A small mass difference between Hydrogen and Helium The
... The Structure of Main Sequence Stars The Power Source of Main Sequence Stars MS stars fuse hydrogen into helium, releasing prodigious amounts of energy in the process. Their fuel source is the matter of which they are made The Powerhouse ...
... The Structure of Main Sequence Stars The Power Source of Main Sequence Stars MS stars fuse hydrogen into helium, releasing prodigious amounts of energy in the process. Their fuel source is the matter of which they are made The Powerhouse ...
Galaxy Formation,! Reionization, ! the First Stars and Quasars! Ay 127!
... Gas infall into the potential wells of the dark matter fluctuations leads to increased density, formation of H2, molecular line cooling, further condensation and cloud fragmentation, leading to the formation of the first stars! ...
... Gas infall into the potential wells of the dark matter fluctuations leads to increased density, formation of H2, molecular line cooling, further condensation and cloud fragmentation, leading to the formation of the first stars! ...
GUM31 Y ALREDEDORES
... WR 55 is the only massive star related to RCW 78 and the main responsible for the ionization of the gas. The HI gas emission distribution reveals an HI shell associated with RCW 78, which can be interpreted as an HI bubble linked to the ionized ring nebula. CO observations show the presence of ...
... WR 55 is the only massive star related to RCW 78 and the main responsible for the ionization of the gas. The HI gas emission distribution reveals an HI shell associated with RCW 78, which can be interpreted as an HI bubble linked to the ionized ring nebula. CO observations show the presence of ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... • A galaxy that emits unusually large quantities of radio waves • Thought to contain an active galactic nuclei ...
... • A galaxy that emits unusually large quantities of radio waves • Thought to contain an active galactic nuclei ...
The Ursa Major Moving Cluster, Collinder 285
... approximately in the same spatial direction, and thus drift commonly through their cosmic neighborhood - a property typically found for members of a physical star cluster. The cluster is currently approaching us at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluste ...
... approximately in the same spatial direction, and thus drift commonly through their cosmic neighborhood - a property typically found for members of a physical star cluster. The cluster is currently approaching us at 10 km/sec, and its spatial velocity relative to our Sun is about 46 km/s. This cluste ...
in the milky way - Chandra X
... velocity (i.e. speed) of a few hundred kilometers per second, completing one orbit around the center of the Milky Way about every 230 million years. In addition, the solar system is moving at about 20 kilometers per second with respect to the nearby stars. There is also a small amount of motion with ...
... velocity (i.e. speed) of a few hundred kilometers per second, completing one orbit around the center of the Milky Way about every 230 million years. In addition, the solar system is moving at about 20 kilometers per second with respect to the nearby stars. There is also a small amount of motion with ...
Lecture5 - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... If outside the Galaxy big fast motion (fraction of speed of light) ...
... If outside the Galaxy big fast motion (fraction of speed of light) ...
File - greenscapes4you
... entire sky. Only slightly larger than the , it is only 8 light years away ...
... entire sky. Only slightly larger than the , it is only 8 light years away ...
September 3 and 5 slides
... Curtis noted that many of the spirals had dark, thick bands of obscuring material and gave 3 big “ifs”: (1) if the MW has such a band, (2) if we are located in the mid-plane of the band, and (3) if the spirals are located outside the MW, then the Zone of Avoidance is caused by the obscuring material ...
... Curtis noted that many of the spirals had dark, thick bands of obscuring material and gave 3 big “ifs”: (1) if the MW has such a band, (2) if we are located in the mid-plane of the band, and (3) if the spirals are located outside the MW, then the Zone of Avoidance is caused by the obscuring material ...
Summary of recent research activities
... The luminosity-metallicity relation of dIrr galaxies The very low oxygen content of SagDIG, despite a continuous SFH, could be due to galactic winds removing metals from the main body of the galaxy; indeed, for its oxygen abundance, a close-box model would predict a higher gas mass fraction than is ...
... The luminosity-metallicity relation of dIrr galaxies The very low oxygen content of SagDIG, despite a continuous SFH, could be due to galactic winds removing metals from the main body of the galaxy; indeed, for its oxygen abundance, a close-box model would predict a higher gas mass fraction than is ...
Document
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
Chemical Evolution of the Galaxy and its satellites
... namely that first collapses the gas which forms the inner parts and then the gas which forms the outer parts • Namely, if one assumes a timescale for the formation of the disk increasing with galactocentric distance, the gradients are well reproduced if ...
... namely that first collapses the gas which forms the inner parts and then the gas which forms the outer parts • Namely, if one assumes a timescale for the formation of the disk increasing with galactocentric distance, the gradients are well reproduced if ...
The life of Stars
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
... Mira Stars • Mira (=wonderful, lat.) [o Ceti]: sometimes visible with bare eye, sometimes faint • Long period variable star: 332 days period • Cool red giants • Sometimes periodic, sometimes irregular • some eject gas into space ...
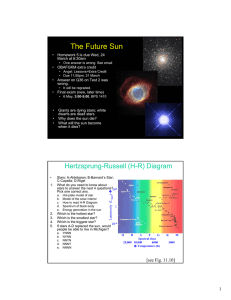
The Future Sun • Homework 5 is due Wed, 24 March at 6:30am
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
... In what ways are HR diagrams of H+χ Perseus, Pleiades, Hyades, & NGC188 different? Q Which is false a. Hottest stars in Perseus are hotter than hottest stars in Pleiades. b. Most stars are on the main sequence. c. NGC188 has small range of luminosity d. Some clusters have giants. ...
When Stars Go Boom
... helium. Energy is released in such a reaction, and this energy supplies pressure that can halt the gravitational contraction—at least temporarily. Think of it as floating in a swimming pool. The pressure of the water on your back is enough to keep you floating 10 feet above the bottom of the pool de ...
... helium. Energy is released in such a reaction, and this energy supplies pressure that can halt the gravitational contraction—at least temporarily. Think of it as floating in a swimming pool. The pressure of the water on your back is enough to keep you floating 10 feet above the bottom of the pool de ...
Study Guide for the Final Astronomy Exam
... A) Be able to write down the mass, luminosity, radius, temperature, and lifetime in solar units of main sequence O, G and M stars. 11) Unit 62Giant Stars A) Describe how shell burning creates giant stars 12) Unit 64: Post-Main Sequence of the Sun (low mass stars) A) Match the method of energy produc ...
... A) Be able to write down the mass, luminosity, radius, temperature, and lifetime in solar units of main sequence O, G and M stars. 11) Unit 62Giant Stars A) Describe how shell burning creates giant stars 12) Unit 64: Post-Main Sequence of the Sun (low mass stars) A) Match the method of energy produc ...
Stars - Haag
... Astronomers use a tool called a spectrograph, which breaks down light into its different wavelengths. ...
... Astronomers use a tool called a spectrograph, which breaks down light into its different wavelengths. ...
Stellar populations and dynamics in the Milky Way galaxy
... radiative de-excitation. Clearly, particles with small crosssection per unit mass for collisions, such as stars, will not dissipate their random kinetic energy efficiently, so that dissipation must occur prior to star formation, while the galaxy is still gaseous. The virial temperature of a typical ...
... radiative de-excitation. Clearly, particles with small crosssection per unit mass for collisions, such as stars, will not dissipate their random kinetic energy efficiently, so that dissipation must occur prior to star formation, while the galaxy is still gaseous. The virial temperature of a typical ...
For instance, two hydrogen atoms may fuse together to form one
... Astronomers classify stars based on their age, color, and brightness. These characteris tics help them identify and understand the different kinds of stars. A star’s surface temperature determines the amount of visible light given off (its brightness) and the color we perceive the star to be. For ex ...
... Astronomers classify stars based on their age, color, and brightness. These characteris tics help them identify and understand the different kinds of stars. A star’s surface temperature determines the amount of visible light given off (its brightness) and the color we perceive the star to be. For ex ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 31 - Kinematics of galaxies 31
... visible matter in the Milky Way is about 1011 solar masses, as previously mentioned. However, not all of this mass lies within Ro: in fact, if the mass were uniformly distributed throughout the disk, only (8 / 25)2 = 10% of it would lie within Ro = 8 kpc. This is our first hint that there is perhaps ...
... visible matter in the Milky Way is about 1011 solar masses, as previously mentioned. However, not all of this mass lies within Ro: in fact, if the mass were uniformly distributed throughout the disk, only (8 / 25)2 = 10% of it would lie within Ro = 8 kpc. This is our first hint that there is perhaps ...
Phys 214. Planets and Life
... chemical composition of the Universe. Calculations predict that the composition of the Universe should be about three fourths hydrogen and one fourth helium by mass, being a closed match to the overall chemical composition of the universe. This prediction implies that the universe was born only with ...
... chemical composition of the Universe. Calculations predict that the composition of the Universe should be about three fourths hydrogen and one fourth helium by mass, being a closed match to the overall chemical composition of the universe. This prediction implies that the universe was born only with ...
JPL Small-Body Database Browser
... Proper Motion Proper motion was discovered by Edmund Halley. He compared the positions of bright stars that had been recorded by (Ptolemy). http://www.hwy.com.au/~sjquirk/images/film/barnard.html Barnard’s Star has the highest known proper motion of 10.3”/year. Even at that rate, Barnard’s Star wil ...
... Proper Motion Proper motion was discovered by Edmund Halley. He compared the positions of bright stars that had been recorded by (Ptolemy). http://www.hwy.com.au/~sjquirk/images/film/barnard.html Barnard’s Star has the highest known proper motion of 10.3”/year. Even at that rate, Barnard’s Star wil ...
Lecture 33: The Lives of Stars Astronomy 141
... Main Sequence stars are powered by the fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in their cores The more massive a star is, the shorter its lifetime. Low-Mass stars are long-lived, spend some time as Red Giants, then leave behind a White Dwarf. Very high-mass stars have very short lives, spend a short time as ...
... Main Sequence stars are powered by the fusion of Hydrogen into Helium in their cores The more massive a star is, the shorter its lifetime. Low-Mass stars are long-lived, spend some time as Red Giants, then leave behind a White Dwarf. Very high-mass stars have very short lives, spend a short time as ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.