Chapter 6: International Trade, Exchange Rates, and
... 5. What is meant by purchasing power parity? How can this be used to determine if a currency is overvalued or undervalued relative to other currencies? 6. What factors interfere with purchasing power parity theory? ...
... 5. What is meant by purchasing power parity? How can this be used to determine if a currency is overvalued or undervalued relative to other currencies? 6. What factors interfere with purchasing power parity theory? ...
Tema 15
... • in August 2007 Slovakia fulfilled this criteria inflation rate was on 1.9% • nowadays the rate is on 2.9% but the criteria today is about 3.2% - meets the requirements ...
... • in August 2007 Slovakia fulfilled this criteria inflation rate was on 1.9% • nowadays the rate is on 2.9% but the criteria today is about 3.2% - meets the requirements ...
Money, Banking, and Financial Markets (Econ 353): Section 1
... 6) If there are five goods in a barter economy, one needs to know ten prices in order to exchange one good for another. If, however, there are ten goods in a barter economy, then one needs to know _____ prices in order to exchange one good for another. A) 20 B) 25 C) 30 D) 45 7) In which of the foll ...
... 6) If there are five goods in a barter economy, one needs to know ten prices in order to exchange one good for another. If, however, there are ten goods in a barter economy, then one needs to know _____ prices in order to exchange one good for another. A) 20 B) 25 C) 30 D) 45 7) In which of the foll ...
the international monetary and financial environment
... ■ Economic growth is the increase in value of the goods and services produced by an economy. ■ Typically measured as the annual increase in real GDP, where inflation rate is subtracted from the economic growth rate to obtain a more accurate measure. ■ Innovation and entrepreneurship drive business a ...
... ■ Economic growth is the increase in value of the goods and services produced by an economy. ■ Typically measured as the annual increase in real GDP, where inflation rate is subtracted from the economic growth rate to obtain a more accurate measure. ■ Innovation and entrepreneurship drive business a ...
FIN_250_Chap02_shrtnd_0
... It is likely that the U.S. dollar will lose its place as the dominant world currency. The euro and the U.S. dollar will be the two major currencies.???? Is it?? China, Arab World, India ...
... It is likely that the U.S. dollar will lose its place as the dominant world currency. The euro and the U.S. dollar will be the two major currencies.???? Is it?? China, Arab World, India ...
スライド 1 - GRIPS
... - P1/P2 = MRSA = MRSB = MRT i.e., the rate at which firms can transform one good into another = the rate at which consumers are willing to substitute between the goods. ...
... - P1/P2 = MRSA = MRSB = MRT i.e., the rate at which firms can transform one good into another = the rate at which consumers are willing to substitute between the goods. ...
Trade, Exchange Rates, and Public Policy
... If you have a fixed exchange, you give up control of your monetary policy because you are buying and selling securities to maintain your domestic interest rate at the same level as the foreign interest rate. Without capital controls you cannot maintain a fixed exchange rate without losing control of ...
... If you have a fixed exchange, you give up control of your monetary policy because you are buying and selling securities to maintain your domestic interest rate at the same level as the foreign interest rate. Without capital controls you cannot maintain a fixed exchange rate without losing control of ...
The exchange raTe as a moneTary policy insTrumenT
... of imported goods, supporting demand for goods of domestic origin on the Czech market. Households and firms will see that it does not pay to wait for prices to fall further, and a proportion of households (especially medium- and high-income ones) and firms will start consuming and investing more. Cz ...
... of imported goods, supporting demand for goods of domestic origin on the Czech market. Households and firms will see that it does not pay to wait for prices to fall further, and a proportion of households (especially medium- and high-income ones) and firms will start consuming and investing more. Cz ...
Bank of Slovenia`s Operational Monetary Policy
... the nominal tolar exchange rate • central parity rate: 1 € = 239.640 SIT – lower point: 203.694 SIT – upper point: 275.586 SIT ...
... the nominal tolar exchange rate • central parity rate: 1 € = 239.640 SIT – lower point: 203.694 SIT – upper point: 275.586 SIT ...
No Slide Title
... Questions on Assessing Performance in US Dollars in Foreign Markets Are emerging markets riskier Is exchange rate risk important in ...
... Questions on Assessing Performance in US Dollars in Foreign Markets Are emerging markets riskier Is exchange rate risk important in ...
Why do prices change?
... The rate of inflation is forecast to be 10% and the bank is currently offering 7% interest on its passbook savings accounts. What is the real interest rate earned on these accounts? ...
... The rate of inflation is forecast to be 10% and the bank is currently offering 7% interest on its passbook savings accounts. What is the real interest rate earned on these accounts? ...
Chater 29 Open economy macroeconomics
... Open economy macroeconomics • … is the study of economies in which international transactions play a significant role – international considerations are especially important for open economies like the UK, Germany or the Netherlands ...
... Open economy macroeconomics • … is the study of economies in which international transactions play a significant role – international considerations are especially important for open economies like the UK, Germany or the Netherlands ...
Slide_6-1
... rise following a fall in the exchange rate of the importing country © Brian Titley 2012: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute ...
... rise following a fall in the exchange rate of the importing country © Brian Titley 2012: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute ...
Document
... Price and wage flexibility are particularly important in the very short run to facilitate the adjustment process following a shock. Alternatively, if nominal prices and wages are downward rigid some measure of real flexibility could be achieved by means of exchange rate adjustments. Capital mobility ...
... Price and wage flexibility are particularly important in the very short run to facilitate the adjustment process following a shock. Alternatively, if nominal prices and wages are downward rigid some measure of real flexibility could be achieved by means of exchange rate adjustments. Capital mobility ...
View Slide Show for Lesson 5-2
... A fixed basket excludes new goods and services. Changing the basket of goods obviously changes the price index, but a static basket of goods quickly becomes nonsensical in a rapidly changing world. How valid is a CPI that does not include cell phones or internet charges, but these things did not ex ...
... A fixed basket excludes new goods and services. Changing the basket of goods obviously changes the price index, but a static basket of goods quickly becomes nonsensical in a rapidly changing world. How valid is a CPI that does not include cell phones or internet charges, but these things did not ex ...
Currency Policy - Harvard Kennedy School
... Announcing a policy target π = 0 is time-inconsistent, because a CB with discretion will inflate ex post, and everyone knows this ex ante. ...
... Announcing a policy target π = 0 is time-inconsistent, because a CB with discretion will inflate ex post, and everyone knows this ex ante. ...
davies on argentina
... limped through four decades of protectionism, monetary abuse (printing money for shortterm objectives), and extreme structural inefficiencies. In addition, “the bloodiest military government in recent South American history held power in Argentina from 1976 to 1983.”3 Although democracy returned to ...
... limped through four decades of protectionism, monetary abuse (printing money for shortterm objectives), and extreme structural inefficiencies. In addition, “the bloodiest military government in recent South American history held power in Argentina from 1976 to 1983.”3 Although democracy returned to ...
Foreign Exchange and the Canadian Dollar: A
... into international markets. Canadian workers are paid more than U.S. workers. Yet average productivity in Canadian industries is about 15% lower than in the U.S. (mostly because of a lack of capital investment by Canadian businesses). Given these realities, Canadian manufacturers need an exchange ra ...
... into international markets. Canadian workers are paid more than U.S. workers. Yet average productivity in Canadian industries is about 15% lower than in the U.S. (mostly because of a lack of capital investment by Canadian businesses). Given these realities, Canadian manufacturers need an exchange ra ...
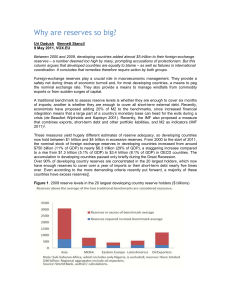
Uri Dadush Bennett Stancil 9 May 2011, VOX.EU
... lower the costs of debt service; for countries with reserves well in excess of benchmarks, such as China and Malaysia, the cost may be as high as 2% of GDP. 4 Reinhart and Rogoff (2008) find that financial crises, on average, reduce per capita GDP by ...
... lower the costs of debt service; for countries with reserves well in excess of benchmarks, such as China and Malaysia, the cost may be as high as 2% of GDP. 4 Reinhart and Rogoff (2008) find that financial crises, on average, reduce per capita GDP by ...
Purchasing power parity
_per_capita_by_countries.png?width=300)
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a component of some economic theories and is a technique used to determine the relative value of different currencies.Theories that invoke purchasing power parity assume that in some circumstances (for example, as a long-run tendency) it would cost exactly the same number of, say, US dollars to buy euros and then to use the proceeds to buy a market basket of goods as it would cost to use those dollars directly in purchasing the market basket of goods.The concept of purchasing power parity allows one to estimate what the exchange rate between two currencies would have to be in order for the exchange to be at par with the purchasing power of the two countries' currencies. Using that PPP rate for hypothetical currency conversions, a given amount of one currency thus has the same purchasing power whether used directly to purchase a market basket of goods or used to convert at the PPP rate to the other currency and then purchase the market basket using that currency. Observed deviations of the exchange rate from purchasing power parity are measured by deviations of the real exchange rate from its PPP value of 1.PPP exchange rates help to minimize misleading international comparisons that can arise with the use of market exchange rates. For example, suppose that two countries produce the same physical amounts of goods as each other in each of two different years. Since market exchange rates fluctuate substantially, when the GDP of one country measured in its own currency is converted to the other country's currency using market exchange rates, one country might be inferred to have higher real GDP than the other country in one year but lower in the other; both of these inferences would fail to reflect the reality of their relative levels of production. But if one country's GDP is converted into the other country's currency using PPP exchange rates instead of observed market exchange rates, the false inference will not occur.