Fluids
... It is assumed that the upper plate has been moving with this constant velocity for a long time, so the flow is steady. It is also assumed that the fluid is incompressible, so (9.2), (9.3) apply. At first glance, given that (9.2) is a nonlinear partial differential equation, finding the velocity and ...
... It is assumed that the upper plate has been moving with this constant velocity for a long time, so the flow is steady. It is also assumed that the fluid is incompressible, so (9.2), (9.3) apply. At first glance, given that (9.2) is a nonlinear partial differential equation, finding the velocity and ...
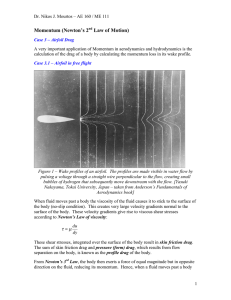
Momentum (Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion)
... Figure 4 – Schematic of a different control volume around an airfoil in free flight. The airfoil is again excluded from the control volume. Assumptions: Steady flow Incompressible flow 2- D flow Viscous effects along the control surface are negligible What else is going on: One flow stream ...
... Figure 4 – Schematic of a different control volume around an airfoil in free flight. The airfoil is again excluded from the control volume. Assumptions: Steady flow Incompressible flow 2- D flow Viscous effects along the control surface are negligible What else is going on: One flow stream ...
fluid transport mechanisms in microfluidic devices
... charged double layer results from an attraction between bound surface charges and ions in the passing fluid. In glass capillaries, surface silanol groups become deprotonated and, therefore, are negatively charged. This negatively charged surface attracts positive ions present in the flow. In the sit ...
... charged double layer results from an attraction between bound surface charges and ions in the passing fluid. In glass capillaries, surface silanol groups become deprotonated and, therefore, are negatively charged. This negatively charged surface attracts positive ions present in the flow. In the sit ...
CSUMS WS 03: Intro to Visual Python Summer 2013 V1
... # 5d. Use a for-loop to generate the particles in the vertical # direction (= along the y-axis). for r in arange(-9.5, 9.5, 0.5): # Use a small sphere to represent a particle of fluid. p = sphere(frame=f, pos=(0,r,0), radius=0.5, color=color.red) # Save the particle’s starting position as a Visual P ...
... # 5d. Use a for-loop to generate the particles in the vertical # direction (= along the y-axis). for r in arange(-9.5, 9.5, 0.5): # Use a small sphere to represent a particle of fluid. p = sphere(frame=f, pos=(0,r,0), radius=0.5, color=color.red) # Save the particle’s starting position as a Visual P ...
buoyant force
... Buoyant Force, final • The buoyant force is exerted by the fluid • Whether an object sinks or floats depends on the relationship between the buoyant force and the weight ...
... Buoyant Force, final • The buoyant force is exerted by the fluid • Whether an object sinks or floats depends on the relationship between the buoyant force and the weight ...
Hydrostatic Forces on Plane Surfaces
... Fluid Mechanics : Study of fluids at rest , in motion , and the effects of fluids on boundaries. This definition outlines the key topics in the study of fluids: (i) fluid static (ii) fluids in motion and (iii) viscous effects and all sections considering pressure forces (effects of fluids on boundar ...
... Fluid Mechanics : Study of fluids at rest , in motion , and the effects of fluids on boundaries. This definition outlines the key topics in the study of fluids: (i) fluid static (ii) fluids in motion and (iii) viscous effects and all sections considering pressure forces (effects of fluids on boundar ...
Lecture 9, February 17, 1997
... With a nozzle or diffuser, we are converting flow and internal energy, represented by Dh =D(u+Pv) into kinetic energy, or vice-versa. ...
... With a nozzle or diffuser, we are converting flow and internal energy, represented by Dh =D(u+Pv) into kinetic energy, or vice-versa. ...
Chapter 6. Fluid Mechanics
... Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel. We can use equation (6.11) to explain the behavior of objects submerged (sometimes not completely) in a fluid, such as water. Let us consider Figure 2 where an obje ...
... Pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel. We can use equation (6.11) to explain the behavior of objects submerged (sometimes not completely) in a fluid, such as water. Let us consider Figure 2 where an obje ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... this is a consequence of Pascal’s Principle. At sea level the atmospheric pressure is ...
... this is a consequence of Pascal’s Principle. At sea level the atmospheric pressure is ...
FLUIDS notes
... Mass Flow Rate the ratio of the mass of a fluid that passes a certain point in a certain interval of time (or, m/t) Volume Rate of Flow the ratio of the volume of a fluid that passes a certain point in a certain interval of time (or, V/t). In SI units, this is m3/sec (or the same thing as the pr ...
... Mass Flow Rate the ratio of the mass of a fluid that passes a certain point in a certain interval of time (or, m/t) Volume Rate of Flow the ratio of the volume of a fluid that passes a certain point in a certain interval of time (or, V/t). In SI units, this is m3/sec (or the same thing as the pr ...
Chapter
... Figure 4 Comparisons of velocity profiles in liquid film; Left: for a water-glycerol mixture on a glass plate without counter-current vapor phase between simulation results and experiment data [7] for ReL =12; Right: for pure water on a stainless steel plate against different ReG for ReL =168. ...
... Figure 4 Comparisons of velocity profiles in liquid film; Left: for a water-glycerol mixture on a glass plate without counter-current vapor phase between simulation results and experiment data [7] for ReL =12; Right: for pure water on a stainless steel plate against different ReG for ReL =168. ...
Elastic liquids - damtp - University of Cambridge
... Applicable to flows with a stagnation point ...
... Applicable to flows with a stagnation point ...
Sediment-induced stratification and density current in
... During the first half of the flood tide (Figure 1b, II-III), the mobile mud layer was entrained. We observed the reformation of the mobile mud layer during an unexpectedly early stage of the flood phase (III). This is interpreted to result from a super-saturated situation after the flood accelerati ...
... During the first half of the flood tide (Figure 1b, II-III), the mobile mud layer was entrained. We observed the reformation of the mobile mud layer during an unexpectedly early stage of the flood phase (III). This is interpreted to result from a super-saturated situation after the flood accelerati ...