Universe 8e Lecture Chapter 24 Galaxies
... Distance to Galaxies: Standard candles, such as Cepheid variables and the most luminous supergiants, globular clusters, H II regions, and supernovae in a galaxy, are used in estimating intergalactic distances. The Tully-Fisher relation, which correlates the width of the 21-cm line of hydrogen in a s ...
... Distance to Galaxies: Standard candles, such as Cepheid variables and the most luminous supergiants, globular clusters, H II regions, and supernovae in a galaxy, are used in estimating intergalactic distances. The Tully-Fisher relation, which correlates the width of the 21-cm line of hydrogen in a s ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • After correcting for absorption by dust, it is possible to plot location of O- and B- (hot young stars) which tend to be concentrated in the spiral arms • Radio frequency observations reveal the distribution of hydrogen (atomic) and molecular clouds ...
... • After correcting for absorption by dust, it is possible to plot location of O- and B- (hot young stars) which tend to be concentrated in the spiral arms • Radio frequency observations reveal the distribution of hydrogen (atomic) and molecular clouds ...
BAS Visit to the Norman Lockyer Observatory, October 2015
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
... Omicron Ceti, better known as Mira in the constellation Cetus, is a binary star consisting of a red giant and a companion star. The system is approximately 400 light years distant. See page 13 for star map and location. Mira A, a red giant belonging to the spectral type M7 IIIe, is an oscillating va ...
Double Stars in Scorpio`s Claws
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
... but you should be able to see two dim red stars that form a line with brighter ρ Scorpii between them. ...
stars-notes
... Composition of Stars, continued • A continuous spectrum shows all of the colors, while an absorption spectrum shows which wavelengths of light are absorbed. • The spectrum of a star is an absorption spectrum because the atmosphere of the star absorbs certain portions of the light produced by the sta ...
... Composition of Stars, continued • A continuous spectrum shows all of the colors, while an absorption spectrum shows which wavelengths of light are absorbed. • The spectrum of a star is an absorption spectrum because the atmosphere of the star absorbs certain portions of the light produced by the sta ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... •Spectroscopic parallax is an astronomical method for measuring the distances to stars. Despite its name, it does not rely on the apparent change in the position of the star. •This technique can be applied to any main sequence star for which a spectrum can be recorded •It uses the absorption spectru ...
... •Spectroscopic parallax is an astronomical method for measuring the distances to stars. Despite its name, it does not rely on the apparent change in the position of the star. •This technique can be applied to any main sequence star for which a spectrum can be recorded •It uses the absorption spectru ...
Distance measurement in Astronomy
... You can find the distances of stars that are ‘relatively close’ to the Earth using parallax. A very simple example of parallax is to hold one forefinger upright about 30 cm in front of your nose and close your right eye. Using just your left eye line up your forefinger with an object on the other si ...
... You can find the distances of stars that are ‘relatively close’ to the Earth using parallax. A very simple example of parallax is to hold one forefinger upright about 30 cm in front of your nose and close your right eye. Using just your left eye line up your forefinger with an object on the other si ...
What kind of stuff
... How far? Summary • Measuring distances is essential to learn how big is the universe and how much stuff there is in it • To measure distances of far away objects, more than 100kpc or so, astronomers use “standard candles” such as Supernovae • Using Supernovae or other standard candles, astronomers ...
... How far? Summary • Measuring distances is essential to learn how big is the universe and how much stuff there is in it • To measure distances of far away objects, more than 100kpc or so, astronomers use “standard candles” such as Supernovae • Using Supernovae or other standard candles, astronomers ...
Lecture2 - UCSB Physics
... How far? Summary • Measuring distances is essential to learn how big is the universe and how much stuff there is in it • To measure distances of far away objects, more than 100kpc or so, astronomers use “standard candles” such as Supernovae • Using Supernovae or other standard candles, astronome ...
... How far? Summary • Measuring distances is essential to learn how big is the universe and how much stuff there is in it • To measure distances of far away objects, more than 100kpc or so, astronomers use “standard candles” such as Supernovae • Using Supernovae or other standard candles, astronome ...
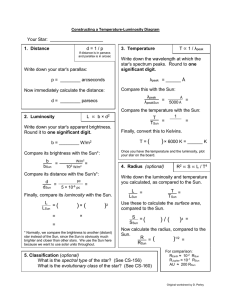
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... Minor caveat: The apparent brightnesses quoted here are integrated brightnesses at all wavelengths, including IR and UV. These values have also been corrected for absorption due to interstellar dust, which can be extremely significant for distant, blue stars. ...
... Minor caveat: The apparent brightnesses quoted here are integrated brightnesses at all wavelengths, including IR and UV. These values have also been corrected for absorption due to interstellar dust, which can be extremely significant for distant, blue stars. ...
Chapter 27 Quasars, Active Galaxies, and Gamma
... 4. The star becomes obscured by more and more interstellar dust. ...
... 4. The star becomes obscured by more and more interstellar dust. ...
Synthetic color-magnitude diagrams: the ingredients
... studied by Tout (1991), who suggested that the f(q) function can be derived by randomly extracting secondary stars from the “adopted” (observed) initial mass function; ...
... studied by Tout (1991), who suggested that the f(q) function can be derived by randomly extracting secondary stars from the “adopted” (observed) initial mass function; ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... light, giving off even more light than our Sun even though it is not nearly as hot. When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevent ...
... light, giving off even more light than our Sun even though it is not nearly as hot. When a temperature of about 27,000,000°F is reached, nuclear fusion begins. This is the nuclear reaction in which hydrogen atoms are converted to helium atoms plus energy. This energy (radiation) production prevent ...
C H A P T E R 2
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
FREE Sample Here
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
... You have the option of including The Sky software CD with your students’ texts. The primary function of The Sky software is to serve as a planetarium on your computer. There are many demonstrations you can do or have your students do as lab experiments to illustrate concepts from this chapter. Set t ...
Reach for the Stars – Div. B
... from the nebula’s extended clouds of gas and dust. Located 22 000 light-years away from the Sun, it is the closest region of this kind known in our galaxy, providing astronomers with a local test bed for studying the intense star formation processes, very common in other galaxies, but hard to observ ...
... from the nebula’s extended clouds of gas and dust. Located 22 000 light-years away from the Sun, it is the closest region of this kind known in our galaxy, providing astronomers with a local test bed for studying the intense star formation processes, very common in other galaxies, but hard to observ ...
Project 4: The HR diagram. Open clusters
... apparent magnitude m, or V, rather than absolute magnitude may be used in the Y axis of the HR diagram. This is valid as all the stars in the cluster are effectively at the same distance away from us hence any differences in apparent magnitude are due to actual diffe ...
... apparent magnitude m, or V, rather than absolute magnitude may be used in the Y axis of the HR diagram. This is valid as all the stars in the cluster are effectively at the same distance away from us hence any differences in apparent magnitude are due to actual diffe ...
1/20/09 301 Physics Chapter 12 The Family of Stars Triangulation
... also differ in average density, not just diameter • Typical density of main-sequence star is 1 g/cm3, while for a giant it is 10-6 g/cm3 ...
... also differ in average density, not just diameter • Typical density of main-sequence star is 1 g/cm3, while for a giant it is 10-6 g/cm3 ...
Ch13_Lecture - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... • A spectrum also can reveal a star’s composition, temperature, luminosity, velocity in space, rotation speed, and other properties • On certain occasions, it may reveal mass and ...
... • A spectrum also can reveal a star’s composition, temperature, luminosity, velocity in space, rotation speed, and other properties • On certain occasions, it may reveal mass and ...
Name
... This is an instrument that enables you to establish the angle between two visually notable objects that appear some distance away from your vantage point. Notice that the telescope-like eyepiece is aimed at a surface comprised of a piece of clear glass and a mirror. With the sextant held vertically, ...
... This is an instrument that enables you to establish the angle between two visually notable objects that appear some distance away from your vantage point. Notice that the telescope-like eyepiece is aimed at a surface comprised of a piece of clear glass and a mirror. With the sextant held vertically, ...
September Globular Clusters - Salisbury Plain Observing Group
... long time, a matter of some debate over whether it was a loose globular cluster or older, compact open cluster. It can be spotted in binoculars, but ...
... long time, a matter of some debate over whether it was a loose globular cluster or older, compact open cluster. It can be spotted in binoculars, but ...
slides - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Stars have different apparent brightness. In astronomy apparent brightness of a star (or other celestial object) is given by a number called the magnitude. It is a backward scale, smaller the magnitude number brighter the star and vice versa. Star magnitude ...
... Stars have different apparent brightness. In astronomy apparent brightness of a star (or other celestial object) is given by a number called the magnitude. It is a backward scale, smaller the magnitude number brighter the star and vice versa. Star magnitude ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... observation; sky lore and celestial myth; symbolic representation of celestial objects, concepts, and events; astronomical orientation of tombs, temples, shrines, and urban centers;” and other, similar trappings of culture. While some of these aspects might better be classified as “ethnoastronomy,” ...
... observation; sky lore and celestial myth; symbolic representation of celestial objects, concepts, and events; astronomical orientation of tombs, temples, shrines, and urban centers;” and other, similar trappings of culture. While some of these aspects might better be classified as “ethnoastronomy,” ...
Lesson 3: Calculating distances to stars
... from a given parallax angle or vice versa. The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will a ...
... from a given parallax angle or vice versa. The distances to stars can’t always be calculated from the parallax method. If the star is very far away, then the brightness of the star can be used to estimate the distance to the star. It is a rather simple principle; if a star is close by then it will a ...
What color are stars?
... 1: Describe the observations necessary for the determination of basic physical properties of stars such as mass, temperature, luminosity, chemical composition, sizes, and motions. 2: Explain the classification of stars according to their spectra and their luminosity. 3: Draw and describe the H-R dia ...
... 1: Describe the observations necessary for the determination of basic physical properties of stars such as mass, temperature, luminosity, chemical composition, sizes, and motions. 2: Explain the classification of stars according to their spectra and their luminosity. 3: Draw and describe the H-R dia ...
Malmquist bias
The Malmquist bias is an effect in observational astronomy which leads to the preferential detection of intrinsically bright objects. It was first described in 1922 by Swedish astronomer Gunnar Malmquist (1893–1982), who then greatly elaborated upon this work in 1925. In statistics, this bias is referred to as a selection bias and affects the survey results in a brightness limited survey, where stars below a certain apparent brightness are not included. Since observed stars and galaxies appear dimmer when farther away, the brightness that is measured will fall off with distance until their brightness falls below the observational threshold. Objects which are more luminous, or intrinsically brighter, can be observed at a greater distance, creating a false trend of increasing intrinsic brightness, and other related quantities, with distance. This effect has led to many spurious claims in the field of astronomy. Properly correcting for these effects has become an area of great focus.