PDF
... January 2011. As many of you will already know, Gordon is a world renowned specialist in the field of human and mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. Neurodevelopment is another key and expanding area of developmental biology for Development, and to strengthen our handling of both neurodevelopm ...
... January 2011. As many of you will already know, Gordon is a world renowned specialist in the field of human and mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. Neurodevelopment is another key and expanding area of developmental biology for Development, and to strengthen our handling of both neurodevelopm ...
Chapter 20 – Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of aldosterone (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of aldosterone (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
2.1-3
... – every cell has genes that regulate growth & development – mutation in those genes due to radiation or chemical agents causes excess production of growth factors ...
... – every cell has genes that regulate growth & development – mutation in those genes due to radiation or chemical agents causes excess production of growth factors ...
Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
... cells line organs and form a protective barrier b) What are the functions of plant dermal tissues?Forms a single layer of tightly packed cells that protects the plant and prevents water loss by forming a barrier between the plant and its external environment c) What are the similarities and differen ...
... cells line organs and form a protective barrier b) What are the functions of plant dermal tissues?Forms a single layer of tightly packed cells that protects the plant and prevents water loss by forming a barrier between the plant and its external environment c) What are the similarities and differen ...
Cell Specialization
... phase called GO. Depending on environmental signals, they may reenter the cell cycle or remain in GO permanently. A cell specializes while in interphase or GO. The process in which a cell becomes specialized is called differentiation and occurs when the cell selectively activates or inactivates spec ...
... phase called GO. Depending on environmental signals, they may reenter the cell cycle or remain in GO permanently. A cell specializes while in interphase or GO. The process in which a cell becomes specialized is called differentiation and occurs when the cell selectively activates or inactivates spec ...
begins during female`s embryonic development Ovaries
... f) at Puberty FSH triggers completion of meiosis I with unequal cytokinesis – this makes sure that the developing embryo (later) has enough organelles …. for survival g) Secondary oocyte (1N) -with most of the cytoplasm is formed & the other is a polar body (ultimately disintegrates) h) ovulation a ...
... f) at Puberty FSH triggers completion of meiosis I with unequal cytokinesis – this makes sure that the developing embryo (later) has enough organelles …. for survival g) Secondary oocyte (1N) -with most of the cytoplasm is formed & the other is a polar body (ultimately disintegrates) h) ovulation a ...
Review PPT – Life Science – Cells and Human
... – Living things have specialized structures with specialized functions ...
... – Living things have specialized structures with specialized functions ...
Course Specifications
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
... First cells in the evolution of the earth and definition of life Chemical substances of biological material and all kinds of chemical bonds and interactions important in the function of cells Structure of pro- and of eukaryotic cells; intercellular interactions and exchange Cell cycle , cell activit ...
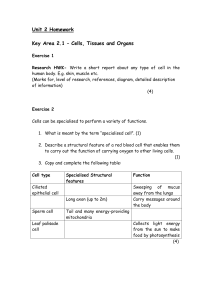
Unit 2 Homework
... 2. Name the two main types of stem cell. (2) 3. Write down one key characteristic of each type of stem cell that you have named in question 2. (2) Embryonic 4. Describe two different medical uses for stem cells. (2) 5. Write a paragraph on the ethical issues surrounding the use of stem cells for med ...
... 2. Name the two main types of stem cell. (2) 3. Write down one key characteristic of each type of stem cell that you have named in question 2. (2) Embryonic 4. Describe two different medical uses for stem cells. (2) 5. Write a paragraph on the ethical issues surrounding the use of stem cells for med ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... 1. Cellular differentiation occurs when cells become specialized in their structure and function. 2. Morphogenesis produces a change in the shape and form of a body part; this includes both early cell movement and later pattern formation. 3. Pattern formation refers to how tissues and organs are arr ...
... 1. Cellular differentiation occurs when cells become specialized in their structure and function. 2. Morphogenesis produces a change in the shape and form of a body part; this includes both early cell movement and later pattern formation. 3. Pattern formation refers to how tissues and organs are arr ...
Immunological Methods AppendixIII
... CFSE is partitioned equally among daughter cells with each division. These properties allows simultaneous analysis of cell number, position, as well as division status. • Fluorochromes compatible with fluorescein can be used to probe other cellular properties. Dilution of CFSE with cell division ...
... CFSE is partitioned equally among daughter cells with each division. These properties allows simultaneous analysis of cell number, position, as well as division status. • Fluorochromes compatible with fluorescein can be used to probe other cellular properties. Dilution of CFSE with cell division ...
Gastrulation
... respiratory passages. It also forms many glands, such as the liver and pancreas. The mesoderm forms the somites, the notochord, and the mesenchyme, which give rise to the muscles, circulatory and excretory systems of the body. ...
... respiratory passages. It also forms many glands, such as the liver and pancreas. The mesoderm forms the somites, the notochord, and the mesenchyme, which give rise to the muscles, circulatory and excretory systems of the body. ...
Respiratory System
... o Site of gas XΔ b/w air & blood Alveolar Lining Cells (lines interalveolar septae & alveolar membrane) o Squamous Alveolar Cells a.k.a. Type I alveolar cells or Type I pneumocytes Form lining of alveolus Freely permeable to gases Covers 95% of the surface (very thin cytoplasm) o Great Alv ...
... o Site of gas XΔ b/w air & blood Alveolar Lining Cells (lines interalveolar septae & alveolar membrane) o Squamous Alveolar Cells a.k.a. Type I alveolar cells or Type I pneumocytes Form lining of alveolus Freely permeable to gases Covers 95% of the surface (very thin cytoplasm) o Great Alv ...
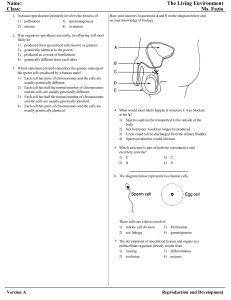
Reproduction and Development
... Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. Much of this repair is due to the activity of stem cells. These cells resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. ...
... Almost all human tissue can repair itself to some extent. Much of this repair is due to the activity of stem cells. These cells resemble those of a developing embryo in their ability to reproduce repeatedly, forming exact copies of themselves. They may also form many other different kinds of cells. ...
Honors Biology Botany Lab Practical Review
... Honors Biology Botany Lab Practical Review You may make a word bank on your own 46 questions Plants: Helpful pages in book: roots: page 484, 485 leaves: page 483 stems: page 481 Dicot Root: be able to id as dicot, id xylem, phloem, and amyloplast MonocotRoot: be able to id as monocot, Id root and pi ...
... Honors Biology Botany Lab Practical Review You may make a word bank on your own 46 questions Plants: Helpful pages in book: roots: page 484, 485 leaves: page 483 stems: page 481 Dicot Root: be able to id as dicot, id xylem, phloem, and amyloplast MonocotRoot: be able to id as monocot, Id root and pi ...
Clinical pathology
... ,late nucleus become non viable adult red cells anuclear in mammals biconcave disc ...
... ,late nucleus become non viable adult red cells anuclear in mammals biconcave disc ...
Patterns_In_Nature
... In heterotrophic organisms the digestive system provides the means by which nutrients are taken in and broken down. Large insoluble food molecules are converted into small soluble ones that can be absorbed and made available to the body cells. ...
... In heterotrophic organisms the digestive system provides the means by which nutrients are taken in and broken down. Large insoluble food molecules are converted into small soluble ones that can be absorbed and made available to the body cells. ...
Body Systems Work Together
... 6. Use the information and the provided pictures to answer the following questions. Moss cells are approximately 1% salt and 99% water. Tap water is approximately 1% salt and 99% water. A saline solution contains 6% salt and 94% water. a) What would happen to the moss cells placed in the saline solu ...
... 6. Use the information and the provided pictures to answer the following questions. Moss cells are approximately 1% salt and 99% water. Tap water is approximately 1% salt and 99% water. A saline solution contains 6% salt and 94% water. a) What would happen to the moss cells placed in the saline solu ...
Basic Medical Sciences
... transmitting electrical impulses – Found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
... transmitting electrical impulses – Found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... The auditory space map of the barn owl exhibits prominent plasticity where the visual system provides an instructive learning. Descending auditory pathways SOC -> CN, cochlea medial olivocochlear (MOC) neurons to the outer hair cells (mediating gain control of the cochlear amplifier); lateral olivoc ...
... The auditory space map of the barn owl exhibits prominent plasticity where the visual system provides an instructive learning. Descending auditory pathways SOC -> CN, cochlea medial olivocochlear (MOC) neurons to the outer hair cells (mediating gain control of the cochlear amplifier); lateral olivoc ...
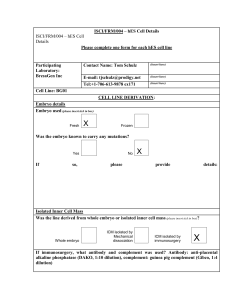
ISCI/FRM/004 – hES Cell Details
... appropriate) Cell Characteristics X Karyotype X Differentiation X Other If YES, please provide details: (Culture conditions) BG01 cells were first isolated in a 20% FBS containing medium. Subsequent passaging was performed in hESC medium (above) or hESC medium conditioned on MEFs prior to use (MEF-C ...
... appropriate) Cell Characteristics X Karyotype X Differentiation X Other If YES, please provide details: (Culture conditions) BG01 cells were first isolated in a 20% FBS containing medium. Subsequent passaging was performed in hESC medium (above) or hESC medium conditioned on MEFs prior to use (MEF-C ...
Biotechnology Unit 8L1.4
... cells of a plan in order to introduce a new gene to that plant. Undifferentiated cells: cells which have not become specialized ...
... cells of a plan in order to introduce a new gene to that plant. Undifferentiated cells: cells which have not become specialized ...
Do not write on this paper
... Write the letter of the correct word or words that structures called best complete each sentence on your notebook A bacteria. paper. Words may be used only once. B organelles. A. chlorophyll C membranes. B. cambium D mitochondria. C. photosynthesis 2. Which structure is found in plant cells but not ...
... Write the letter of the correct word or words that structures called best complete each sentence on your notebook A bacteria. paper. Words may be used only once. B organelles. A. chlorophyll C membranes. B. cambium D mitochondria. C. photosynthesis 2. Which structure is found in plant cells but not ...
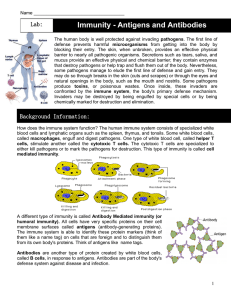
Antigens and Antibodies
... clumping or linking them together to make it easier for them to be engulfed by phagocytes. They can also rupture foreign cells and inactivate any toxins they produce. Some of the antibody producing cells remains in the body's immune system as memory cells. These specialized cells can quickly mount a ...
... clumping or linking them together to make it easier for them to be engulfed by phagocytes. They can also rupture foreign cells and inactivate any toxins they produce. Some of the antibody producing cells remains in the body's immune system as memory cells. These specialized cells can quickly mount a ...
Lecture Outline
... B. Complex animals exhibit levels of organization. 1. A tissue is an aggregation of cells and intercellular substances that function in one or more specialized activities (division of labor). 2. Various types of tissues can combine to form organs, such as the heart. 3. Organs may interact to form or ...
... B. Complex animals exhibit levels of organization. 1. A tissue is an aggregation of cells and intercellular substances that function in one or more specialized activities (division of labor). 2. Various types of tissues can combine to form organs, such as the heart. 3. Organs may interact to form or ...
Embryonic stem cell
Embryonic stem cells (ES cells) are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage preimplantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage should be considered to have the same moral or legal status as more developed human beings.Human ES cells measure approximately 14 μm while mouse ES cells are closer to 8 μm.