4-eclipses-and-tides
... every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approxi ...
... every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approxi ...
File - peter ditchon velarde
... Unique Features of Jupiter: Many Moon So far, Jupiter has 63 confirmed moons. Four massive moons, called the “Galilean moons” were discovered back in 1610 by Galileo Galilei, this is be the Unique Features of Jupiter. These moons are Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Ganymede is the largest moon, ...
... Unique Features of Jupiter: Many Moon So far, Jupiter has 63 confirmed moons. Four massive moons, called the “Galilean moons” were discovered back in 1610 by Galileo Galilei, this is be the Unique Features of Jupiter. These moons are Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Ganymede is the largest moon, ...
Solar System: Planets Asteroids Comets
... 1.524 AU, Jupiter at 5.204 AU, Saturn at 9.582AU. Amazingly, Uranus at 19.23AU was determined in 1781 to be a planet an not a star. The gap at 2.8 is located in the belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. The dwarf planet Ceres at 2.766AU was discovered in 1801 at almost exactly the predicted lo ...
... 1.524 AU, Jupiter at 5.204 AU, Saturn at 9.582AU. Amazingly, Uranus at 19.23AU was determined in 1781 to be a planet an not a star. The gap at 2.8 is located in the belt of asteroids between Mars and Jupiter. The dwarf planet Ceres at 2.766AU was discovered in 1801 at almost exactly the predicted lo ...
4-eclipses-and-tides
... every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approxi ...
... every 28.5 hours. The changing brightness is the result of the planet blocking some of the starlight when it is between Ogle-Tr-3 and Earth. This observation allowed scientists to find not only the planet, but also to determine the planet’s mass and density The mass has been calculated to be approxi ...
Nov 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and c ...
... longer in its group. west after sunset or in the east before sunrise. Jupiter can be out Globular Clusters look like fuzzy balls because they contain all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and c ...
High Contrast - University of Arizona
... Current theories of disk/planet evolution suggest a presumed epoch of planet-building via the formation and agglomerative growth of embryonic bodies, and the subsequent accretion of gaseous atmospheres onto hot giant planets, is attendant with a significant decline in the gas-to-dust ratios in the r ...
... Current theories of disk/planet evolution suggest a presumed epoch of planet-building via the formation and agglomerative growth of embryonic bodies, and the subsequent accretion of gaseous atmospheres onto hot giant planets, is attendant with a significant decline in the gas-to-dust ratios in the r ...
Earth Moon Sun System PPT
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
Earth Moon Sun System PPT
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
... • Solar eclipses can occur because the Sun and Moon have the same angular diameter in the sky (.5°), so aligned correctly, the moon will either partially or totally block out the sun. • The Sun is 400x larger than the moon, but also exactly 400x further away from Earth than the moon – this is what m ...
NATS1311_090908_bw
... Because the crescent phase is nearly a new moon as seen from Earth, the Earth is nearly full as viewed from the moon. The light of Earth illuminates the night moonscape - just as the full moon illuminates the Earth landscape. Because Earth is much larger than the Moon, the full earth is much bigger ...
... Because the crescent phase is nearly a new moon as seen from Earth, the Earth is nearly full as viewed from the moon. The light of Earth illuminates the night moonscape - just as the full moon illuminates the Earth landscape. Because Earth is much larger than the Moon, the full earth is much bigger ...
Working with the Illinois Learning Standards: A Constructivist
... compare -- use the “Alticator” supplied in the Observational Astronomy guide • chart the motion across the sky using a stick to cast a shadow • create and use a sundial to illustration the regular motion of the sun across the sky • use a globe and a light bulb to simulate the earth and sun; illustra ...
... compare -- use the “Alticator” supplied in the Observational Astronomy guide • chart the motion across the sky using a stick to cast a shadow • create and use a sundial to illustration the regular motion of the sun across the sky • use a globe and a light bulb to simulate the earth and sun; illustra ...
1 Lunar Standstills and Chimney Rock Thomas Hockey To
... everything I’ve said about moonrise also applies to moonset, but at Chimney Rock it’s the moonrise in which we’re interested! We might mention that the sunrise and sunset directions also “swing” back and forth across segments of the eastern and western horizons. The Earth revolves about the Sun rath ...
... everything I’ve said about moonrise also applies to moonset, but at Chimney Rock it’s the moonrise in which we’re interested! We might mention that the sunrise and sunset directions also “swing” back and forth across segments of the eastern and western horizons. The Earth revolves about the Sun rath ...
MSWord version
... everything I’ve said about moonrise also applies to moonset, but at Chimney Rock it’s the moonrise in which we’re interested! We might mention that the sunrise and sunset directions also “swing” back and forth across segments of the eastern and western horizons. The Earth revolves about the Sun rath ...
... everything I’ve said about moonrise also applies to moonset, but at Chimney Rock it’s the moonrise in which we’re interested! We might mention that the sunrise and sunset directions also “swing” back and forth across segments of the eastern and western horizons. The Earth revolves about the Sun rath ...
Galileo & the Telescope— Sept 20
... fixed stars, the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about the four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
... fixed stars, the Milky Way, nebulous stars, but especially about the four planets flying around the star of Jupiter at unequal intervals and periods with wonderful swiftness; which unknown by anyone until this day, the first author detected recently and decided to name Midicean Stars. Venice ...
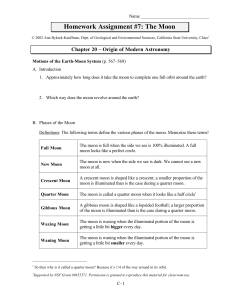
Homework Assignment #7: The Moon
... So then why is it called a quarter moon? Because it’s 1/4 of the way around in its orbit. ...
... So then why is it called a quarter moon? Because it’s 1/4 of the way around in its orbit. ...
Solar System Lesson Organizer
... Domain Vocabulary: day, orbit, rotate, planet, solar system, star, sun, year, constellation, asteroid, comet, sunspot, satellite, crater, crescent, new moon, half moon, gibbous moon ...
... Domain Vocabulary: day, orbit, rotate, planet, solar system, star, sun, year, constellation, asteroid, comet, sunspot, satellite, crater, crescent, new moon, half moon, gibbous moon ...
EarthScience_Topic 3
... • Meteorite: meteor that reaches Earth’s surface • Comets: a dirty ice ball that revolves around the sun – When close enough to the sun, exhibits a tail ...
... • Meteorite: meteor that reaches Earth’s surface • Comets: a dirty ice ball that revolves around the sun – When close enough to the sun, exhibits a tail ...
society journal - Auckland Astronomical Society
... below which radiation may be harmless. It claimed that there are many places on Earth where the natural background radiation is tens or even hundreds of times higher than in the Chernobyl exclusion zone. Yet studies of populations who live in these natural radiation hotspots have consistently failed ...
... below which radiation may be harmless. It claimed that there are many places on Earth where the natural background radiation is tens or even hundreds of times higher than in the Chernobyl exclusion zone. Yet studies of populations who live in these natural radiation hotspots have consistently failed ...
ph507-16-1exo2
... Currently the most important class of exoplanets are those that transit the disk of their parent stars, allowing for a determination of planetary radii. SELECTION: Of course, while planets close to their parent stars will preferentially be found, due to their shorter orbital periods and greater like ...
... Currently the most important class of exoplanets are those that transit the disk of their parent stars, allowing for a determination of planetary radii. SELECTION: Of course, while planets close to their parent stars will preferentially be found, due to their shorter orbital periods and greater like ...
ppt
... Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii larger than 1.1 RJup. ...
... Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii larger than 1.1 RJup. ...
Mercury_Orbit_Lab_1_(better_than_2)
... How do we know what the orbit of a planet is like? At first glance this appears to be a difficult question, but in many cases it is surprisingly easy to derive an orbit from basic observations. In this exercise you will use a set of simple observations, which you could have made yourself, to discove ...
... How do we know what the orbit of a planet is like? At first glance this appears to be a difficult question, but in many cases it is surprisingly easy to derive an orbit from basic observations. In this exercise you will use a set of simple observations, which you could have made yourself, to discove ...
Light of Distant Stars - Glasgow Science Centre
... searching for extrasolar planets, and, despite it having revealed a number of planets, it’s actually the worst way of doing it. Ask the group to discuss why they think this is a particularly poor way of searching for planets. Hopefully someone will hit along the idea that the probability of a planet ...
... searching for extrasolar planets, and, despite it having revealed a number of planets, it’s actually the worst way of doing it. Ask the group to discuss why they think this is a particularly poor way of searching for planets. Hopefully someone will hit along the idea that the probability of a planet ...
A report of the SEEDS Direct Imaging Survey
... 120 nights from 2009; finished in 2015 Jan, only <1 night loss due to HiCIAO NIR direct imaging and census of giant planets in the outer regions (10-100AU) around ~500 solar-type and massive stars Exploring protoplanetary disks and debris disks for the origin of their diversity and evolution at the ...
... 120 nights from 2009; finished in 2015 Jan, only <1 night loss due to HiCIAO NIR direct imaging and census of giant planets in the outer regions (10-100AU) around ~500 solar-type and massive stars Exploring protoplanetary disks and debris disks for the origin of their diversity and evolution at the ...
Activities, In the Footsteps of Galileo
... locate the Big Dipper. Then draw another imaginary line northeastward, this time beginning at the two stars at the back of the bowl. (A line drawn from the two stars at the front of the bowl intersects the North Star.) That straight line intersects Deneb, one of the stars in the Summer Triangle. In ...
... locate the Big Dipper. Then draw another imaginary line northeastward, this time beginning at the two stars at the back of the bowl. (A line drawn from the two stars at the front of the bowl intersects the North Star.) That straight line intersects Deneb, one of the stars in the Summer Triangle. In ...
What we know about Jupiter
... Its strong gravitational influence has helped to move material around our solar system, potentially scattering ice, water and organic molecules from the outer cold regions of the solar system into the This magnetic field traps charged particles inner solar system where it could be captured by electr ...
... Its strong gravitational influence has helped to move material around our solar system, potentially scattering ice, water and organic molecules from the outer cold regions of the solar system into the This magnetic field traps charged particles inner solar system where it could be captured by electr ...
Satellite system (astronomy)

A satellite system is a set of gravitationally bound objects in orbit around a planetary mass object or minor planet. Generally speaking, it is a set of natural satellites (moons), although such systems may also consist of bodies such as circumplanetary disks, ring systems, moonlets, minor-planet moons and artificial satellites any of which may themselves have satellite systems of their own. Some satellite systems have complex interactions with both their parent and other moons, including magnetic, tidal, atmospheric and orbital interactions such as orbital resonances and libration. Individually major satellite objects are designated in Roman numerals. Satellite systems are referred to either by the possessive adjectives of their primary (e.g. ""Jovian system""), or less commonly by the name of their primary (e.g. ""Jupiter system""). Where only one satellite is known, or it is a binary orbiting a common centre of gravity, it may be referred to using the hyphenated names of the primary and major satellite (e.g. the ""Earth-Moon system"").Many Solar System objects are known to possess satellite systems, though their origin is still unclear. Notable examples include the largest satellite system, the Jovian system, with 67 known moons (including the large Galilean moons) and the Saturnian System with 62 known moons (and the most visible ring system in the Solar System). Both satellite systems are large and diverse. In fact all of the giant planets of the Solar System possess large satellite systems as well as planetary rings, and it is inferred that this is a general pattern. Several objects farther from the Sun also have satellite systems consisting of multiple moons, including the complex Plutonian system where multiple objects orbit a common center of mass, as well as many asteroids and plutinos. Apart from the Earth-Moon system and Mars' system of two tiny natural satellites, the other terrestrial planets are generally not considered satellite systems, although some have been orbited by artificial satellites originating from Earth.Little is known of satellite systems beyond the Solar System, although it is inferred that natural satellites are common. J1407b is an example of an extrasolar satellite system. It is also theorised that Rogue planets ejected from their planetary system could retain a system of satellites.