Nutrient Deficiency Identification Guide
... nutrients from the soil firstly it must be sufficiently moist to allow root uptake. Second, the pH of the soil must be within a certain range for nutrients to be released (see chart on page 6). Third, the soil temperature must be within a certain range for nutrient uptake to occur. The optimum balan ...
... nutrients from the soil firstly it must be sufficiently moist to allow root uptake. Second, the pH of the soil must be within a certain range for nutrients to be released (see chart on page 6). Third, the soil temperature must be within a certain range for nutrient uptake to occur. The optimum balan ...
Causes of Salinization - Keele Research Repository
... This resource was created by the University of Keele and released as an open educational resource through the 'C-change in GEES' project exploring the open licensing of climate change and sustainability resources in the Geography, Earth and Environmental Sciences. The C-change in GEES project was f ...
... This resource was created by the University of Keele and released as an open educational resource through the 'C-change in GEES' project exploring the open licensing of climate change and sustainability resources in the Geography, Earth and Environmental Sciences. The C-change in GEES project was f ...
Researchers discover tree trunks act as methane source
... of this greenhouse gas is critical for measuring and Warner visited the site over the course of one understanding its implications across ecosystems. growing season, April to December, and measured the carbon dioxide and methane fluxes of the soil, tree trunks and CWD to determine whether those Upla ...
... of this greenhouse gas is critical for measuring and Warner visited the site over the course of one understanding its implications across ecosystems. growing season, April to December, and measured the carbon dioxide and methane fluxes of the soil, tree trunks and CWD to determine whether those Upla ...
EFFECT OF SOIL VARIABILITY ON THE BEARING CAPACITY OF
... in several layers. For such cases, reliable estimation of bearing capacity is extremely complicated. Modern computation techniques, such as the finite element method, require considerable effort before reliable estimates can ultimately be achieved. The question arises whether a simple hand calculati ...
... in several layers. For such cases, reliable estimation of bearing capacity is extremely complicated. Modern computation techniques, such as the finite element method, require considerable effort before reliable estimates can ultimately be achieved. The question arises whether a simple hand calculati ...
Does organic farming reduce environmental impacts?
... emissions per product unit were higher from organic systems. Organic systems had lower energy requirements, but higher land use, eutrophication potential and acidification potential per product unit. The variation within the results across different studies was wide due to differences in the systems ...
... emissions per product unit were higher from organic systems. Organic systems had lower energy requirements, but higher land use, eutrophication potential and acidification potential per product unit. The variation within the results across different studies was wide due to differences in the systems ...
Title (NOT ALL CAPITAL LETTERS)
... collaboration with FAO’s Global Soil Partnership (GSP), FAO's Global Forum for Food Security and Nutrition (FSN Forum) and the World Bank. The ECFS was established by the Government of the Russian Federation at Moscow State University as a follow up to the commitment made by G8 leaders, known as the ...
... collaboration with FAO’s Global Soil Partnership (GSP), FAO's Global Forum for Food Security and Nutrition (FSN Forum) and the World Bank. The ECFS was established by the Government of the Russian Federation at Moscow State University as a follow up to the commitment made by G8 leaders, known as the ...
Quantifying the impact of land degradation on crop
... and crop production (Ferreira et al., 2015). Isolating these is especially difficult for Senegal because there are no historical records available on fertilizer application. While an experimental field trial can for given observed biophysical conditions simulate various intensities of land degradati ...
... and crop production (Ferreira et al., 2015). Isolating these is especially difficult for Senegal because there are no historical records available on fertilizer application. While an experimental field trial can for given observed biophysical conditions simulate various intensities of land degradati ...
S115 Forage Facts Notebook - Missouri State University
... Residue is essential because it reduces soil erosion from wind and water, therefore, it is important to keep some residue in the field. The amount of residue required to minimize erosion varies with the type of residue present, type of soil, the slope of the land, and the presence of barriers (terra ...
... Residue is essential because it reduces soil erosion from wind and water, therefore, it is important to keep some residue in the field. The amount of residue required to minimize erosion varies with the type of residue present, type of soil, the slope of the land, and the presence of barriers (terra ...
Mitigation Measures for Runoff - TOPPS
... • protect the soil surface by plant cover / organic matter cover to reduce damage of soil surface due to heavy rains. • rotation of different crops in large fields and / or in the landscape can serve the function of buffers by reducing speed of water flow and reducing runoff through infiltration (st ...
... • protect the soil surface by plant cover / organic matter cover to reduce damage of soil surface due to heavy rains. • rotation of different crops in large fields and / or in the landscape can serve the function of buffers by reducing speed of water flow and reducing runoff through infiltration (st ...
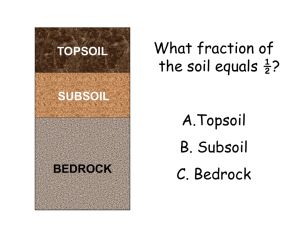
SAND - Soil Scientists Wiki
... field, and tomatoes in 1/8 of his field. Using the key, color his field to show these fractions. ...
... field, and tomatoes in 1/8 of his field. Using the key, color his field to show these fractions. ...
`Environmental Risks Arising from Changes in Ammunition Materials`
... shooting range, we usually see: Organic rich horizons descending into less organic rich layers of weathered soils, overlying un-weathered substrata and parent rock. Grasses, herbs, mosses and lichens; rooted in and underlying thatch and dark organic rich horizon. Surface conditions are typically pH ...
... shooting range, we usually see: Organic rich horizons descending into less organic rich layers of weathered soils, overlying un-weathered substrata and parent rock. Grasses, herbs, mosses and lichens; rooted in and underlying thatch and dark organic rich horizon. Surface conditions are typically pH ...
Chapter 12
... yellow clay overlying the weathered basalt varies from 5 m to over 20 m. The soils are remarkably uniform and are stone-free; they shrink and crack extensively during the dry season. About 85% of the area was cultivated, with wheat, pulses and linseed the main crops grown in the post-monsoon season. ...
... yellow clay overlying the weathered basalt varies from 5 m to over 20 m. The soils are remarkably uniform and are stone-free; they shrink and crack extensively during the dry season. About 85% of the area was cultivated, with wheat, pulses and linseed the main crops grown in the post-monsoon season. ...
THE RELATION BETWEEN THE VALUES pH, V AND S (HUMUS
... THE RELATION BETWEEN THE VALUES pH, V AND S (HUMUS) OF SOME HUMUS SOILS. S (HUMUS). AND V OF THESE SOILS WITH pH = 7. THE EQUIVALENT ...
... THE RELATION BETWEEN THE VALUES pH, V AND S (HUMUS) OF SOME HUMUS SOILS. S (HUMUS). AND V OF THESE SOILS WITH pH = 7. THE EQUIVALENT ...
The impact of structural Fe(III) reduction by bacteria on
... oxides with a related organism Shewanella alga strain BrY (Roden and Zachara, 1996). 3.1. Variety of Soil Bacteria Capable of Smectite Reduction If clay mineral reduction was only carried out by one or a few strains of soil bacteria, then this process may not be as important as perceived in the lite ...
... oxides with a related organism Shewanella alga strain BrY (Roden and Zachara, 1996). 3.1. Variety of Soil Bacteria Capable of Smectite Reduction If clay mineral reduction was only carried out by one or a few strains of soil bacteria, then this process may not be as important as perceived in the lite ...
Perspectives of plant-associated microbes in heavy metal
... siderophore producing microbes influence the heavy metal mobilization and its uptake by plants in multi metal-polluted soils is critical. 2.2. Organic acids Low molecular weight organic acids (LMWOAs) produced by plant-associated microbes have received much attention over the last decades, largely be ...
... siderophore producing microbes influence the heavy metal mobilization and its uptake by plants in multi metal-polluted soils is critical. 2.2. Organic acids Low molecular weight organic acids (LMWOAs) produced by plant-associated microbes have received much attention over the last decades, largely be ...
Consolidation of Soil for Foundation by Using Sand Drains - iep-sac
... become the path of low energy potential and sub soil water flows vertically and radially through sand columns under the hydraulic gradient produced by the fill. As a result, the length of the drainage path becomes very short which helps to speed up the drainage process and consequently the consolida ...
... become the path of low energy potential and sub soil water flows vertically and radially through sand columns under the hydraulic gradient produced by the fill. As a result, the length of the drainage path becomes very short which helps to speed up the drainage process and consequently the consolida ...
PSFA Trench Rescue
... -1 cubic foot of dirt weighs ___ lbs -1 cubic yard of dirt weighs 2,700-3,500 lbs -1 cubic foot of dirt will fill ____ 1 gallon buckets -1 cubic yard of dirt will fill _____ 1 gallon buckets Soil Types -Type ___-Most stable:clay, silty clay and hardpan (resists penetration) No soil is type A if it i ...
... -1 cubic foot of dirt weighs ___ lbs -1 cubic yard of dirt weighs 2,700-3,500 lbs -1 cubic foot of dirt will fill ____ 1 gallon buckets -1 cubic yard of dirt will fill _____ 1 gallon buckets Soil Types -Type ___-Most stable:clay, silty clay and hardpan (resists penetration) No soil is type A if it i ...
Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks
... WEATHERING and the BREAKDOWN of ROCKS SOILS AND SOIL FORMATION Mechanical and chemical weathering of sediment and pre-existing bedrock below produces REGOLITH. REGOLITH is all the material above the bedrock. ...
... WEATHERING and the BREAKDOWN of ROCKS SOILS AND SOIL FORMATION Mechanical and chemical weathering of sediment and pre-existing bedrock below produces REGOLITH. REGOLITH is all the material above the bedrock. ...
Creeping Thistle. Successful control in organic farming.
... conditions, the thistle develops into a biennial plant. If disturbed in its development by agricultural interference, such as cutting and hoeing, it reacts by intensified production of roots and shoots. Creeping thistle occurs on almost all soil types but finds optimal conditions on nutrient-rich, d ...
... conditions, the thistle develops into a biennial plant. If disturbed in its development by agricultural interference, such as cutting and hoeing, it reacts by intensified production of roots and shoots. Creeping thistle occurs on almost all soil types but finds optimal conditions on nutrient-rich, d ...
Guidance on the use of BSI PAS 100 compost in topsoil
... The purpose of topsoil manufacturing is to create an effective soil for the establishment of vegetation. The term topsoil manufacturing, as used in this technical document, refers to the blending of soils available on site along with potentially other organic or inorganic materials with BSI PAS 100 ...
... The purpose of topsoil manufacturing is to create an effective soil for the establishment of vegetation. The term topsoil manufacturing, as used in this technical document, refers to the blending of soils available on site along with potentially other organic or inorganic materials with BSI PAS 100 ...
Soil-Disturbance Field Guide
... The information contained in this publication has been developed for the guidance of employees of the Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, its contractors, and cooperating Federal and State agencies. The Forest Service assumes no responsibility for the interpretation or use of this inform ...
... The information contained in this publication has been developed for the guidance of employees of the Forest Service, U.S. Department of Agriculture, its contractors, and cooperating Federal and State agencies. The Forest Service assumes no responsibility for the interpretation or use of this inform ...
Chapter 10 Keeping nutrients on farm
... Along with the question of sustainable use, the possibility of adverse environmental impacts also attracts the interest of community groups. Hence, both have the potential to result in regulations on fertiliser use and / or consumer action to demand improved management. Studies of dairy farms across ...
... Along with the question of sustainable use, the possibility of adverse environmental impacts also attracts the interest of community groups. Hence, both have the potential to result in regulations on fertiliser use and / or consumer action to demand improved management. Studies of dairy farms across ...
POTASSIUM - Agronomy - K
... does not move readily in most soils. When potassium fertilizers are applied to medium- or fine-textured soils, it takes many years for K+ ions to move over an inch or two by natural processes. In these soils, potassium is considered an immobile nutrient. In very sandy soils, K+ is somewhat mobile an ...
... does not move readily in most soils. When potassium fertilizers are applied to medium- or fine-textured soils, it takes many years for K+ ions to move over an inch or two by natural processes. In these soils, potassium is considered an immobile nutrient. In very sandy soils, K+ is somewhat mobile an ...
Fall Term 2006
... ENT 311 – Intro to Insect Pest Management+ ENT 322 – Honey Bee Biology & Beekeeping+ CROP 330 – World Food Crops+ HORT 330/ENT 300/BI 300 – Plagues, Pests, & Politics+ ENT/HORT 331 – Pollinators in Peril (Syn.CGI) SOIL 335 – Intro to Water Science & Policy+ CROP 340 – Pens & Plows: Writings of Worki ...
... ENT 311 – Intro to Insect Pest Management+ ENT 322 – Honey Bee Biology & Beekeeping+ CROP 330 – World Food Crops+ HORT 330/ENT 300/BI 300 – Plagues, Pests, & Politics+ ENT/HORT 331 – Pollinators in Peril (Syn.CGI) SOIL 335 – Intro to Water Science & Policy+ CROP 340 – Pens & Plows: Writings of Worki ...
A Comparison of Landscape Mulches
... Pine straw has the most effect on soil pH, followed by pine bark, then cypress Termites eat all mulches except Melaleuca Cypress, Pine bark and Melaleuca demonstrated the best color retention ...
... Pine straw has the most effect on soil pH, followed by pine bark, then cypress Termites eat all mulches except Melaleuca Cypress, Pine bark and Melaleuca demonstrated the best color retention ...