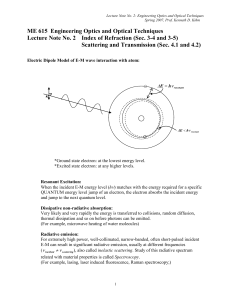
Machine Vision Systems as Shop Floor Metrology Tool
... This is the area where machine vision based tools start to excel. Machine vision in general has been used for everything from guiding the insertion of electronic chips on circuit boards to inspecting bottles at several per second in bottling lines. A natural extension of machine vision inspection is ...
... This is the area where machine vision based tools start to excel. Machine vision in general has been used for everything from guiding the insertion of electronic chips on circuit boards to inspecting bottles at several per second in bottling lines. A natural extension of machine vision inspection is ...
Adaptive Optics and the cone mosaic
... achieve microscopic resolution. High-order aberrations, unlike low-order, are not stable over time, and may change with frequencies between 10 Hz and 100 Hz. The correction of these aberrations requires continuous, high-frequency measurement and compensation. ...
... achieve microscopic resolution. High-order aberrations, unlike low-order, are not stable over time, and may change with frequencies between 10 Hz and 100 Hz. The correction of these aberrations requires continuous, high-frequency measurement and compensation. ...
Conference title, upper and lower case, bolded, 18 point
... layers in the same direction [8]. As shown in Fig. 2(b), note that the length of the coupler could be less than 50 µm in comparison to inverse-taper-based coupler that requires >150 µm [4]. In Fig. 2(a-c), electrical contacts and hence pumping in the taper region is neglected. However, if we need to ...
... layers in the same direction [8]. As shown in Fig. 2(b), note that the length of the coupler could be less than 50 µm in comparison to inverse-taper-based coupler that requires >150 µm [4]. In Fig. 2(a-c), electrical contacts and hence pumping in the taper region is neglected. However, if we need to ...
Direct Laser Writing: Versatile Tool for Microfabrication of Lithium
... optical image shown in Fig. 4(a). While elongation of the focus limits the axial resolution of DLW, it may be helpful for fast fabrication of thick DOEs. Precise reason for such elongation is not clear at the moment, but is likely related to strong, spatially varying optical nonlinearity of photoexc ...
... optical image shown in Fig. 4(a). While elongation of the focus limits the axial resolution of DLW, it may be helpful for fast fabrication of thick DOEs. Precise reason for such elongation is not clear at the moment, but is likely related to strong, spatially varying optical nonlinearity of photoexc ...
Mechanical momentum transfer to magneto
... model. Two-level atoms were considered interacting with two, counterpropagating laser pulses. To include the effects of spontaneous emission, the master equation for the density matrix in monentum space was simulated. This was achieved by using the momentum-space Schrödinger equation for a two-level ...
... model. Two-level atoms were considered interacting with two, counterpropagating laser pulses. To include the effects of spontaneous emission, the master equation for the density matrix in monentum space was simulated. This was achieved by using the momentum-space Schrödinger equation for a two-level ...
Strong critical coupling and polaritonic coherent perfect
... experiments on a photonic crystal bare resonator (transmission spectrum of a membrane with no active quantum wells) and on the plain, unpatterned quantum well heterostructure, as detailed in Extended Data Figure 1. The proximity of the absorption to the 50% value is very promising for the observati ...
... experiments on a photonic crystal bare resonator (transmission spectrum of a membrane with no active quantum wells) and on the plain, unpatterned quantum well heterostructure, as detailed in Extended Data Figure 1. The proximity of the absorption to the 50% value is very promising for the observati ...
Deriving the Snel–Descartes law for a single photon
... Using the law of conservation of energy, the mechanical wave theory of light held either the elasticity or the density to remain constant across an interface. Augustine-Louis Cauchy, Franz Neumann, and James MacCullagh initially derived the laws of reflection and refraction by assuming that the dens ...
... Using the law of conservation of energy, the mechanical wave theory of light held either the elasticity or the density to remain constant across an interface. Augustine-Louis Cauchy, Franz Neumann, and James MacCullagh initially derived the laws of reflection and refraction by assuming that the dens ...
Photonic laser thruster

A photonic laser thruster is an amplified laser thruster that generates thrust directly from the laser photon momentum, rather than laser-heating propellant. The concept of single-bounce laser-pushed lightsails that utilize the photon momentum was first developed in the 1960s, however, its conversion of laser power to thrust is highly inefficient, thus has been considered impractical. Over 50 years, there had been numerous theoretical and experimental efforts to increase the conversion efficiency by recycling photons, bouncing them repetitively between two reflective mirrors in an empty optical cavity, without success. In December 2006, Young Bae successfully solved this problem and demonstrated the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor of 100 and a photon thrust of 35 micronewtons by putting the laser energizing media between the two mirrors as in typical lasers, and the photonic laser thruster was born. In August 2015, the photonic laser thruster was demonstrated to increase the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor over 1,000 and to achieve a photon thrust of 3.5 millinewtons at Y.K. Bae Corporation. In addition, Propelling, slowing and stopping of a small satellite, 1U CubeSat, in simulated zero-gravity were demonstrated. The photonic laser thruster was initially developed for use in nanometer precision spacecraft formation, for forming ultralarge space telescopes and radars. The photonic laser thruster is currently developed for high-precision and high-speed maneuver of small spacecraft, such as formation flying, orbit adjustments, drag compensation, and rendezvous and docking. The photonic laser thruster can be used for beaming thrust from a conventional heavy resource vehicle to a more expensive & lightweight mission vehicle, similar to tankers in aerial refueling.The practical usage of the photonic laser thruster for main space propulsion would require extremely high laser powers and overcoming technological challenges in achieving the laser power and fabricating the required optics. Photonic laser thrusters have a very high specific impulse, and can permit spacecraft reach much higher speeds than with conventional rockets, which are limited by the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. If the photonic laser thruster is scalable for the use in such main space propulsion, multiple photonic laser thrusters can be used to construct a 'photonic railway' that has been proposed as a potential permanent transport infrastructure for interplanetary or interstellar commutes, allowing the transport craft themselves to carry very little fuel.