a soap film apparatus to study two- dime sio al hydrody amic phe
... 4. Run experimental tests with non-cylindrical shapes and multiple obstructions to investigate different wake patterns that are not as well understood. 5. Compare experimental results with results from computer simulations of twodimensional flows. Materials and Methods Enhancements of Soap Film Tunn ...
... 4. Run experimental tests with non-cylindrical shapes and multiple obstructions to investigate different wake patterns that are not as well understood. 5. Compare experimental results with results from computer simulations of twodimensional flows. Materials and Methods Enhancements of Soap Film Tunn ...
Dynamics and stability of a fluid filled cylinder rolling on an inclined
... of steady flow induced by rotating cylindrical walls has been addressed well in literature.1–4 These studies were all performed on a system where the cylindrical wall rotates at a constant angular velocity. In the current study, we analyze the dynamics of a system where the cylindrical wall accelera ...
... of steady flow induced by rotating cylindrical walls has been addressed well in literature.1–4 These studies were all performed on a system where the cylindrical wall rotates at a constant angular velocity. In the current study, we analyze the dynamics of a system where the cylindrical wall accelera ...
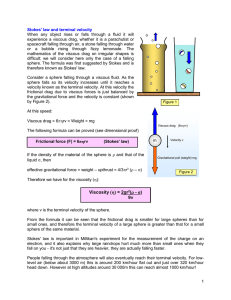
Stokes` law - schoolphysics
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
... electron, and it also explains why large raindrops hurt much more than small ones when they fall on you - it's not just that they are heavier, they are actually falling faster. People falling through the atmosphere will also eventually reach their terminal velocity. For lowlevel air (below about 300 ...
ATM 316 - Balanced flow
... the fVR term is positive in the Northern Hemisphere. Similarly, for CW motion, R < 0 and V > Vg . For the same pressure gradient, anticyclonic flow is supergeostrophic. That was the math, now let’s look at the physics. Consider the northbound parcel illustrated in the figure below. If the isobars we ...
... the fVR term is positive in the Northern Hemisphere. Similarly, for CW motion, R < 0 and V > Vg . For the same pressure gradient, anticyclonic flow is supergeostrophic. That was the math, now let’s look at the physics. Consider the northbound parcel illustrated in the figure below. If the isobars we ...
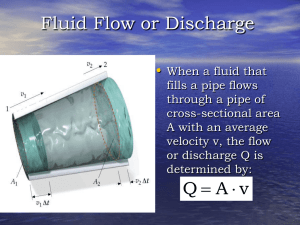
Closed Conduit: Measurement Techniques
... Estimate the orifice diameter that will result in a 100 kPa pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measure ...
... Estimate the orifice diameter that will result in a 100 kPa pressure drop in a 6.35 mm I.D. pipe with a flow rate of 80 mL/s. The orifice coefficient (Korifice) is 0.6. What is the ratio of orifice diameter to pipe diameter? If the smallest pressure differential that can accurately be measure ...
Numerical Modeling of Lava Flow Behavior on Earth and Mars
... parameters are well known for any particular flow, and therefore lava flow modeling must make simplifying assumptions, such as utilizing an idealized rheology. Many studies have successfully used simplified models to characterize flow evolution [2], especially for cases of purely molten lava without ...
... parameters are well known for any particular flow, and therefore lava flow modeling must make simplifying assumptions, such as utilizing an idealized rheology. Many studies have successfully used simplified models to characterize flow evolution [2], especially for cases of purely molten lava without ...
Physics PowerPoint
... Law of Motion A body in motion will remain in motion. A body at rest will remain at rest. UNLESS there is a force acting on that object. ...
... Law of Motion A body in motion will remain in motion. A body at rest will remain at rest. UNLESS there is a force acting on that object. ...
Phy_103_-3
... the fluid. For example, a large rock at the bottom of a stream would be easily lifted compare to lifting it from the ground. As the rock breaks through the surface of the water, it becomes heavier. This phenomenon is as a result of upward force called the buoyant force (upthrust) acting on the rock ...
... the fluid. For example, a large rock at the bottom of a stream would be easily lifted compare to lifting it from the ground. As the rock breaks through the surface of the water, it becomes heavier. This phenomenon is as a result of upward force called the buoyant force (upthrust) acting on the rock ...
Chapter3
... Introduction For any surface in contact with a flowing fluid, skin friction will exist. In addition to skin drag, if the fluid has to change its direction to pass around a solid body such as sphere, significant additional frictional losses ...
... Introduction For any surface in contact with a flowing fluid, skin friction will exist. In addition to skin drag, if the fluid has to change its direction to pass around a solid body such as sphere, significant additional frictional losses ...
Fluids
... A. In steady flow the velocity of the fluid is time independent at each point in space. B. In irrotational flow a small paddlewheel placed in the fluid would not spin. C. In laminar flow the streamlines never cross. ...
... A. In steady flow the velocity of the fluid is time independent at each point in space. B. In irrotational flow a small paddlewheel placed in the fluid would not spin. C. In laminar flow the streamlines never cross. ...
Fluid Mechanics II
... Similar idea stemming from the internal flow solution In internal flow BL edges make contact The BL edge pressure is not constant anymore In external flow there is no BL contact! The BL edge pressure is constant (for flat plate) This approximation is valid for 5×105< Re<107 We use the power-law velo ...
... Similar idea stemming from the internal flow solution In internal flow BL edges make contact The BL edge pressure is not constant anymore In external flow there is no BL contact! The BL edge pressure is constant (for flat plate) This approximation is valid for 5×105< Re<107 We use the power-law velo ...
Turbulence

In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and flow velocity in space and time.Flow in which the kinetic energy dies out due to the action of fluid molecular viscosity is called laminar flow. While there is no theorem relating the non-dimensional Reynolds number (Re) to turbulence, flows at Reynolds numbers larger than 5000 are typically (but not necessarily) turbulent, while those at low Reynolds numbers usually remain laminar. In Poiseuille flow, for example, turbulence can first be sustained if the Reynolds number is larger than a critical value of about 2040; moreover, the turbulence is generally interspersed with laminar flow until a larger Reynolds number of about 4000.In turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear on many scales and interact with each other. Drag due to boundary layer skin friction increases. The structure and location of boundary layer separation often changes, sometimes resulting in a reduction of overall drag. Although laminar-turbulent transition is not governed by Reynolds number, the same transition occurs if the size of the object is gradually increased, or the viscosity of the fluid is decreased, or if the density of the fluid is increased. Nobel Laureate Richard Feynman described turbulence as ""the most important unsolved problem of classical physics.""