GPSR: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing for Wireless Networks
... address) and position. We encode position as two four-byte floatingpoint quantities, for x and y coordinate values. To avoid synchronization of neighbors’ beacons, as observed by Floyd and Jacobson [8], we jitter each beacon’s transmission by 50% of the interval B between beacons, such that the mean ...
... address) and position. We encode position as two four-byte floatingpoint quantities, for x and y coordinate values. To avoid synchronization of neighbors’ beacons, as observed by Floyd and Jacobson [8], we jitter each beacon’s transmission by 50% of the interval B between beacons, such that the mean ...
A Routing Underlay for Overlay Networks Department of Computer Science Princeton University
... a node being ping. On PlanetLab, for example, we recently measured 1GB-per-day of ping traffic (outbound only), corresponding to a little over one ping per second per node across approximately 125 nodes. Although it is difficult to quantify how many concurrent overlays a network could support—or wha ...
... a node being ping. On PlanetLab, for example, we recently measured 1GB-per-day of ping traffic (outbound only), corresponding to a little over one ping per second per node across approximately 125 nodes. Although it is difficult to quantify how many concurrent overlays a network could support—or wha ...
Enterprise Council Comms overview
... – Potentially insecure, does not scale well for large environments, difficult to deploy when network requires access to many centralised services like Fileservers, Routers and Internet access – Does not scale for large networks when using public IP addressing ...
... – Potentially insecure, does not scale well for large environments, difficult to deploy when network requires access to many centralised services like Fileservers, Routers and Internet access – Does not scale for large networks when using public IP addressing ...
GPSR: Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing for Wireless Networks
... Greedy forwarding’s great advantage is its reliance only on knowledge of the forwarding node’s immediate neighbors. The state required is negligible, and dependent on the density of nodes in the wireless network, not the total number of destinations in the network.1 On networks where multi-hop routi ...
... Greedy forwarding’s great advantage is its reliance only on knowledge of the forwarding node’s immediate neighbors. The state required is negligible, and dependent on the density of nodes in the wireless network, not the total number of destinations in the network.1 On networks where multi-hop routi ...
Benefits of an Implementation of H-P2PSIP
... in all peers, since each peer needs to maintain each level of the hierarchy. Other issues related with hierarchical ring topologies are published in [17]. Additional improvements and algorithms that are more complex can be used if necessary. Cyclone [18] builds a hierarchical DHT overlay network in ...
... in all peers, since each peer needs to maintain each level of the hierarchy. Other issues related with hierarchical ring topologies are published in [17]. Additional improvements and algorithms that are more complex can be used if necessary. Cyclone [18] builds a hierarchical DHT overlay network in ...
Wireless TCP(September 20)
... “Incompatible” timers cause retransmission by both parties. Unless the packet loss rate is high (more than about 10%), competing retransmissions by the link and transport layers often lead to significant performance degradation. When packets are lost, link-layer protocols do not attempt in-order ...
... “Incompatible” timers cause retransmission by both parties. Unless the packet loss rate is high (more than about 10%), competing retransmissions by the link and transport layers often lead to significant performance degradation. When packets are lost, link-layer protocols do not attempt in-order ...
Relay Node Placement for Performance Enhancement with
... These authors, which also make the use of a linear program formulation, have considered as objective maximizing network utilization when RNs can be deployed only in a set of feasible sites. Kashyap et al. [18] studied the placement of RNs with the goal of reducing maximum link load for a given traff ...
... These authors, which also make the use of a linear program formulation, have considered as objective maximizing network utilization when RNs can be deployed only in a set of feasible sites. Kashyap et al. [18] studied the placement of RNs with the goal of reducing maximum link load for a given traff ...
GF2310821087
... nodes. In AODV, a routing table expires, if not used recently, thus decreasing the overhead. AODV uses destination sequence numbers to ensure that all routes are loop free and it contains the most recent information. Each node has its own sequence number and broadcast-identifier. The sequence number ...
... nodes. In AODV, a routing table expires, if not used recently, thus decreasing the overhead. AODV uses destination sequence numbers to ensure that all routes are loop free and it contains the most recent information. Each node has its own sequence number and broadcast-identifier. The sequence number ...
Factors that influence TCP performance
... Sender and receiver have static IP addresses (at least for the duration of the session) No handoffs While packet routes may vary, routing nodes form a fixed network, i.e., they do not drop into and out of the network and they maintain a fixed topology relative to one another ...
... Sender and receiver have static IP addresses (at least for the duration of the session) No handoffs While packet routes may vary, routing nodes form a fixed network, i.e., they do not drop into and out of the network and they maintain a fixed topology relative to one another ...
ICS 156: Advanced Computer Networks
... After each lab session, you prepare a lab report that summarizes and analyzes the findings from the lab session. A notepad symbol indicates an assignment for the lab report. The lab reports should be submitted as a typewritten ...
... After each lab session, you prepare a lab report that summarizes and analyzes the findings from the lab session. A notepad symbol indicates an assignment for the lab report. The lab reports should be submitted as a typewritten ...
Document
... On the other hand, sensing fixed events allows the network to work in a reactive mode while dynamic events in most applications require periodic reporting to the BS. ...
... On the other hand, sensing fixed events allows the network to work in a reactive mode while dynamic events in most applications require periodic reporting to the BS. ...
Multihoming support based on mobile node protocol LIN6
... identity and its location. In LIN6 architecture, we divide a 128bit-long IPv6 address into two parts. The first half is called “locator” and the second half “identifier”. A locator only depicts a location and an identifier only depicts an identity. A LIN6 node can identify a corresponding node by exami ...
... identity and its location. In LIN6 architecture, we divide a 128bit-long IPv6 address into two parts. The first half is called “locator” and the second half “identifier”. A locator only depicts a location and an identifier only depicts an identity. A LIN6 node can identify a corresponding node by exami ...
Document
... Packet switching is more suitable for WAN » Line efficiency – Single node to node link can be shared by many connections over time – Packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible » Data rate conversion – Each station connects to the local node at its own speed – Nodes buffer data if required t ...
... Packet switching is more suitable for WAN » Line efficiency – Single node to node link can be shared by many connections over time – Packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible » Data rate conversion – Each station connects to the local node at its own speed – Nodes buffer data if required t ...
22-IPv6-BF - EECS People Web Server
... addresses, address prefixes, and other parameters. • Routers use ND to advertise their presence, configure host parameters, inform hosts of next-hop address and on-link prefixes. • Nodes use ND to resolve link-layer address of a neighboring node to see if it has changed and to determine if IPv6 pack ...
... addresses, address prefixes, and other parameters. • Routers use ND to advertise their presence, configure host parameters, inform hosts of next-hop address and on-link prefixes. • Nodes use ND to resolve link-layer address of a neighboring node to see if it has changed and to determine if IPv6 pack ...
Physical Topologies in Computer Networks
... wireless networks, from this point of view access points also serve as a bridge and they enable such devices like a printer that doesn’t have wireless property [11]. In addition to this access points strengthens the incoming signals to transmit them further. By using lots of access points the length ...
... wireless networks, from this point of view access points also serve as a bridge and they enable such devices like a printer that doesn’t have wireless property [11]. In addition to this access points strengthens the incoming signals to transmit them further. By using lots of access points the length ...
A Protocol for a Wireless ... Xiaolan Qian
... Abstract Recent trends in wireless network development have focused on higher bandwidth and robust performance. However, a network of small, cost effective single frequency radios is advantagous when used by a class of applications that do not require the high performance that more sophisticated rad ...
... Abstract Recent trends in wireless network development have focused on higher bandwidth and robust performance. However, a network of small, cost effective single frequency radios is advantagous when used by a class of applications that do not require the high performance that more sophisticated rad ...
Q and A for Ch. 17
... Q: Could you explain the Distributed Spanning Tree? A: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is 802.1d. A spanning tree is the set of links that connect all devices, without any loops. Each switch is configured (at the factory) to belong to a special multicast MAC group. The switches send many messages to ea ...
... Q: Could you explain the Distributed Spanning Tree? A: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is 802.1d. A spanning tree is the set of links that connect all devices, without any loops. Each switch is configured (at the factory) to belong to a special multicast MAC group. The switches send many messages to ea ...
Error Detection and Correction
... Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is the cell relay protocol designed by the ATM Forum and adopted by the ITU-T. ...
... Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is the cell relay protocol designed by the ATM Forum and adopted by the ITU-T. ...
Chapter 4 PowerPoint Slides
... Network of networks that use the TCP/IP protocol Contain gateways to computers that do not use TCP/IP Provides four basic functions: ...
... Network of networks that use the TCP/IP protocol Contain gateways to computers that do not use TCP/IP Provides four basic functions: ...
Symantec Enterprise Firewalls
... next-generation firewall appliance that integrates full packet inspection firewall technology with intrusion prevention intelligence at the gateway between the Internet and corporate network or between network segments. • The solution leverages tightly integrated, industry-leading technologies to co ...
... next-generation firewall appliance that integrates full packet inspection firewall technology with intrusion prevention intelligence at the gateway between the Internet and corporate network or between network segments. • The solution leverages tightly integrated, industry-leading technologies to co ...
Computer Networks(Routing and IPv6).
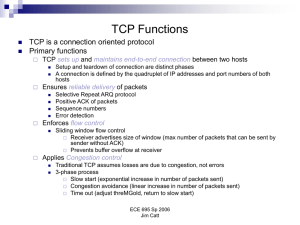
... • When the window size is 0, the sender stop sending data to receiver except – Urgent data may be sent. – Send a 1-byte segment to make the receiver reannounce the next byte expected and window size. ...
... • When the window size is 0, the sender stop sending data to receiver except – Urgent data may be sent. – Send a 1-byte segment to make the receiver reannounce the next byte expected and window size. ...
Routing and Clustering
... • A node q’s position P(q) = where qi is
#hops from node q to beacon i
• Distance function δ(p, d) to measure how good p would
be as a next hop to reach the destination d
– Choose a node whose coordinates are more to the sink’s
...
... • A node q’s position P(q) =
Computer Networks - Network Optiminization Research Group
... • When the window size is 0, the sender stop sending data to receiver except – Urgent data may be sent. – Send a 1-byte segment to make the receiver reannounce the next byte expected and window size. ...
... • When the window size is 0, the sender stop sending data to receiver except – Urgent data may be sent. – Send a 1-byte segment to make the receiver reannounce the next byte expected and window size. ...
VPN Traffic Explorer
... Network engineers can analyze traffic trends on every link in the network, projecting future traffic levels, and easily determining when user-specified thresholds will be reached. Projections can be based on total link traffic, thereby anticipating and helping avoid network congestion, or by CoS, as ...
... Network engineers can analyze traffic trends on every link in the network, projecting future traffic levels, and easily determining when user-specified thresholds will be reached. Projections can be based on total link traffic, thereby anticipating and helping avoid network congestion, or by CoS, as ...