LANdesign
... Network diameter – how many devices must packet pass through? Keep it low. Bandwidth aggregation – combine ports where high bandwidth is needed. Redundant links/devices – in core and distribution layers. Too expensive for access. Start design at the access layer. How many devices, how much bandwidth ...
... Network diameter – how many devices must packet pass through? Keep it low. Bandwidth aggregation – combine ports where high bandwidth is needed. Redundant links/devices – in core and distribution layers. Too expensive for access. Start design at the access layer. How many devices, how much bandwidth ...
ppt - BNRG
... • One big risk factor: the number of network services that are accessible to outsiders • This suggests a possible defense – Reduce risk by blocking, in the network, outsiders from being able to access many network services running on company machines ...
... • One big risk factor: the number of network services that are accessible to outsiders • This suggests a possible defense – Reduce risk by blocking, in the network, outsiders from being able to access many network services running on company machines ...
A Scalable Fault-Tolerant Layer 2 Data Center Network Fabric
... Hence, the current assumption is that the vision of a unified plug-and-play large-scale network fabric is unachievable, leaving data center network architects to adopt ad hoc partitioning and configuration to support large-scale deployments. Recent work in SEATTLE [10] makes dramatic advances toward ...
... Hence, the current assumption is that the vision of a unified plug-and-play large-scale network fabric is unachievable, leaving data center network architects to adopt ad hoc partitioning and configuration to support large-scale deployments. Recent work in SEATTLE [10] makes dramatic advances toward ...
TKN Dynamic shortcut circuits - concept and case study for static scenarios
... 2.4 Gbps per flow, 40% for load equal to 2.0 Gbps per flow, and 50% for load 1.6 Gbps per flow (see Figures 4 and 5). Choosing circuit capacity above these values means prioritization of packets in the new circuits over other packets (degradation of QoS they experience). 3.3.2 Choice of the circuit ...
... 2.4 Gbps per flow, 40% for load equal to 2.0 Gbps per flow, and 50% for load 1.6 Gbps per flow (see Figures 4 and 5). Choosing circuit capacity above these values means prioritization of packets in the new circuits over other packets (degradation of QoS they experience). 3.3.2 Choice of the circuit ...
HIgh PErformance Radio Local Network (HIPERLAN) – Type 1
... Wireless Mobile Network Lab. C.S. TKU ...
... Wireless Mobile Network Lab. C.S. TKU ...
module10b
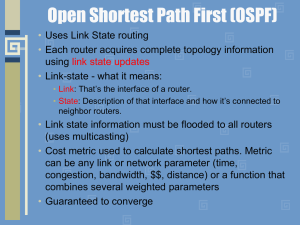
... Point to Point Links • For a point-to-point link running say HDLC. You can see that we have a neighbor but we didn’t do an election for DR or BDR. Makes sense because there is always only one router on the other side. ...
... Point to Point Links • For a point-to-point link running say HDLC. You can see that we have a neighbor but we didn’t do an election for DR or BDR. Makes sense because there is always only one router on the other side. ...
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
... The default gateway has two configurable bits in its Router Advertisement (RA) available for this purpose: • O bit — When this bit is set, the client can use DHCPv6 to retrieve other configuration parameters (for example, TFTP server address or DNS server address) but not the client's IP address. • ...
... The default gateway has two configurable bits in its Router Advertisement (RA) available for this purpose: • O bit — When this bit is set, the client can use DHCPv6 to retrieve other configuration parameters (for example, TFTP server address or DNS server address) but not the client's IP address. • ...
ppt - CSE Labs User Home Pages
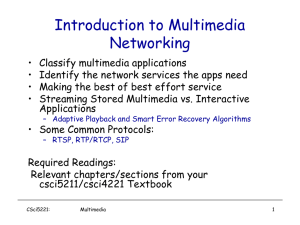
... • does not restrict how forward, etc. streamed media is transported; it can be RTSP: RFC 2326 transported over UDP or • Client-server application TCP layer protocol. • For user to control display: • does not specify how the media player buffers rewind, fast forward, audio/video pause, resume, reposi ...
... • does not restrict how forward, etc. streamed media is transported; it can be RTSP: RFC 2326 transported over UDP or • Client-server application TCP layer protocol. • For user to control display: • does not specify how the media player buffers rewind, fast forward, audio/video pause, resume, reposi ...
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS)
... networks and is standardized by the IETF in RFC 3031. It is deployed to connect as few as two facilities to very large deployments. For example, in the retail sector, it is not uncommon to see deployments of 2000 to 5000 locations to communicate transaction data to a headquarters data center. • In p ...
... networks and is standardized by the IETF in RFC 3031. It is deployed to connect as few as two facilities to very large deployments. For example, in the retail sector, it is not uncommon to see deployments of 2000 to 5000 locations to communicate transaction data to a headquarters data center. • In p ...
Extended Distance Technologies Version 1.4
... extension technologies and information to consider when working with extended distance. IP-based distance extension solutions are also included. E-Lab would like to thank all the contributors to this document, including EMC engineers, EMC field personnel, and partners. Your contributions are invalua ...
... extension technologies and information to consider when working with extended distance. IP-based distance extension solutions are also included. E-Lab would like to thank all the contributors to this document, including EMC engineers, EMC field personnel, and partners. Your contributions are invalua ...
power-point presentation - UNT College of Engineering
... Spans a city or a big campus with range up to 200 km (125 miles) Earlier technologies used for MANs were: Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Switched Megabit Data Service (as defined by IEEE 802.6 MAN standard) using either B-ISDN or Distributed Dual-Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) with speeds 1.5/45 Mbs ...
... Spans a city or a big campus with range up to 200 km (125 miles) Earlier technologies used for MANs were: Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Switched Megabit Data Service (as defined by IEEE 802.6 MAN standard) using either B-ISDN or Distributed Dual-Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) with speeds 1.5/45 Mbs ...
Pi: A Path Identification Mechanism to Defend against DDoS attacks
... that run a variety of IGP routing RX, will be marked with M (RX → R3) = H(RX || R3), protocols internally (such as OSPF or RIP), and then exwhere the function H returns the n least significant bits of port address prefixes externally using the Border Gateway the MD5 hash and ‘||’ represents concaten ...
... that run a variety of IGP routing RX, will be marked with M (RX → R3) = H(RX || R3), protocols internally (such as OSPF or RIP), and then exwhere the function H returns the n least significant bits of port address prefixes externally using the Border Gateway the MD5 hash and ‘||’ represents concaten ...
d ienco - IndexMed 2016
... A graph is generally composed by a set of Vertices and a set of Edges: G = (V,E) An edge is a pair of nodes that are linked each other Node ...
... A graph is generally composed by a set of Vertices and a set of Edges: G = (V,E) An edge is a pair of nodes that are linked each other Node ...
power-point presentation
... Spans a city or a big campus with range up to 200 km (125 miles) Earlier technologies used for MANs were: Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Switched Megabit Data Service (as defined by IEEE 802.6 MAN standard) using either B-ISDN or Distributed Dual-Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) with speeds 1.5/45 Mbs ...
... Spans a city or a big campus with range up to 200 km (125 miles) Earlier technologies used for MANs were: Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) Switched Megabit Data Service (as defined by IEEE 802.6 MAN standard) using either B-ISDN or Distributed Dual-Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) with speeds 1.5/45 Mbs ...
Opportunities and Challenges of Community
... Houses talk to immediate neighbors, All links have capacity 1, 802.11 MAC, Question: Multipath routing. Are 3 radios better than 2? What is the optimum number? ...
... Houses talk to immediate neighbors, All links have capacity 1, 802.11 MAC, Question: Multipath routing. Are 3 radios better than 2? What is the optimum number? ...
22-05-0007-47-0000 - IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee
... An 802.22 system MUST consist of one base station radio and one or more Consumer Premise Equipment (CPE) radios, i.e. an 802.22 base station and one or more stationary CPE radios communicating using the 802.22 MAC and PHY protocols. Proposals for 802.22 MAY also include a description of how repeater ...
... An 802.22 system MUST consist of one base station radio and one or more Consumer Premise Equipment (CPE) radios, i.e. an 802.22 base station and one or more stationary CPE radios communicating using the 802.22 MAC and PHY protocols. Proposals for 802.22 MAY also include a description of how repeater ...
Resilient Optical Network Design:
... Originally, networks were engineered to provide only one type of service, i.e. either voice or data, so only one level of resiliency was requested. This trend has changed, and today’s approach in service provisioning is quite different. A Service Level Agreement (SLA) stipulated between users and se ...
... Originally, networks were engineered to provide only one type of service, i.e. either voice or data, so only one level of resiliency was requested. This trend has changed, and today’s approach in service provisioning is quite different. A Service Level Agreement (SLA) stipulated between users and se ...
THE OPTIMIZATION OF STEPPING STONE DETECTION: PACKET CAPTURING STEPS MOHD NIZAM OMAR
... optimized to copy blocks of packets at a time. This buffer allows all the memory to be used to store network bursts. The entire kernel buffer is usually copied by mean of a single read(), thus decreasing the number of system calls and therefore, the number of context switches between user and kernel ...
... optimized to copy blocks of packets at a time. This buffer allows all the memory to be used to store network bursts. The entire kernel buffer is usually copied by mean of a single read(), thus decreasing the number of system calls and therefore, the number of context switches between user and kernel ...
Chapter 7
... how does callee advertise its IP address, port number, encoding algorithms? Multimedia Networking ...
... how does callee advertise its IP address, port number, encoding algorithms? Multimedia Networking ...
Slide 1
... INVITE: Start sessions and advertise endpoint capabilities ACK: Acknowledge to the called SIP peer that an INVITE has succeeded BYE: This method is used when the call is completed CANCEL: This method is used during attempts to override a prior request that has not yet been completed OPTIONS: Query a ...
... INVITE: Start sessions and advertise endpoint capabilities ACK: Acknowledge to the called SIP peer that an INVITE has succeeded BYE: This method is used when the call is completed CANCEL: This method is used during attempts to override a prior request that has not yet been completed OPTIONS: Query a ...
Lecture5 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Kerberos uses as its basis the symmetric Needham-Schroeder protocol. It makes use of a trusted third party, termed a key distribution center (KDC), which consists of two logically separate parts: an Authentication Server (AS) and a Ticket Granting Server (TGS). Kerberos works on the basis of "ticket ...
... Kerberos uses as its basis the symmetric Needham-Schroeder protocol. It makes use of a trusted third party, termed a key distribution center (KDC), which consists of two logically separate parts: an Authentication Server (AS) and a Ticket Granting Server (TGS). Kerberos works on the basis of "ticket ...