Qubits with electrons on liquid helium
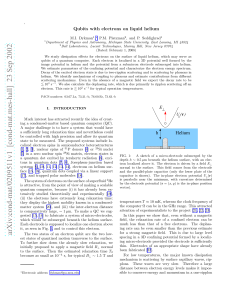
... This energy is very sensitive to dij and can be increased by reducing the inter-electron distance. Eqs. (4), (5) apply for dij less than the distance from the electrons to the grounded plate in Fig. 1; for larger dij the interaction is screened and falls down as d−5 ij . In practice it means that th ...
... This energy is very sensitive to dij and can be increased by reducing the inter-electron distance. Eqs. (4), (5) apply for dij less than the distance from the electrons to the grounded plate in Fig. 1; for larger dij the interaction is screened and falls down as d−5 ij . In practice it means that th ...
Chapter 13 NUCLEAR FUSION
... understand how protons are created by energy drawn from the aether, as was proved in Part II of this work, and so he was unaware that the virtual muons of the aether could intrude in the nuclear energy game and play a part which triggers the cold fusion reaction. Nor did Sir Harrie Massey know that ...
... understand how protons are created by energy drawn from the aether, as was proved in Part II of this work, and so he was unaware that the virtual muons of the aether could intrude in the nuclear energy game and play a part which triggers the cold fusion reaction. Nor did Sir Harrie Massey know that ...
Introducing many-body physics using atomic
... atomic spectroscopy (i.e., Rydberg series, Fano profiles, Cooper minima, and giant resonances) as examples for illustrating the influence of many-body effects (see Section III). We employ the photoabsorption cross section as a characteristic quantity, because it is experimentally accessible through ...
... atomic spectroscopy (i.e., Rydberg series, Fano profiles, Cooper minima, and giant resonances) as examples for illustrating the influence of many-body effects (see Section III). We employ the photoabsorption cross section as a characteristic quantity, because it is experimentally accessible through ...
Lesson 5: The Parallel Plate System
... distance apart. One plate is given a positive charge and the other plate is given a negative ...
... distance apart. One plate is given a positive charge and the other plate is given a negative ...
Lect05
... Motion of a Charge in a Field •An electron passes between two charged plates (cathode ray tube in your television set) •While the electron is between the plates, it experiences an acceleration in the y-direction due to the electric field E ...
... Motion of a Charge in a Field •An electron passes between two charged plates (cathode ray tube in your television set) •While the electron is between the plates, it experiences an acceleration in the y-direction due to the electric field E ...
Deflection of a Magnetic Needle in a Static Electric Field which Varies
... I. INTRODUCTION Electrically charged particles, such as electrons and protons, are everywhere. In contrast, elementary particles with a net magnetic charge, predicted by Dirac [1], have never been observed despite intensive and prolonged searches [2-13]. Recently, some condensed matter systems showe ...
... I. INTRODUCTION Electrically charged particles, such as electrons and protons, are everywhere. In contrast, elementary particles with a net magnetic charge, predicted by Dirac [1], have never been observed despite intensive and prolonged searches [2-13]. Recently, some condensed matter systems showe ...
Identity Charge and the Origin of Life
... Below I briefly review the chain of 4x3 fractal resonances leading into and prefiguring the form of the biological realm. I begin the list (arbitrarily) with: 1) Four conservation laws connected in triplets: the "Word" or "Tetrahedron Model" of conservation law. 2) These manifest as the four forces ...
... Below I briefly review the chain of 4x3 fractal resonances leading into and prefiguring the form of the biological realm. I begin the list (arbitrarily) with: 1) Four conservation laws connected in triplets: the "Word" or "Tetrahedron Model" of conservation law. 2) These manifest as the four forces ...
Atomic Structure
... mass, no matter the amount. Based off of this idea, Proust developed the law of definite proportions which was published in 1799. To illustrate this, suppose compound AB is made of element A and element B. Regardless of how much AB is present, the ratio between the mass of A and the mass of B will b ...
... mass, no matter the amount. Based off of this idea, Proust developed the law of definite proportions which was published in 1799. To illustrate this, suppose compound AB is made of element A and element B. Regardless of how much AB is present, the ratio between the mass of A and the mass of B will b ...
coulomb energy of a solitary dust grain in dusty plasma
... Radio Physics Department, Kiev National University, Kiev, Ukraine, email:[email protected] ...
... Radio Physics Department, Kiev National University, Kiev, Ukraine, email:[email protected] ...
Learning station IX : Spin and its applications - Quantum Spin-Off
... (Source Phet Colorad o http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/stern -gerlach/sterngerlach_en.html) ...
... (Source Phet Colorad o http://phet.colorado.edu/sims/stern -gerlach/sterngerlach_en.html) ...
Phenomenology Beyond the Standard Model
... What attitude towards LEP, NuTeV? Do all the data tell the same story? ...
... What attitude towards LEP, NuTeV? Do all the data tell the same story? ...
Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... Electric Forces and Fields Properties of electric charges Only two types of charge have been discovered – positive (due to protons) and negative (due to electrons). Charge on a proton exactly equals the magnitude of the charge of an electron. e = 1.60 X 10-19 C e = elementary charge (magnitude of ...
... Electric Forces and Fields Properties of electric charges Only two types of charge have been discovered – positive (due to protons) and negative (due to electrons). Charge on a proton exactly equals the magnitude of the charge of an electron. e = 1.60 X 10-19 C e = elementary charge (magnitude of ...
Lepton
A lepton is an elementary, half-integer spin (spin 1⁄2) particle that does not undergo strong interactions, but is subject to the Pauli exclusion principle. The best known of all leptons is the electron, which is directly tied to all chemical properties. Two main classes of leptons exist: charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons), and neutral leptons (better known as neutrinos). Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed.There are six types of leptons, known as flavours, forming three generations. The first generation is the electronic leptons, comprising the electron (e−) and electron neutrino (νe); the second is the muonic leptons, comprising the muon (μ−) and muon neutrino (νμ); and the third is the tauonic leptons, comprising the tau (τ−) and the tau neutrino (ντ). Electrons have the least mass of all the charged leptons. The heavier muons and taus will rapidly change into electrons through a process of particle decay: the transformation from a higher mass state to a lower mass state. Thus electrons are stable and the most common charged lepton in the universe, whereas muons and taus can only be produced in high energy collisions (such as those involving cosmic rays and those carried out in particle accelerators).Leptons have various intrinsic properties, including electric charge, spin, and mass. Unlike quarks however, leptons are not subject to the strong interaction, but they are subject to the other three fundamental interactions: gravitation, electromagnetism (excluding neutrinos, which are electrically neutral), and the weak interaction. For every lepton flavor there is a corresponding type of antiparticle, known as antilepton, that differs from the lepton only in that some of its properties have equal magnitude but opposite sign. However, according to certain theories, neutrinos may be their own antiparticle, but it is not currently known whether this is the case or not.The first charged lepton, the electron, was theorized in the mid-19th century by several scientists and was discovered in 1897 by J. J. Thomson. The next lepton to be observed was the muon, discovered by Carl D. Anderson in 1936, which was classified as a meson at the time. After investigation, it was realized that the muon did not have the expected properties of a meson, but rather behaved like an electron, only with higher mass. It took until 1947 for the concept of ""leptons"" as a family of particle to be proposed. The first neutrino, the electron neutrino, was proposed by Wolfgang Pauli in 1930 to explain certain characteristics of beta decay. It was first observed in the Cowan–Reines neutrino experiment conducted by Clyde Cowan and Frederick Reines in 1956. The muon neutrino was discovered in 1962 by Leon M. Lederman, Melvin Schwartz and Jack Steinberger, and the tau discovered between 1974 and 1977 by Martin Lewis Perl and his colleagues from the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center and Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. The tau neutrino remained elusive until July 2000, when the DONUT collaboration from Fermilab announced its discovery.Leptons are an important part of the Standard Model. Electrons are one of the components of atoms, alongside protons and neutrons. Exotic atoms with muons and taus instead of electrons can also be synthesized, as well as lepton–antilepton particles such as positronium.




![Chapter 20: Particle Kinetics of Plasma [version 1220.1.K]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002301794_1-5f49f2e75dc2dc8d81fa0b28a3afc171-300x300.png)


















