Section 4
... discovered a planet revolving around another ordinary star. They used a method similar to the one used in studying binary stars. The astronomers observed that a star was moving slightly toward and away from us. They knew that the invisible object causing the movement didn’t have enough mass to be a ...
... discovered a planet revolving around another ordinary star. They used a method similar to the one used in studying binary stars. The astronomers observed that a star was moving slightly toward and away from us. They knew that the invisible object causing the movement didn’t have enough mass to be a ...
First Light for May, 2001 - South Bay Astronomical Society
... Galileo’s discovery of Jupiter’s moons showed a solar system in miniature that provided a model of the whole solar system. It was soon realized that the stars were much more distant. So, then the question became could there be planets around other stars? As early as 1584, Giordano Bruno posited the ...
... Galileo’s discovery of Jupiter’s moons showed a solar system in miniature that provided a model of the whole solar system. It was soon realized that the stars were much more distant. So, then the question became could there be planets around other stars? As early as 1584, Giordano Bruno posited the ...
Chapter 20. Galaxies
... AGNs that are predominantly found at high redshift (i.e. very distant from us). This is partly because they are a rare phenomenon and partly because they were more common earlier in the history of the Universe. Quasars occur when the central black holes are massive and fed large amounts of gas, resu ...
... AGNs that are predominantly found at high redshift (i.e. very distant from us). This is partly because they are a rare phenomenon and partly because they were more common earlier in the history of the Universe. Quasars occur when the central black holes are massive and fed large amounts of gas, resu ...
Searching for HI emission from distant galaxies
... for star formation) exist in the redshift range in which the star the earth HIPASS HI emission survey formation shows very rapid evolution at z =rate 0 (Zwaan et al. ...
... for star formation) exist in the redshift range in which the star the earth HIPASS HI emission survey formation shows very rapid evolution at z =rate 0 (Zwaan et al. ...
Galactic Evolution:
... and object is still lacking. There are attempts to construct some comprehensive and software package for study of the galactic evolution. I just mention th Galaxy Evolution tool (GEtool) that is a software package currently being developed to selfconsistently model of chemical and spectral evolution ...
... and object is still lacking. There are attempts to construct some comprehensive and software package for study of the galactic evolution. I just mention th Galaxy Evolution tool (GEtool) that is a software package currently being developed to selfconsistently model of chemical and spectral evolution ...
here - IPAC
... in two science products: J (1.1 m), H (1.6 m) and Ks (2.2 m) 3-band image atlas and a tabular catalog. The images will have a typical angular resolution of ~2 to 3 and the catalogue will include flux, size and morphology information. At the completion of the 2MASS survey, the atlas will be fully ...
... in two science products: J (1.1 m), H (1.6 m) and Ks (2.2 m) 3-band image atlas and a tabular catalog. The images will have a typical angular resolution of ~2 to 3 and the catalogue will include flux, size and morphology information. At the completion of the 2MASS survey, the atlas will be fully ...
The Milky Way: Home to Star Clusters
... increasing in mass. It has long been known that our galaxy has fed on stars from other galaxies within our local group (e.g., the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy). In fact, one theory goes even further and implies that all globular clusters within the Milky Way are the leftovers of dwarf galaxies that have ...
... increasing in mass. It has long been known that our galaxy has fed on stars from other galaxies within our local group (e.g., the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy). In fact, one theory goes even further and implies that all globular clusters within the Milky Way are the leftovers of dwarf galaxies that have ...
Here you can get a Science reprint
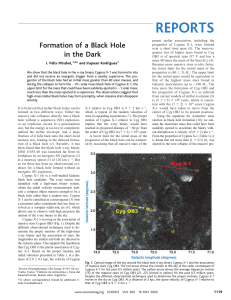
... It is believed that stellar black holes can be formed in two different ways: Either the massive star collapses directly into a black hole without a supernova (SN) explosion, or an explosion occurs in a protoneutron star, but the energy is too low to completely unbind the stellar envelope, and a larg ...
... It is believed that stellar black holes can be formed in two different ways: Either the massive star collapses directly into a black hole without a supernova (SN) explosion, or an explosion occurs in a protoneutron star, but the energy is too low to completely unbind the stellar envelope, and a larg ...
The Milky Way and Its Neighbors
... in spiral arms is very bright in UV Young stars emit towards UV Several types shown below ...
... in spiral arms is very bright in UV Young stars emit towards UV Several types shown below ...
Supernovas 10/19
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
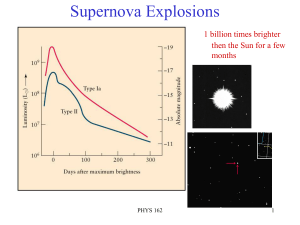
... maximum and then fall steadily in brightness, fading in just a few weeks. Type II supernovae remain bright for a longer period of time as energy is provided by the decay of radioactive products produced in the explosion. From observations of the light curve of SN1994i in M51, determine whether the e ...
... maximum and then fall steadily in brightness, fading in just a few weeks. Type II supernovae remain bright for a longer period of time as energy is provided by the decay of radioactive products produced in the explosion. From observations of the light curve of SN1994i in M51, determine whether the e ...
A Study of the Spiral Galaxy M101 Elizabeth City State University
... three different types of galaxies, spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Figures 1a, b, and c show examples of each type. Galaxies have an enormous range in mass and size as indicated in Table 1. Galaxies are separated by vast gulfs of space. For example, our own Milky Way is over 160,000 light years a ...
... three different types of galaxies, spiral, elliptical, and irregular. Figures 1a, b, and c show examples of each type. Galaxies have an enormous range in mass and size as indicated in Table 1. Galaxies are separated by vast gulfs of space. For example, our own Milky Way is over 160,000 light years a ...
W The X-Ray Universe X-ray images of the Universe are
... nuclei of galaxies, and hot gas in intergalactic space. The X rays detected by X-ray astronomers, like those put to use in industry, medicine, and laboratory research, must be produced by high-energy particles. It is not surprising, then, that an X-ray image of the sky can look markedly different fr ...
... nuclei of galaxies, and hot gas in intergalactic space. The X rays detected by X-ray astronomers, like those put to use in industry, medicine, and laboratory research, must be produced by high-energy particles. It is not surprising, then, that an X-ray image of the sky can look markedly different fr ...
20 pm - Starmap
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... ...
... Many deep sky objects like galaxies and clusters will be within reach. Jupiter satellites and Saturn’s rings will also be visible. A spectacular experience for beginners in astronomy... ...
Astro 10B Study Questions for Each Chapter
... How are galaxies, groups and clusters distributed through space? Which type of clusters contain the most giant elliptical galaxies? Where would you find a galaxy which is the result of several mergers? What happens when galaxies collide? How would you explain a galaxy having multiple nuclei? Why do ...
... How are galaxies, groups and clusters distributed through space? Which type of clusters contain the most giant elliptical galaxies? Where would you find a galaxy which is the result of several mergers? What happens when galaxies collide? How would you explain a galaxy having multiple nuclei? Why do ...
Results from the search for tidal disruption flares in the GALEX Deep
... If MBH > 108 Msun then RBB < 6Rg, and the black hole must have spin! ...
... If MBH > 108 Msun then RBB < 6Rg, and the black hole must have spin! ...
Lecture 17: Black Holes
... interacting, massive dark matter particle • Dark matter particles are captured by stars, and settle in the center to a thermal distribution. • If sufficient dark matter accumulates, it collapses into a self-gravitating object in the star center. • If the dark matter mass is greater than its Chandras ...
... interacting, massive dark matter particle • Dark matter particles are captured by stars, and settle in the center to a thermal distribution. • If sufficient dark matter accumulates, it collapses into a self-gravitating object in the star center. • If the dark matter mass is greater than its Chandras ...
Lecture 11
... – Hot gas in accretion disks can emit X-rays – The accretion disk can dump material which may become hot and dense enough to under nuclear fusion. • What is a white dwarf supernova – White dwarf accretes gas from companion until it exceeds 1.4 solar masses – which undergoes collapse and destruct ...
... – Hot gas in accretion disks can emit X-rays – The accretion disk can dump material which may become hot and dense enough to under nuclear fusion. • What is a white dwarf supernova – White dwarf accretes gas from companion until it exceeds 1.4 solar masses – which undergoes collapse and destruct ...
Exploring the physical properties of the first galaxies
... the study of the early Universe allowing us to push to much higher redshift and fainter luminosities. NIRSpec will also allow us to study optical emission lines in galaxies to z~7 (making confirmation possible for many candidates) as well as identifying the presence of Pop-III stars (through HeII em ...
... the study of the early Universe allowing us to push to much higher redshift and fainter luminosities. NIRSpec will also allow us to study optical emission lines in galaxies to z~7 (making confirmation possible for many candidates) as well as identifying the presence of Pop-III stars (through HeII em ...
Lecture 2: Gravitational wave sources
... binary neutron star systems deservedly resulted in the 1993 Nobel Prize in physics going to Hulse and Taylor, who discovered the first such binary. We are therefore quite confident that, at least in weak gravity, gravitational radiation exists as advertised. What happens in strong gravity? That is a ...
... binary neutron star systems deservedly resulted in the 1993 Nobel Prize in physics going to Hulse and Taylor, who discovered the first such binary. We are therefore quite confident that, at least in weak gravity, gravitational radiation exists as advertised. What happens in strong gravity? That is a ...
Archaeology of the Milky Way - Max-Planck
... main mirror that is to collect the light of distant stars and galaxies in the European Extremely Large Telescope in Chile from the next decade on. Astronomers at the institute are involved in developing two cameras for what will become the largest telescope on Earth. But until it has been built, the ...
... main mirror that is to collect the light of distant stars and galaxies in the European Extremely Large Telescope in Chile from the next decade on. Astronomers at the institute are involved in developing two cameras for what will become the largest telescope on Earth. But until it has been built, the ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... to collapse. The star's outer layers may blast away into space, or they may fall into the black hole to make it heavier. ...
... to collapse. The star's outer layers may blast away into space, or they may fall into the black hole to make it heavier. ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.