The mechanism for continuum polarization in laser induced
... harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser (Continuum Surelite, 532 nm, 4 ns pulse width) to ablate the sample. A variable neutral density filter was placed before the focusing optics to set the pulse energy of the beam between 9 μJ and 4 mJ. The laser was focused onto the sample by a 100 mm focal length convex lens ...
... harmonic of a Nd:YAG laser (Continuum Surelite, 532 nm, 4 ns pulse width) to ablate the sample. A variable neutral density filter was placed before the focusing optics to set the pulse energy of the beam between 9 μJ and 4 mJ. The laser was focused onto the sample by a 100 mm focal length convex lens ...
Strong enhancement of light extraction efficiency in GaInAsP 2D
... the internal efficiency. Another problem is its geometry, which makes a current injection device difficult. The top contact layer and metal electrodes necessary for injection devices will essentially change the expected effects, since the effects must strongly depend on upper and lower boundary cond ...
... the internal efficiency. Another problem is its geometry, which makes a current injection device difficult. The top contact layer and metal electrodes necessary for injection devices will essentially change the expected effects, since the effects must strongly depend on upper and lower boundary cond ...
Rayleigh scattering by gas molecules: why is the sky blue?
... molecule to oscillate at the frequency and in the direction of its electric field whereas the heavier nucleus remains essentially stationary. The molecule is therefore an oscillating charge dipole and, if it is spherically symmetric, we expect the amplitude of oscillation of the electrons to be inde ...
... molecule to oscillate at the frequency and in the direction of its electric field whereas the heavier nucleus remains essentially stationary. The molecule is therefore an oscillating charge dipole and, if it is spherically symmetric, we expect the amplitude of oscillation of the electrons to be inde ...
Gigahertz frequency comb offset stabilization
... Optical frequency combs consist of ultrafine optical lines that are equally spaced in the frequency domain with an uncertainty down to the 10−19 level [1]. Over the past 15 years, the generation and stabilization of such combs [2–4] has enabled control of the cycles of light, which represents a majo ...
... Optical frequency combs consist of ultrafine optical lines that are equally spaced in the frequency domain with an uncertainty down to the 10−19 level [1]. Over the past 15 years, the generation and stabilization of such combs [2–4] has enabled control of the cycles of light, which represents a majo ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... an incident wave and its ref lection from the mirror. These waves are ref lected by the grating induced by the former strong counterpropagating pair of waves, if their frequency is inside the bandwidth of the grating (the Bragg zone). The ref lection of each of the weak waves interferes with the cor ...
... an incident wave and its ref lection from the mirror. These waves are ref lected by the grating induced by the former strong counterpropagating pair of waves, if their frequency is inside the bandwidth of the grating (the Bragg zone). The ref lection of each of the weak waves interferes with the cor ...
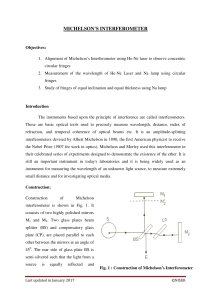
Michelson Interferometer
... beam is approximately parallel with the top of the interferometer and strikes the mirror at the centre. 5. Set the viewing screen opposite of the adjustable mirror M2. Note that the viewing screen should be placed at 1-2meter from the adjustable mirror to get better resolution. 6. To get circular fr ...
... beam is approximately parallel with the top of the interferometer and strikes the mirror at the centre. 5. Set the viewing screen opposite of the adjustable mirror M2. Note that the viewing screen should be placed at 1-2meter from the adjustable mirror to get better resolution. 6. To get circular fr ...
Document
... light range. Short bunches are useful in generating coherent synchrotron radiation in the far-infrared region. Moreover it may generate laser light of a few tzm to 100 /zm wavelength range when a mirror is placed around the electron orbit. This novel laser source is called the photon storage ring (P ...
... light range. Short bunches are useful in generating coherent synchrotron radiation in the far-infrared region. Moreover it may generate laser light of a few tzm to 100 /zm wavelength range when a mirror is placed around the electron orbit. This novel laser source is called the photon storage ring (P ...
Initial observations from the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter (LOLA)
... pulses. The surface reflectance is also required for corrections to other measurements of interest to LOLA’s performance such as pulse width and time walk. While the instrument does not have a self‐calibration source in flight, the reflectance measurement is calibrated in a relative sense with respe ...
... pulses. The surface reflectance is also required for corrections to other measurements of interest to LOLA’s performance such as pulse width and time walk. While the instrument does not have a self‐calibration source in flight, the reflectance measurement is calibrated in a relative sense with respe ...
Exp. 71 - Caltech
... Fabry-Perot cavities (also called Fabry-Perot etalons) are ubiquitous elements in optical physics, and they are used for such applications as sensitive wavelength discriminators, as stable frequency references, and for building up large field intensities with low input powers. Also, lasers are all ma ...
... Fabry-Perot cavities (also called Fabry-Perot etalons) are ubiquitous elements in optical physics, and they are used for such applications as sensitive wavelength discriminators, as stable frequency references, and for building up large field intensities with low input powers. Also, lasers are all ma ...
Time-Delay Interferometry - Center for Gravitational Wave Physics
... • Time-delay interferometry provides many ways—Michelson and others—to combine these links with appropriate time delays, canceling principal noises even with unequal and time-varying arms. • Provides a framework for analysis of signals, noises, sensitivity, and some design tradeoffs (e.g. Doppler sh ...
... • Time-delay interferometry provides many ways—Michelson and others—to combine these links with appropriate time delays, canceling principal noises even with unequal and time-varying arms. • Provides a framework for analysis of signals, noises, sensitivity, and some design tradeoffs (e.g. Doppler sh ...
Open Frame CD/DVD Reader
... allows an infinitesimal focused spot size. That means furthermore the photons have to pass a channel with zero volume and can be localised exactly. But this would violate the fundamental Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. ...
... allows an infinitesimal focused spot size. That means furthermore the photons have to pass a channel with zero volume and can be localised exactly. But this would violate the fundamental Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle. ...
Photonic laser thruster

A photonic laser thruster is an amplified laser thruster that generates thrust directly from the laser photon momentum, rather than laser-heating propellant. The concept of single-bounce laser-pushed lightsails that utilize the photon momentum was first developed in the 1960s, however, its conversion of laser power to thrust is highly inefficient, thus has been considered impractical. Over 50 years, there had been numerous theoretical and experimental efforts to increase the conversion efficiency by recycling photons, bouncing them repetitively between two reflective mirrors in an empty optical cavity, without success. In December 2006, Young Bae successfully solved this problem and demonstrated the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor of 100 and a photon thrust of 35 micronewtons by putting the laser energizing media between the two mirrors as in typical lasers, and the photonic laser thruster was born. In August 2015, the photonic laser thruster was demonstrated to increase the conversion efficiency enhancement by a factor over 1,000 and to achieve a photon thrust of 3.5 millinewtons at Y.K. Bae Corporation. In addition, Propelling, slowing and stopping of a small satellite, 1U CubeSat, in simulated zero-gravity were demonstrated. The photonic laser thruster was initially developed for use in nanometer precision spacecraft formation, for forming ultralarge space telescopes and radars. The photonic laser thruster is currently developed for high-precision and high-speed maneuver of small spacecraft, such as formation flying, orbit adjustments, drag compensation, and rendezvous and docking. The photonic laser thruster can be used for beaming thrust from a conventional heavy resource vehicle to a more expensive & lightweight mission vehicle, similar to tankers in aerial refueling.The practical usage of the photonic laser thruster for main space propulsion would require extremely high laser powers and overcoming technological challenges in achieving the laser power and fabricating the required optics. Photonic laser thrusters have a very high specific impulse, and can permit spacecraft reach much higher speeds than with conventional rockets, which are limited by the Tsiolkovsky rocket equation. If the photonic laser thruster is scalable for the use in such main space propulsion, multiple photonic laser thrusters can be used to construct a 'photonic railway' that has been proposed as a potential permanent transport infrastructure for interplanetary or interstellar commutes, allowing the transport craft themselves to carry very little fuel.

![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852277_1-2045a3551aa6b77e10f6e1bfc991b19e-300x300.png)