International Trade
... Can the balance of payments offset the balance of trade? Money can leave a country because of trade - but more money can enter the country in other areas ...
... Can the balance of payments offset the balance of trade? Money can leave a country because of trade - but more money can enter the country in other areas ...
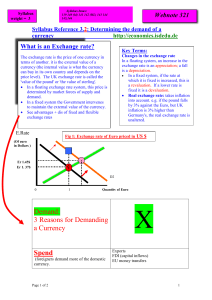
Demand for a currency - yELLOWSUBMARINER.COM
... Real exchange rate: takes inflation into account. e.g. if the pound falls by 3% against the Euro, but UK inflation is 3% higher than Germany's, the real exchange rate is unaltered. ...
... Real exchange rate: takes inflation into account. e.g. if the pound falls by 3% against the Euro, but UK inflation is 3% higher than Germany's, the real exchange rate is unaltered. ...
2015-05-22 17:00:39.740 GMT (Adds Kelimbetov
... billion trying to slow the ruble’s drop as oil prices fell and U.S. and European Union sanctions choked off foreign funding. “In Russia, instability was imported ...
... billion trying to slow the ruble’s drop as oil prices fell and U.S. and European Union sanctions choked off foreign funding. “In Russia, instability was imported ...
3.E Money in the European Union High School Lesson Plan
... To introduce the idea of the lesson, teacher will ask students if any have ever traveled outside of the United States. If so, teacher will ask that student whether they were able to use dollars to buy things in that other country. The student may explain that they were not able to use US dollars, bu ...
... To introduce the idea of the lesson, teacher will ask students if any have ever traveled outside of the United States. If so, teacher will ask that student whether they were able to use dollars to buy things in that other country. The student may explain that they were not able to use US dollars, bu ...
single global currency
... the world should proceed to the next level of currency consolidation: a single global currency, to be managed by an international central bank. Such a single global currency would eliminate worldwide currency trading costs, eliminate currency-related investment risks and eliminate Balance of Payment ...
... the world should proceed to the next level of currency consolidation: a single global currency, to be managed by an international central bank. Such a single global currency would eliminate worldwide currency trading costs, eliminate currency-related investment risks and eliminate Balance of Payment ...
The main qualities of an orthodox currency board are
... A currency board's foreign currency reserves must be sufficient to ensure that all holders of its notes and coins (and all banks creditor of a Reserve Account at the currency board) can convert them into the reserve currency (usually 110–115% of the monetary base M0). A currency board maintains abso ...
... A currency board's foreign currency reserves must be sufficient to ensure that all holders of its notes and coins (and all banks creditor of a Reserve Account at the currency board) can convert them into the reserve currency (usually 110–115% of the monetary base M0). A currency board maintains abso ...
Business in the Global Economy
... Money passes from one country to another through investments and tourism Citizens may invest in foreign countries Businesses may invest in a factory in another country ...
... Money passes from one country to another through investments and tourism Citizens may invest in foreign countries Businesses may invest in a factory in another country ...
Vocabulary, Economic terms, page 99
... The study was supported by a $70 000 grant from a research group. They were awarded grants to develop new methods of crop production. currency ...
... The study was supported by a $70 000 grant from a research group. They were awarded grants to develop new methods of crop production. currency ...
Currency

A currency (from Middle English: curraunt, ""in circulation"", from Latin: currens, -entis) in the most specific use of the word refers to money in any form when in actual use or circulation as a medium of exchange, especially circulating banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a system of money (monetary units) in common use, especially in a nation. Under this definition, British pounds, U.S. dollars, and European euros are examples of currency. These various currencies are stores of value, and are traded between nations in foreign exchange markets, which determine the relative values of the different currencies. Currencies in this sense are defined by governments, and each type has limited boundaries of acceptance.Other definitions of the term ""currency"" are discussed in their respective synonymous articles banknote, coin, and money. The latter definition, pertaining to the currency systems of nations, is the topic of this article. Currencies can be classified into two monetary systems: fiat money and commodity money, depending on what guarantees the value (the economy at large vs. the government's physical metal reserves). Some currencies are legal tender in certain jurisdictions, which means they cannot be refused as payment for debt. Others are simply traded for their economic value. Digital currency arose with the popularity of computers and the Internet.