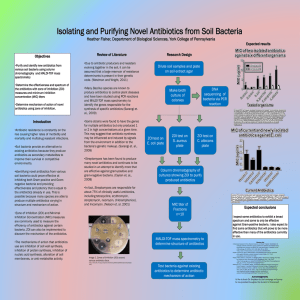
(MIC) titers Determine mechanism of action of novel antibiotics using
... studied in an attempt to identify more that are effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. (Ceylan et. al., ...
... studied in an attempt to identify more that are effective against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. (Ceylan et. al., ...
Garden Activities Schedule
... K-LS1-1. Observe and communicate that animals (including humans) and plants need food, water, and air to survive. Animals get food from plants or other animals. Plants make their own food and need light to live and grow. K-LS1-1(MA0 recognize that all plants and animals grow and change over time. 1- ...
... K-LS1-1. Observe and communicate that animals (including humans) and plants need food, water, and air to survive. Animals get food from plants or other animals. Plants make their own food and need light to live and grow. K-LS1-1(MA0 recognize that all plants and animals grow and change over time. 1- ...
Organic garden products guide
... which is intended, or offered to be used for improving or maintaining the growth of plants, or the fertility of the soil. An inorganic fertilizer is :A chemically composed substance, which contains one or more of the plant nutrients Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) or Potassium (K); and that it shall no ...
... which is intended, or offered to be used for improving or maintaining the growth of plants, or the fertility of the soil. An inorganic fertilizer is :A chemically composed substance, which contains one or more of the plant nutrients Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P) or Potassium (K); and that it shall no ...
Running title: Climate change dominates future carbon export
... (mm-1), and i0 is a reference gradient (0.5×10-4 mm-1). For the residence time of water in the lake, we assume it is 10 times longer than that of river in the same grid cell. Different carbon species are assumed to distribute evenly in each river body and move downstream with water. More detailed de ...
... (mm-1), and i0 is a reference gradient (0.5×10-4 mm-1). For the residence time of water in the lake, we assume it is 10 times longer than that of river in the same grid cell. Different carbon species are assumed to distribute evenly in each river body and move downstream with water. More detailed de ...
Watering Trees - City of Springfield, MO
... An excessive amount of water, especially in heavy or tight clay soils, may force air from the soil and cause roots to suffocate. However, many more planted trees are lost from dryness than from overwatering. Keep soil moist, but not soggy. Well established trees are rarely affected by overwatering, ...
... An excessive amount of water, especially in heavy or tight clay soils, may force air from the soil and cause roots to suffocate. However, many more planted trees are lost from dryness than from overwatering. Keep soil moist, but not soggy. Well established trees are rarely affected by overwatering, ...
soil development on dolomites of the cambrian
... crystalline limestone or marble. The genesis of these highly structured, uniform textured, red soils has long been a matter of controversy. The ‘residual theory’ suggests that the development of the Terra Rossa is the result of carbonate dissolution and the subsequent accumulation of limestone resid ...
... crystalline limestone or marble. The genesis of these highly structured, uniform textured, red soils has long been a matter of controversy. The ‘residual theory’ suggests that the development of the Terra Rossa is the result of carbonate dissolution and the subsequent accumulation of limestone resid ...
3-5-ch7
... Deserts have little precipitation and little vegetation. (annual precipitation- less than 10 inches or 25cm) Found in tropical, temperate and polar regions. Desert plants have adaptations that help them stay cool and get enough water. Plant adaptations: Why are deserts cold at night? How ...
... Deserts have little precipitation and little vegetation. (annual precipitation- less than 10 inches or 25cm) Found in tropical, temperate and polar regions. Desert plants have adaptations that help them stay cool and get enough water. Plant adaptations: Why are deserts cold at night? How ...
Soil acidity
... nutrient cycling, biological nitrogen fixation, nutrient uptake, disease control/prevention and production of growth hormones. These organisms interact with one another in the soil giving rise to diverse relationships/interactions such as symbiosis, parasitism, commensalism, protocooperation, neutra ...
... nutrient cycling, biological nitrogen fixation, nutrient uptake, disease control/prevention and production of growth hormones. These organisms interact with one another in the soil giving rise to diverse relationships/interactions such as symbiosis, parasitism, commensalism, protocooperation, neutra ...
Document
... Earth’s External Processes • Weathering – disintegration of rock at or near the earth’s surface • Mass wasting – transfer of material down slope in response to gravity • Erosion – transportation of material by a mobile agent such as water, wind, or ice ...
... Earth’s External Processes • Weathering – disintegration of rock at or near the earth’s surface • Mass wasting – transfer of material down slope in response to gravity • Erosion – transportation of material by a mobile agent such as water, wind, or ice ...
pub2794l
... composting, soil microbes increase rapidly. As the materials decompose, some kinds of microbes dominate. But as they complete a certain function, these microbes decline while others build up and continue the breakdown. As microbes decompose the organic materials, temperatures within the pile may app ...
... composting, soil microbes increase rapidly. As the materials decompose, some kinds of microbes dominate. But as they complete a certain function, these microbes decline while others build up and continue the breakdown. As microbes decompose the organic materials, temperatures within the pile may app ...
SKE2 Students will describe the physical attributes of rocks and soils
... a. Use senses to observe and group rocks by physical attributes such as large/small, heavy/light, smooth/ rough, dark/light, etc. b. Use senses to observe soils by physical attributes such as smell, texture, color, particle/grain size. c. Recognize earth materials— soil, rocks, water, air, etc. Back ...
... a. Use senses to observe and group rocks by physical attributes such as large/small, heavy/light, smooth/ rough, dark/light, etc. b. Use senses to observe soils by physical attributes such as smell, texture, color, particle/grain size. c. Recognize earth materials— soil, rocks, water, air, etc. Back ...
Soil Erosion
... o A greater percentage of the rainfall will become runoff during periods of frequent rainfall. o This is due to high soil moisture or saturated conditions. ...
... o A greater percentage of the rainfall will become runoff during periods of frequent rainfall. o This is due to high soil moisture or saturated conditions. ...
Human body
... Relate some common diseases (i.e., cold, influenza, strep throat, dysentery, fungal infections) to the organisms that cause them (bacteria, viruses, protests, fungi) Differentiate between infectious and noninfectious diseases Explain the role of antibiotics and vaccines in the treatment and preventi ...
... Relate some common diseases (i.e., cold, influenza, strep throat, dysentery, fungal infections) to the organisms that cause them (bacteria, viruses, protests, fungi) Differentiate between infectious and noninfectious diseases Explain the role of antibiotics and vaccines in the treatment and preventi ...
CHAPTER 11CSOIL AS A RESOURCE
... 2. Soil is an essential resource because agriculture depends on soil. Soil degradation is a worldwide concern. 3. Weathering encompasses three types of processes: Mechanical weathering is the physical breakup of rock with no change in the rock's chemical composition; however, mechanical weathering i ...
... 2. Soil is an essential resource because agriculture depends on soil. Soil degradation is a worldwide concern. 3. Weathering encompasses three types of processes: Mechanical weathering is the physical breakup of rock with no change in the rock's chemical composition; however, mechanical weathering i ...
Levels of Organization
... A FOOD CHAIN is the transfer of energy from one organism to another in an ecosystem in a line. ...
... A FOOD CHAIN is the transfer of energy from one organism to another in an ecosystem in a line. ...
Single-Celled Organisms and Viruses
... • All living things interact with their environment to meet their needs. ...
... • All living things interact with their environment to meet their needs. ...
C-ID Handout
... fertilization, and cell and tissue differentiation; compare plant and animal reproductive strategies 7. Demonstrate knowledge of energy transformations and transfer within cells, including respiration, fermentation, and photosynthesis 8. Demonstrate knowledge of plant and animal physiology, includin ...
... fertilization, and cell and tissue differentiation; compare plant and animal reproductive strategies 7. Demonstrate knowledge of energy transformations and transfer within cells, including respiration, fermentation, and photosynthesis 8. Demonstrate knowledge of plant and animal physiology, includin ...
54 - GEOCITIES.ws
... Primary producers include plants, algae, and many species of bacteria Many primary and higher-order consumers are opportunistic feeders Decomposition interconnects all trophic levels 3. Explain how decomposition connects all trophic levels in an ecosystem. a. Organisms are recycled b. Their matter, ...
... Primary producers include plants, algae, and many species of bacteria Many primary and higher-order consumers are opportunistic feeders Decomposition interconnects all trophic levels 3. Explain how decomposition connects all trophic levels in an ecosystem. a. Organisms are recycled b. Their matter, ...
Soil content and structure • Soil analysis and
... availability of nutrients in a soil. The regular addition texture and development. Deficiency will limit crop growth Organic matter influences: of manures so that the physical conditions and and increase susceptibility to disease whilst excessive levels • The amount of nitrogen released (minerali ...
... availability of nutrients in a soil. The regular addition texture and development. Deficiency will limit crop growth Organic matter influences: of manures so that the physical conditions and and increase susceptibility to disease whilst excessive levels • The amount of nitrogen released (minerali ...
The Characteristics of Living Things: Biology Scientists are
... those who find a new species get to name it! So far scientists have named and recorded 1.3 million species that have lived or are living on earth. A Canadian scientist, Boris Worm, estimates that there are 8.7 million species on the planet. Thus, our biological picture of our planet is not yet compl ...
... those who find a new species get to name it! So far scientists have named and recorded 1.3 million species that have lived or are living on earth. A Canadian scientist, Boris Worm, estimates that there are 8.7 million species on the planet. Thus, our biological picture of our planet is not yet compl ...
rhododendron and azalea
... using a long-handled wand with a water breaker to reach under foliage and deeply water the rootball, applying water evenly and deeply over all the roots. A deep soaking once or twice (if hot and dry) weekly should suffice. Keep plants evenly moist, but be careful not to over-water. If leaves are rol ...
... using a long-handled wand with a water breaker to reach under foliage and deeply water the rootball, applying water evenly and deeply over all the roots. A deep soaking once or twice (if hot and dry) weekly should suffice. Keep plants evenly moist, but be careful not to over-water. If leaves are rol ...
PRINTER`S NO. 3178 THE GENERAL ASSEMBLY OF
... Scientist in July 1974, Mr. Lipscomb assisted with field program appraisals and contributed to or managed soil survey manuscripts; and WHEREAS, Mr. Lipscomb served as State Soil Scientist from 1981 until his retirement in March 1994; and WHEREAS, Throughout his career Mr. Lipscomb worked cooperative ...
... Scientist in July 1974, Mr. Lipscomb assisted with field program appraisals and contributed to or managed soil survey manuscripts; and WHEREAS, Mr. Lipscomb served as State Soil Scientist from 1981 until his retirement in March 1994; and WHEREAS, Throughout his career Mr. Lipscomb worked cooperative ...
Geomorphological survey of the area of archaeological site Bosilkovo
... The profile M1 is characteristic for eluvium deposits, e.g. they are formed as a result from weathering (destruction) of gneisses. These rocks are building the bornhardt and they are more stable than the other rocks in the area. The obtained results show that there are two main layers: upper – up to ...
... The profile M1 is characteristic for eluvium deposits, e.g. they are formed as a result from weathering (destruction) of gneisses. These rocks are building the bornhardt and they are more stable than the other rocks in the area. The obtained results show that there are two main layers: upper – up to ...
2J04 Mid-Term Review STAR Questions L1
... Ecosystem – grouping of species (plants, animals…) in a given area and interacting with each other and their environment. Ecology – the study of ecosystems and interactions among organisms and their environment. Biotic – (Living) community in a specific environment. Abiotic – (non living) in ...
... Ecosystem – grouping of species (plants, animals…) in a given area and interacting with each other and their environment. Ecology – the study of ecosystems and interactions among organisms and their environment. Biotic – (Living) community in a specific environment. Abiotic – (non living) in ...























