations 1.1.
... the nearby Coma cluster and the Shapley Supercluster of galaxies, studying galaxies of a wide luminosity (i.e. mass) range with moderate resolution but high accuracy spectra. A fixed aperture size is used for each galaxy, corresponding to a fixed physical size for each of the two galaxy clusters. Th ...
... the nearby Coma cluster and the Shapley Supercluster of galaxies, studying galaxies of a wide luminosity (i.e. mass) range with moderate resolution but high accuracy spectra. A fixed aperture size is used for each galaxy, corresponding to a fixed physical size for each of the two galaxy clusters. Th ...
STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTICS AND STELLAR
... A few galaxies such as UGC 12695 have very bright H II regions. These may skew the luminosity weighted colors towards those of the H II regions. These can have peculiar colors because of the complex, rapidly evolving population of massive stars (Campbell & Terlevich 1984, McGaugh 1991), and because ...
... A few galaxies such as UGC 12695 have very bright H II regions. These may skew the luminosity weighted colors towards those of the H II regions. These can have peculiar colors because of the complex, rapidly evolving population of massive stars (Campbell & Terlevich 1984, McGaugh 1991), and because ...
Stars, neutral hydrogen and ionised gas in early
... as 5.9×109 M . On the basis of these observations, we included IC 4200 in our sample for the study of the relation between stellar and H i properties in early-type galaxies. We characterised the environment of IC 4200 by looking for extragalactic objects within 100 arcmin (∼1.6 Mpc at this redshift ...
... as 5.9×109 M . On the basis of these observations, we included IC 4200 in our sample for the study of the relation between stellar and H i properties in early-type galaxies. We characterised the environment of IC 4200 by looking for extragalactic objects within 100 arcmin (∼1.6 Mpc at this redshift ...
Autumn 2016 Midterm Review - Autumn 2015 Questions
... 23. Geomagnetic storms provide the energy that produce the aurorae at Earth’s poles. Complete the following sentence: The magnetic field of the Earth interacts with the solar wind, a. stretches almost to breaking, snaps back, and excites electrons in the atmosphere. b. causing the charged particles ...
... 23. Geomagnetic storms provide the energy that produce the aurorae at Earth’s poles. Complete the following sentence: The magnetic field of the Earth interacts with the solar wind, a. stretches almost to breaking, snaps back, and excites electrons in the atmosphere. b. causing the charged particles ...
$doc.title
... nuclear-burning occurs partly under convective conditions. This process is generally known as hot bottom burning (HBB; Iben, 1973). Under these conditions, carbon, on the one hand, is converted into nitrogen, keeping the C/O ratio below 1, and on the other hand 7 Li is produced very efficiently by t ...
... nuclear-burning occurs partly under convective conditions. This process is generally known as hot bottom burning (HBB; Iben, 1973). Under these conditions, carbon, on the one hand, is converted into nitrogen, keeping the C/O ratio below 1, and on the other hand 7 Li is produced very efficiently by t ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.