kuroseSlides-chapter1
... FDM: 50 kHz - 1 MHz for downstream 4 kHz - 50 kHz for upstream 0 kHz - 4 kHz for ordinary telephone Introduction ...
... FDM: 50 kHz - 1 MHz for downstream 4 kHz - 50 kHz for upstream 0 kHz - 4 kHz for ordinary telephone Introduction ...
Chapter 4 Routing Protocols
... Routing in sensor networks is a new area of research, with a limited but rapidly growing set of research results We highlight the design trade-offs between energy and communication overhead savings in some of the routing paradigm, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each ...
... Routing in sensor networks is a new area of research, with a limited but rapidly growing set of research results We highlight the design trade-offs between energy and communication overhead savings in some of the routing paradigm, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each ...
A performance analysis modeling of a QoS
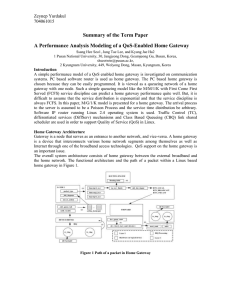
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
... home gateway is composed of two main parts. The first part consists of processors on network interface cards that have functions to receive and transmit packets. The second part is the CPU of the PC machine that forwards packets not destined for itself, and process packets destined for itself. The b ...
Wireless Sensor Networks Using A Delay-Aware
... because all the optimization techniques employed in the top-down approach are carried out individually. Although all the optimization techniques will provide optimum solutions, there is lack of a global optimization method. This makes the topdown approach more effective for smallscale networks, but ...
... because all the optimization techniques employed in the top-down approach are carried out individually. Although all the optimization techniques will provide optimum solutions, there is lack of a global optimization method. This makes the topdown approach more effective for smallscale networks, but ...
Dynamic Routing Protocols
... OSPF Routing Protocol • Link State Protocol – Link is connection between two routers – OSPF routing table stores more information about each link than just its hop count: cost, reliability, etc. – Allows OSPF routers to optimize routing based on these variables Link ...
... OSPF Routing Protocol • Link State Protocol – Link is connection between two routers – OSPF routing table stores more information about each link than just its hop count: cost, reliability, etc. – Allows OSPF routers to optimize routing based on these variables Link ...
Mobility in the Internet
... • MPLS is a traffic engineering tool whereby we allocate specific path and network resources to specific types of traffic ensuring QoS • Supports Multiple protocols like IPv4, IPv6, IPX, AppleTalk at the network layer, and Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, ATM, Frame Relay, PPP at the link layer • Indepen ...
... • MPLS is a traffic engineering tool whereby we allocate specific path and network resources to specific types of traffic ensuring QoS • Supports Multiple protocols like IPv4, IPv6, IPX, AppleTalk at the network layer, and Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, ATM, Frame Relay, PPP at the link layer • Indepen ...
Chapter1_sept_20_05
... = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
... = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 1
... If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form, that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our sl ...
... If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) in substantially unaltered form, that you mention their source (after all, we’d like people to use our book!) If you post any slides in substantially unaltered form on a www site, that you note that they are adapted from (or perhaps identical to) our sl ...
Mobile IP
... In DVP, each node contains a routing table with a list of shortest paths to the other nodes in the network At start, each node has knowledge of its own address and is able to transmit on all links connecting to neighboring nodes If distance to the node is shorter than the distance in the routing tab ...
... In DVP, each node contains a routing table with a list of shortest paths to the other nodes in the network At start, each node has knowledge of its own address and is able to transmit on all links connecting to neighboring nodes If distance to the node is shorter than the distance in the routing tab ...
Chapter 2 Protocols and Architecture
... — Guarantee Error Free Delivery of Message from sourcehost to the destination-host (End-to-End reliability) — Offers connection oriented and connection less services — Reliability includes: Error detection and correction, flow control, packet duplication etc… — Runs only on host not on the network ...
... — Guarantee Error Free Delivery of Message from sourcehost to the destination-host (End-to-End reliability) — Offers connection oriented and connection less services — Reliability includes: Error detection and correction, flow control, packet duplication etc… — Runs only on host not on the network ...
ppt
... • Free BSD with 200 byte UDP traffic at 50 packets/second (G.711 compatible), Nov 27th, 2001 for 2.5 days - have more data but it all looks similar Verify no loss at last hops DAGs provide GPS timestamps ...
... • Free BSD with 200 byte UDP traffic at 50 packets/second (G.711 compatible), Nov 27th, 2001 for 2.5 days - have more data but it all looks similar Verify no loss at last hops DAGs provide GPS timestamps ...
Efficient Resource Management for Hard Real
... – If a large number of real-time flows come on-demand, because the user can be anywhere at anytime on the Internet ... ...
... – If a large number of real-time flows come on-demand, because the user can be anywhere at anytime on the Internet ... ...
Fundamentals of Computer Networks ECE 478/578
... Limitations of the network layer Can drop messages (routers may incurr buffer overflow etc.) Can reorder messages Deliver duplicate copies of the same message Limit messages to finite size (eg. IP size is limited) ...
... Limitations of the network layer Can drop messages (routers may incurr buffer overflow etc.) Can reorder messages Deliver duplicate copies of the same message Limit messages to finite size (eg. IP size is limited) ...
Wireless Networks
... • Multiple BSs can be configured to form a cellular wireless network. The radius of a cell can be 2-40 km while practical one is around 7-8 km with data rate as 70 Mbps per RF channel at a BS • A point-to-point (P2P) or mesh topology also supported by the IEEE 802.16 standard ...
... • Multiple BSs can be configured to form a cellular wireless network. The radius of a cell can be 2-40 km while practical one is around 7-8 km with data rate as 70 Mbps per RF channel at a BS • A point-to-point (P2P) or mesh topology also supported by the IEEE 802.16 standard ...
chapter_19_routing
... provides info about which networks can be reached by a given router and ASs crossed to get there does not include distance or cost estimate hence dispenses with concept of routing metrics ...
... provides info about which networks can be reached by a given router and ASs crossed to get there does not include distance or cost estimate hence dispenses with concept of routing metrics ...
CMPT 880: Internet Architectures and Protocols
... segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app Connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app Connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Chapter 1
... • Regenerate and retransmit data signals. • Maintain information about what pathways exist through the network and internetwork. • Notify other devices of errors and communication failures. • Direct data along alternate pathways when there is a link failure. • Classify and direct messages according ...
... • Regenerate and retransmit data signals. • Maintain information about what pathways exist through the network and internetwork. • Notify other devices of errors and communication failures. • Direct data along alternate pathways when there is a link failure. • Classify and direct messages according ...
paper
... generation-based and sliding window approaches are possible, and a group-block acknowledgment scheme can be implemented by modifying block acknowledgment control type frames. Discussions on potential energy and throughput advantages of network coding are provided. ...
... generation-based and sliding window approaches are possible, and a group-block acknowledgment scheme can be implemented by modifying block acknowledgment control type frames. Discussions on potential energy and throughput advantages of network coding are provided. ...
Digital Television Networks
... resulting in an MPEG transport stream (MTS) that may be multiplexed with other MPEG transport streams for transmission and interconnection. The MPEG-2 is a standard that defines generic syntax for transport of video and associated audio by means of data compression and supports a wide range of perfo ...
... resulting in an MPEG transport stream (MTS) that may be multiplexed with other MPEG transport streams for transmission and interconnection. The MPEG-2 is a standard that defines generic syntax for transport of video and associated audio by means of data compression and supports a wide range of perfo ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 1
... = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
... = L/R, significant for low-speed links dprop = propagation delay a few microsecs to hundreds of msecs ...
Bob - VideoLectures.NET
... (i.e. Bob), who ‘de-onion’ another layer from this set. - Computes intermediate verification, shuffles the result in set ‘S’= {d’m ,d’n ,d’o} and sends S to data miner. ...
... (i.e. Bob), who ‘de-onion’ another layer from this set. - Computes intermediate verification, shuffles the result in set ‘S’= {d’m ,d’n ,d’o} and sends S to data miner. ...
การสื่อสารข้อมูล
... • Transceivers must be within line of sight of each other (directly or via reflection ). • Unlike microwaves, infrared does not penetrate walls. • Very common with remote control devices, but can also be used for device-to-device transfers, such as PDA to computer. Data Communication and Computer Ne ...
... • Transceivers must be within line of sight of each other (directly or via reflection ). • Unlike microwaves, infrared does not penetrate walls. • Very common with remote control devices, but can also be used for device-to-device transfers, such as PDA to computer. Data Communication and Computer Ne ...