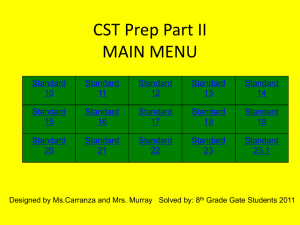
Module 1
... At the end of Module 1 you should be able to do the following: Add decimals using place value strategies and relate those strategies to a written method. Subtract decimals using place value strategies and relate those strategies to a written method. Multiply a decimal fraction by a single dig ...
... At the end of Module 1 you should be able to do the following: Add decimals using place value strategies and relate those strategies to a written method. Subtract decimals using place value strategies and relate those strategies to a written method. Multiply a decimal fraction by a single dig ...
DDC 1012 Slide Topic 2 Powerpoint presentation - Elearning-KL
... • Three actions make a while loop end correctly: 1. Loop control variable is initialized • Prior to entering the loop 2. Loop control variable is tested • If result is true, loop body entered 3. Loop control variable must be updated in loop body • while expression eventually evaluates to false • Loo ...
... • Three actions make a while loop end correctly: 1. Loop control variable is initialized • Prior to entering the loop 2. Loop control variable is tested • If result is true, loop body entered 3. Loop control variable must be updated in loop body • while expression eventually evaluates to false • Loo ...
The Foundations
... s1 can be represented as P(y, min(x,3)) we call any expression that can be put on the argument position of an atomic proposition a term Obviously, constants and variables are terms; moreover,if f is a function of arity n, and t1,...tn are n terms, then so is f(t1,...,tn). Transparency No. 1-25 ...
... s1 can be represented as P(y, min(x,3)) we call any expression that can be put on the argument position of an atomic proposition a term Obviously, constants and variables are terms; moreover,if f is a function of arity n, and t1,...tn are n terms, then so is f(t1,...,tn). Transparency No. 1-25 ...
Program1: Verifying the given number is even or odd #Enter a
... Program1: Verifying the given number is even or odd #Enter a number to verify even or odd num=int(input("enter any value")) if num%2==0: print(" The given number",num,"is even") else: print("The given number",num,"is odd") program 2:# Python program to find the factorial of a number provided by the ...
... Program1: Verifying the given number is even or odd #Enter a number to verify even or odd num=int(input("enter any value")) if num%2==0: print(" The given number",num,"is even") else: print("The given number",num,"is odd") program 2:# Python program to find the factorial of a number provided by the ...