Fluid Flow - Binus Repository
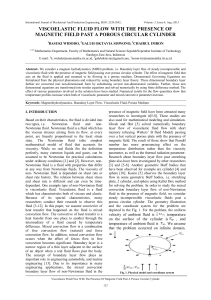
... As the upper plate begins to accelerate the velocity of the fluid in contac with the plate is equal to the velocity of the plate (a no slip condition exists between the plate and the fluid). Fluid molecules in contact with those against the plate will be accelerated due to the viscous attraction be ...
... As the upper plate begins to accelerate the velocity of the fluid in contac with the plate is equal to the velocity of the plate (a no slip condition exists between the plate and the fluid). Fluid molecules in contact with those against the plate will be accelerated due to the viscous attraction be ...
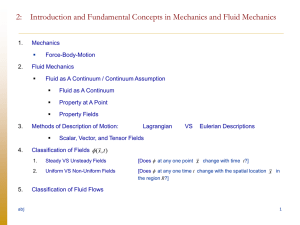
Fluid Mechanics Concepts
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
... An object submerged in a fluid will experience a volume stress. The magnitude of this stress will depend on the pressure of the fluid, the force that the fluid exerts on a unit area of a given surface: The SI unit for pressure is the pascal (Pa): Consider a liquid at rest in a container. If we made ...
Fluid Flow Concepts and Basic Control Volume Equations
... DRAG ON A GOLF BALL comes mainly from pressure drag. The only practical way of reducing pressure drag is to design the ball so that the point of separation moves back further on the ball. The golf ball's dimples increase the turbulence in the inertia of the boundary layer, increase the _______ bound ...
... DRAG ON A GOLF BALL comes mainly from pressure drag. The only practical way of reducing pressure drag is to design the ball so that the point of separation moves back further on the ball. The golf ball's dimples increase the turbulence in the inertia of the boundary layer, increase the _______ bound ...
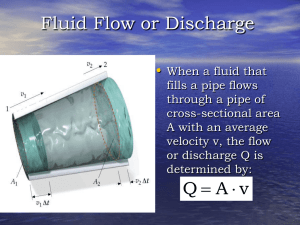
A Tutorial on Pipe Flow Equations
... 2. The maximum difference in friction factor is about 17% which translates to a 8.5% difference in flow. 3. This maximum difference occurs at fairly low Reynolds’ numbers associated with low pressure drop and lessens with increasing pressure drop where it is more important. 4. There is significant s ...
... 2. The maximum difference in friction factor is about 17% which translates to a 8.5% difference in flow. 3. This maximum difference occurs at fairly low Reynolds’ numbers associated with low pressure drop and lessens with increasing pressure drop where it is more important. 4. There is significant s ...
Notes #11
... where f is the external force (in addition to the pressure surface force) acting on any control volume of your choice. 2 Note ...
... where f is the external force (in addition to the pressure surface force) acting on any control volume of your choice. 2 Note ...
CHAPTER 03
... 25.What term is used when the fluid pressure is reduced to the vapor pressure? A. Bernoulli effect B. differential C. cavitation 26.Flow meters based on the Bernoulli equation, used to measure flowrates in open channels such as flumes and irrigation ditches, include devices like the sluice gate and ...
... 25.What term is used when the fluid pressure is reduced to the vapor pressure? A. Bernoulli effect B. differential C. cavitation 26.Flow meters based on the Bernoulli equation, used to measure flowrates in open channels such as flumes and irrigation ditches, include devices like the sluice gate and ...
Slide 1
... = 0, or effect of viscous stress can be neglected. The number of spatial coordinates x, y, z, that is required to specify the velocity field. Laminar: Smooth and orderly (non-random), can be steady or unsteady. ...
... = 0, or effect of viscous stress can be neglected. The number of spatial coordinates x, y, z, that is required to specify the velocity field. Laminar: Smooth and orderly (non-random), can be steady or unsteady. ...
Corelite-1 - Waymond Scott
... end results both closely approximate ideal steady state behavior, HOWEVER ...
... end results both closely approximate ideal steady state behavior, HOWEVER ...
Lecture 38
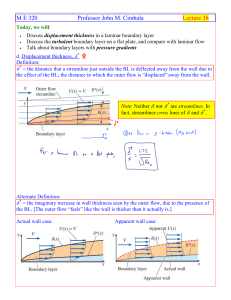
... For most real-life flows, P ≠ constant, and thus dP/dx ≠ 0. Two possibilities: • If dP/dx < 0, dU/dx > 0, the flow is accelerating. This is a favorable pressure gradient. • If dP/dx > 0, dU/dx < 0, the flow is decelerating. This is an unfavorable pressure gradient (also called an adverse pressure gr ...
... For most real-life flows, P ≠ constant, and thus dP/dx ≠ 0. Two possibilities: • If dP/dx < 0, dU/dx > 0, the flow is accelerating. This is a favorable pressure gradient. • If dP/dx > 0, dU/dx < 0, the flow is decelerating. This is an unfavorable pressure gradient (also called an adverse pressure gr ...
Simulation of Flow and Heat Transfer Through Packed Beds of
... COMSOL is designed to be able to handle many types of problems, from electricity and magnetism to structural mechanics and many other problems from different engineering disciplines, while CFD packages focus more specifically on fluid flow. CFD packages excel at modeling turbulence; have better 3D g ...
... COMSOL is designed to be able to handle many types of problems, from electricity and magnetism to structural mechanics and many other problems from different engineering disciplines, while CFD packages focus more specifically on fluid flow. CFD packages excel at modeling turbulence; have better 3D g ...
fluid transport mechanisms in microfluidic devices
... We have investigated transport in microfluidic systems and present experimental studies of pressure-driven and electrokinetic flows. We also present numerical simulations which were performed using the NetFlow module in Memcad (MEMCAD, 1998). The NetFlow module employs a threedimensional finite elem ...
... We have investigated transport in microfluidic systems and present experimental studies of pressure-driven and electrokinetic flows. We also present numerical simulations which were performed using the NetFlow module in Memcad (MEMCAD, 1998). The NetFlow module employs a threedimensional finite elem ...
An Aerodynamicist`s View of Lift, Bernoulli, and Newton
... Analysis of fluid flow is typically presented to engineering students in terms of three fundamental principles: conservation of mass, conservation of momentum, and conservation of energy. Newton’s name seldom comes up, except to encourage student ownership of these principles by reminding the class ...
... Analysis of fluid flow is typically presented to engineering students in terms of three fundamental principles: conservation of mass, conservation of momentum, and conservation of energy. Newton’s name seldom comes up, except to encourage student ownership of these principles by reminding the class ...
Chapter 6 - Equations of Motion and Energy in Cartesian... Equations of motion of a Newtonian fluid The Reynolds number
... function. We have reserved the symbol Φ for the second invariant of the rate of deformation tensor, which however is proportional to the dissipation function for incompressible flow. Υ is the symbol used later for the negative of the dissipation by viscous forces.) The energy equation We need the fo ...
... function. We have reserved the symbol Φ for the second invariant of the rate of deformation tensor, which however is proportional to the dissipation function for incompressible flow. Υ is the symbol used later for the negative of the dissipation by viscous forces.) The energy equation We need the fo ...
Evidence of the influence of plasma jets on a helium flow into open air
... surrounding the helium flow is much more difficult to ionize, and so the propagation of the ionization wave is confined to the volume of the helium channel. The length of the plasma jet is determined by the length of the helium channel and the applied voltage waveform. The plasma so generated has be ...
... surrounding the helium flow is much more difficult to ionize, and so the propagation of the ionization wave is confined to the volume of the helium channel. The length of the plasma jet is determined by the length of the helium channel and the applied voltage waveform. The plasma so generated has be ...
Lecture 10
... to exert a force on a small piston with a circular cross section of radius 5.00cm. The pressure is transmitted by a liquid to a second piston of radius 15.0 cm. What force must the compressed air exert to lift a car weighing 13300N? What air pressure produces this force? ...
... to exert a force on a small piston with a circular cross section of radius 5.00cm. The pressure is transmitted by a liquid to a second piston of radius 15.0 cm. What force must the compressed air exert to lift a car weighing 13300N? What air pressure produces this force? ...
Transport Phenomena 3
... macroscopic or bulk behavior of a fluid rather than with the microscopic or molecular behavior. • In most cases is convenient to think as a continuous distribution of matter or a continuum. • Validity of this concept is seem to be dependent upon the type of information desired rather than the nature ...
... macroscopic or bulk behavior of a fluid rather than with the microscopic or molecular behavior. • In most cases is convenient to think as a continuous distribution of matter or a continuum. • Validity of this concept is seem to be dependent upon the type of information desired rather than the nature ...
Compressible flow

Compressible flow (gas dynamics) is the branch of fluid mechanics that deals with flows having significant changes in fluid density. Gases, but not liquids, display such behaviour. To distinguish between compressible and incompressible flow in air, the Mach number (the ratio of the speed of the flow to the speed of sound) must be greater than about 0.3 (since the density change is greater than 5% in that case) before significant compressibility occurs. The study of compressible flow is relevant to high-speed aircraft, jet engines, rocket motors, hyperloops, high-speed entry into a planetary atmosphere, gas pipelines, commercial applications such as abrasive blasting, and many other fields.