Problem 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... What is the maximum and minimum number of times that the largest element could be moved during the execution of Quicksort? Explain your answer with an example. To answer these questions consider Partition procedure given in your book. ...
... What is the maximum and minimum number of times that the largest element could be moved during the execution of Quicksort? Explain your answer with an example. To answer these questions consider Partition procedure given in your book. ...
Practicals 1 - Roxana Dumitrescu
... Problem 1. Write a C++ program which prints five different basic data types and the number of bytes that each uses. Try out various combinations of long and unsigned etc. Problem 2. Cast char values to int values to find codes used for the characters ’a’, ’z’, ’A’, ’Z’, ’0’, and ’9’. Problem 3. Writ ...
... Problem 1. Write a C++ program which prints five different basic data types and the number of bytes that each uses. Try out various combinations of long and unsigned etc. Problem 2. Cast char values to int values to find codes used for the characters ’a’, ’z’, ’A’, ’Z’, ’0’, and ’9’. Problem 3. Writ ...
advanced algorithms
... 5. Design and implement an approximation algorithm for solving the following k-travelingsalesmen problem. Given are k salesmen and n cities. Each salesman has his own starting city. Find the set of such tours of these salesmen that each city is visited by at least one salesman and total length of to ...
... 5. Design and implement an approximation algorithm for solving the following k-travelingsalesmen problem. Given are k salesmen and n cities. Each salesman has his own starting city. Find the set of such tours of these salesmen that each city is visited by at least one salesman and total length of to ...
Partly Worked Problem
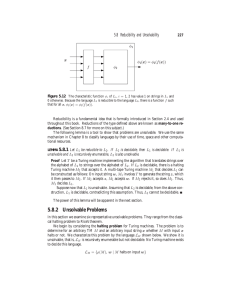
... A “binary tree” is a root “node” and a collection of “child nodes” beneath the root. Each node is an object that has up to two children—a left child and a right child—each of which are themselves binary trees. A binary tree’s “height” is the maximum number of steps it takes to get from the root down ...
... A “binary tree” is a root “node” and a collection of “child nodes” beneath the root. Each node is an object that has up to two children—a left child and a right child—each of which are themselves binary trees. A binary tree’s “height” is the maximum number of steps it takes to get from the root down ...