Draft CCNA 3
... Module 11: TCP/IP Transport and Application Layers 11.1 TCP/IP Transport Layer 11.2 TCP/IP Application Layer Case Study: Structured Cabling What has changed from CCNA versions 2.x? More information on optical and wireless More cable testing terminology and concepts More details on the operation of ...
... Module 11: TCP/IP Transport and Application Layers 11.1 TCP/IP Transport Layer 11.2 TCP/IP Application Layer Case Study: Structured Cabling What has changed from CCNA versions 2.x? More information on optical and wireless More cable testing terminology and concepts More details on the operation of ...
Introduction to Community-based SNMPv2
... Framework for the SNMP version 2 framework (SNMPv2). The SNMPv2 framework is fully described in [1-6]. This framework is derived from the original Internet-standard Network Management Framework (SNMPv1), which consists of these three documents: - STD 16, RFC 1155 [7] which defines the Structure of M ...
... Framework for the SNMP version 2 framework (SNMPv2). The SNMPv2 framework is fully described in [1-6]. This framework is derived from the original Internet-standard Network Management Framework (SNMPv1), which consists of these three documents: - STD 16, RFC 1155 [7] which defines the Structure of M ...
port
... runs a protocal broadly known as Ethernet. If your are running wireless, it's some kind of wireless Ethernet. ...
... runs a protocal broadly known as Ethernet. If your are running wireless, it's some kind of wireless Ethernet. ...
2.1 Idiosyncrasies of Ad Hoc Networks
... Availability Availability requires that network assets are available to authorized parties when needed and ensures the survivability of network services despite denial-ofservice (DOS) attacks, which could be launched at any layer of the ad hoc network. The DOS attack can cause physical jamming, di ...
... Availability Availability requires that network assets are available to authorized parties when needed and ensures the survivability of network services despite denial-ofservice (DOS) attacks, which could be launched at any layer of the ad hoc network. The DOS attack can cause physical jamming, di ...
Wireless Mesh Networks - BWN-Lab
... networks in which each node can communicate directly with one or more peer nodes. The term 'mesh' originally used to suggest that all nodes were connected to all other nodes, but most modern meshes connect only a sub-set of nodes to each other. Still, this is quite different than traditional wir ...
... networks in which each node can communicate directly with one or more peer nodes. The term 'mesh' originally used to suggest that all nodes were connected to all other nodes, but most modern meshes connect only a sub-set of nodes to each other. Still, this is quite different than traditional wir ...
lecture6-Attacks
... • Overwrite IP-to-MAC ARP tables • Alice’s segments will not reach Bob and vice-versa • But attacker continues to hear Bob’s ...
... • Overwrite IP-to-MAC ARP tables • Alice’s segments will not reach Bob and vice-versa • But attacker continues to hear Bob’s ...
A Study on Effective Hash Routing in MANET
... AODV [3],[4] of base of DSDV(Destination Sequenced Distance Vector) supports all of the Unicasts and Multicasts and uses sequence numbers of a DN(Destination Node) to protect loop. It is able to improve performance of entire networks. When a SN (Source Node) would transmit messages for routing to a ...
... AODV [3],[4] of base of DSDV(Destination Sequenced Distance Vector) supports all of the Unicasts and Multicasts and uses sequence numbers of a DN(Destination Node) to protect loop. It is able to improve performance of entire networks. When a SN (Source Node) would transmit messages for routing to a ...
Lecture 4 - Lyle School of Engineering
... Exercises congestion control to maintain network efficiency during heavy traffic loads Allows transport layer to send data from host to host without need to know network details Unlike other layers, nodes need to share information among themselves to make decisions ...
... Exercises congestion control to maintain network efficiency during heavy traffic loads Allows transport layer to send data from host to host without need to know network details Unlike other layers, nodes need to share information among themselves to make decisions ...
IPv6 networks deployments
... • Assign /56 address prefix to each school network • School prefixes are aggregated into /48 prefixes – Address allocation follows the hierarchical structure of the GSN – One /48 prefix is advertised by each of the 8 core nodes – Assign an extra /48 prefix for the backbone ...
... • Assign /56 address prefix to each school network • School prefixes are aggregated into /48 prefixes – Address allocation follows the hierarchical structure of the GSN – One /48 prefix is advertised by each of the 8 core nodes – Assign an extra /48 prefix for the backbone ...
6LoWPAN adaptation layer (cont.)
... To accomplish the multi-hop packet forwarding, 6LoWPAN defined Mesh Header (4 - 5 bytes) as shown in Figure 5. Basically, the Mesh header is used to standardize the way to encode the hop limit and the link layer source and destination of the packets. Since the 802.15.4 standard support for 16- ...
... To accomplish the multi-hop packet forwarding, 6LoWPAN defined Mesh Header (4 - 5 bytes) as shown in Figure 5. Basically, the Mesh header is used to standardize the way to encode the hop limit and the link layer source and destination of the packets. Since the 802.15.4 standard support for 16- ...
- ASU Digital Repository
... devices has been introduced that provides fully integrated support for the use of 802.11 and cellular protocol stacks A new hardware implementation (e.g. start of SoC design, functional decomposition) had been introduced to support this new link layer idea that wireless data frames are processed b ...
... devices has been introduced that provides fully integrated support for the use of 802.11 and cellular protocol stacks A new hardware implementation (e.g. start of SoC design, functional decomposition) had been introduced to support this new link layer idea that wireless data frames are processed b ...
CSC 335 Data Communications and Networking I
... Common routing protocol Set of routers and networks managed by single organization • A connected network – There is at least one route between any pair of nodes ...
... Common routing protocol Set of routers and networks managed by single organization • A connected network – There is at least one route between any pair of nodes ...
New Methods and Combinatorics for Bypassing Intrusion Prevention
... tools have been limited by standard operating systems and their TCP/IP stacks. The limitations are to be expected, as these systems are supposed to follow the conser vative sending behavior requirement. Freeing themselves from these limitations with special low-level tools, including TCP/IP stacks h ...
... tools have been limited by standard operating systems and their TCP/IP stacks. The limitations are to be expected, as these systems are supposed to follow the conser vative sending behavior requirement. Freeing themselves from these limitations with special low-level tools, including TCP/IP stacks h ...
Chapter 2 Internetworking
... Routers use the logical address in a Network layer header to determine the next hop router to forward the packet to. Routers can use access lists, created by an administrator, to control security on the types of packets that are allowed to enter or exit an interface. Routers can provide layer 2 brid ...
... Routers use the logical address in a Network layer header to determine the next hop router to forward the packet to. Routers can use access lists, created by an administrator, to control security on the types of packets that are allowed to enter or exit an interface. Routers can provide layer 2 brid ...
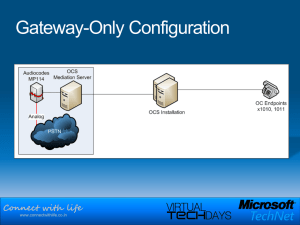
Connect with life
... “Even a 1% loss can significantly degrade the user experience with G.711, which is considered the standard for toll quality” 1 “The default G.729 codec requires packet loss far less than 1% to avoid audible errors” 2 ...
... “Even a 1% loss can significantly degrade the user experience with G.711, which is considered the standard for toll quality” 1 “The default G.729 codec requires packet loss far less than 1% to avoid audible errors” 2 ...
ORA - CASOS cmu
... For multi-time period data spectral analysis and change detection are available (McCulloh et al., 2012). Spectral analysis supports the user in assessing the regularities and anomalies in temporal network data. Graph or node level metrics can be examined over time and the “patterns of life” identif ...
... For multi-time period data spectral analysis and change detection are available (McCulloh et al., 2012). Spectral analysis supports the user in assessing the regularities and anomalies in temporal network data. Graph or node level metrics can be examined over time and the “patterns of life” identif ...
Lecture #23: Link layer - Computer Science & Engineering
... ATM Layer: Virtual Circuits VC transport: cells carried on VC from source to dest call setup, teardown for each call before data can flow ...
... ATM Layer: Virtual Circuits VC transport: cells carried on VC from source to dest call setup, teardown for each call before data can flow ...
lec5-6 - JHU CS
... • Bridges (aka Ethernet switches) were introduced to allow the interconnection of several local area networks (LANs) without a router. • By partitioning a large LAN into multiple smaller networks, there are fewer collisions, and more parallel communications. • It is now common for the port of an Eth ...
... • Bridges (aka Ethernet switches) were introduced to allow the interconnection of several local area networks (LANs) without a router. • By partitioning a large LAN into multiple smaller networks, there are fewer collisions, and more parallel communications. • It is now common for the port of an Eth ...
12Introspection - BNRG - University of California, Berkeley
... network activity, resource availability, denial of service attacks, etc. – Extracting a behavioral model from such use (discover) – Use this model to improve the behavior of the system, by making it more proactive, rather than reactive, to how it is used – Improve performance and fault tolerance, e. ...
... network activity, resource availability, denial of service attacks, etc. – Extracting a behavioral model from such use (discover) – Use this model to improve the behavior of the system, by making it more proactive, rather than reactive, to how it is used – Improve performance and fault tolerance, e. ...
Lecture 16
... • But these do not work well in LANs – Bursty traffic means channel is poorly used • Idle sender eats bandwidth that can be given to busy sender ...
... • But these do not work well in LANs – Bursty traffic means channel is poorly used • Idle sender eats bandwidth that can be given to busy sender ...
192.168.32.112-119
... Modified Routing Algorithm 1. For each routing table entry: perform AND between destination address and entry subnet mask; if result equals the entry network address and entry more specific (i.e., longer subnet mask) than the previous one, keep it and discard the other 2. If matched, and next hop i ...
... Modified Routing Algorithm 1. For each routing table entry: perform AND between destination address and entry subnet mask; if result equals the entry network address and entry more specific (i.e., longer subnet mask) than the previous one, keep it and discard the other 2. If matched, and next hop i ...