Lecture 12 – MAC - UTK-EECS
... out, -r can be used to read packet from a file -s num: get num bytes of data from each packet rather than the default value of 68 src host xyz: true if IP destination field of the packet is ...
... out, -r can be used to read packet from a file -s num: get num bytes of data from each packet rather than the default value of 68 src host xyz: true if IP destination field of the packet is ...
Secure Network Routing: Ariadne and Skipchains
... • Many security properties are vulnerable at several layers: Application – Availability – Location privacy ...
... • Many security properties are vulnerable at several layers: Application – Availability – Location privacy ...
Network Architecture
... Uses either shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable, or coaxial cable Uses UTP or STP cable 100BaseFX uses fiber-optic cable (single-mode, multimode, and plastic) ...
... Uses either shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable, unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable, or coaxial cable Uses UTP or STP cable 100BaseFX uses fiber-optic cable (single-mode, multimode, and plastic) ...
Hardened IDS using IXP
... Chris Clark, Jun Li, Chengai Lu, Weidong Shi, Ashley Thomas, Yi Zhang Motivation ...
... Chris Clark, Jun Li, Chengai Lu, Weidong Shi, Ashley Thomas, Yi Zhang Motivation ...
pptx - Brown Computer Science
... • Switches must be able to, given a packet, determine the outgoing port • 3 ways to do this: – Virtual Circuit Switching – Datagram Switching – Source Routing ...
... • Switches must be able to, given a packet, determine the outgoing port • 3 ways to do this: – Virtual Circuit Switching – Datagram Switching – Source Routing ...
Routing and Switching (CCNA).
... The Routing and Switching Fundamentals Part 1 and 2 brought to you by Pitman Training is the course for you if you are looking to pass the Cisco CCNA exam and build a career in network management or support in a Cisco environment. This course provides knowledge and skills to make connections ...
... The Routing and Switching Fundamentals Part 1 and 2 brought to you by Pitman Training is the course for you if you are looking to pass the Cisco CCNA exam and build a career in network management or support in a Cisco environment. This course provides knowledge and skills to make connections ...
network jeopardy
... holds a special network packet called a token. A: What is a token ring network? ...
... holds a special network packet called a token. A: What is a token ring network? ...
$doc.title
... – Supports dividing a large IP packet into fragments – … in case a link cannot handle a large IP packet ...
... – Supports dividing a large IP packet into fragments – … in case a link cannot handle a large IP packet ...
PDF
... • network level reliability would improve performance. – But this may not benefit all applications • Huge overhead for say Real-Time speech transmission • Need for optional layers ...
... • network level reliability would improve performance. – But this may not benefit all applications • Huge overhead for say Real-Time speech transmission • Need for optional layers ...
Communications and Networks
... manages resources such as user accounts for an entire network. – Host—any computer system that can be accessed over a network. – Router —a node that forwards or routes data packets from one network to their destination in another network ...
... manages resources such as user accounts for an entire network. – Host—any computer system that can be accessed over a network. – Router —a node that forwards or routes data packets from one network to their destination in another network ...
IP Network Addressing
... 3) How large does the Time-To-Live field have to be for a packet to traverse from Ishtar to Apollo? ...
... 3) How large does the Time-To-Live field have to be for a packet to traverse from Ishtar to Apollo? ...
chap01 - cknuckles
... Transport Layer -- End-to-End Service • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) -- Divides data into packets, verifies arrival on the other end, puts packets back together. TCP connections between two computers called sockets. • User Datagram Protocol (UDP) -- No guarantee of delivery, often single pac ...
... Transport Layer -- End-to-End Service • Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) -- Divides data into packets, verifies arrival on the other end, puts packets back together. TCP connections between two computers called sockets. • User Datagram Protocol (UDP) -- No guarantee of delivery, often single pac ...
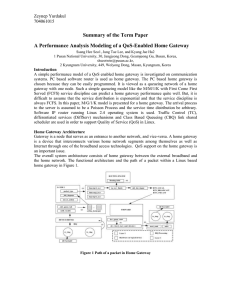
A performance analysis modeling of a QoS
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
lecture 17
... system that runs a network, steering information between computers and managing security and users Packet-switching - Occurs when the sending computer divides a message into a number of efficiently sized units called packets, each of which contains the address of the destination computer Router - An ...
... system that runs a network, steering information between computers and managing security and users Packet-switching - Occurs when the sending computer divides a message into a number of efficiently sized units called packets, each of which contains the address of the destination computer Router - An ...
CHAPTER 6
... Networking Devices, P. II 2. ROUTER – A networking device that connects two or more networks: it routes packets of data from one network to another. The router ensures that information doesn't go where it's not needed. The router makes sure that information does make it to the intended destinat ...
... Networking Devices, P. II 2. ROUTER – A networking device that connects two or more networks: it routes packets of data from one network to another. The router ensures that information doesn't go where it's not needed. The router makes sure that information does make it to the intended destinat ...
Hardware & Communication
... and is a popular type of mobile internet service which can be used on a handheld device, such as a mobile phone or PDA. It enables you to go online while out and about and is especially handy if you want to get the latest news updates, sports scores and travel updates. (Apple phones communicate with ...
... and is a popular type of mobile internet service which can be used on a handheld device, such as a mobile phone or PDA. It enables you to go online while out and about and is especially handy if you want to get the latest news updates, sports scores and travel updates. (Apple phones communicate with ...
IP address format: Dotted decimal notation: 10000000 00001011
... → e.g., DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) → used by access ISPs, enterprises, etc. → specifics: network address translation (NAT) → private/unregistered vs. public/registered IP address → can additionally use port numbers: NAPT ...
... → e.g., DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol) → used by access ISPs, enterprises, etc. → specifics: network address translation (NAT) → private/unregistered vs. public/registered IP address → can additionally use port numbers: NAPT ...
Hermes: An Integrated CPU/GPU Microarchitecture for IP Routing
... Dest Mac :new ---------------------------IP Header: Source IP :x Dest IP :y ---------------------------Data ...
... Dest Mac :new ---------------------------IP Header: Source IP :x Dest IP :y ---------------------------Data ...
HyperText Transfer Protocol
... length data sequences from a source to a destination via one or more networks while maintaining the quality of service requested by the Transport layer. ...
... length data sequences from a source to a destination via one or more networks while maintaining the quality of service requested by the Transport layer. ...
Introduction - Ilam university
... Subsequence packets follow the same circuit Sometimes called connection-oriented model. VCIs is swapped in the switches. Example: Lookup table. In-port ...
... Subsequence packets follow the same circuit Sometimes called connection-oriented model. VCIs is swapped in the switches. Example: Lookup table. In-port ...
Wake-on-LAN
Wake-on-LAN (WoL) is an Ethernet or Token ring computer networking standard that allows a computer to be turned on or awakened by a network message.The message is usually sent by a program executed on another computer on the same local area network. It is also possible to initiate the message from another network by using subnet directed broadcasts or a WOL gateway service. Equivalent terms include wake on WAN, remote wake-up, power on by LAN, power up by LAN, resume by LAN, resume on LAN and wake up on LAN. In case the computer being awakened is communicating via Wi-Fi, a supplementary standard called Wake on Wireless LAN (WoWLAN) must be employed.The WOL and WoWLAN standards are often supplemented by vendors to provide protocol-transparent on-demand services, for example in the Apple Bonjour wake-on-demand (Sleep Proxy) feature.