Neutron Stars PowerPoint
... • Basic physical process – Energy transferred to electrons from magnetic field • Similar to the Sun’s coronal heating ...
... • Basic physical process – Energy transferred to electrons from magnetic field • Similar to the Sun’s coronal heating ...
Projet d`observation
... –The unabsorbed 0.6-10 keV flux during persistent emission was 23% lower in 2003 than in 2007 and supports the conclusion that EXO 048-676 was in a lower state luminosity with respect to other LMBXs analysed. ...
... –The unabsorbed 0.6-10 keV flux during persistent emission was 23% lower in 2003 than in 2007 and supports the conclusion that EXO 048-676 was in a lower state luminosity with respect to other LMBXs analysed. ...
Neutron Stars PowerPoint
... • Basic observations – Supernova remnants emit huge amounts of energy – Rotation rate of neutron stars gradually decreases • Energy expended is same as energy emitted by remnant ...
... • Basic observations – Supernova remnants emit huge amounts of energy – Rotation rate of neutron stars gradually decreases • Energy expended is same as energy emitted by remnant ...
PH607lec12-5gal3
... Conclusion: The stars in a spiral arm cannot always be the same since spiral structure would wind up very tightly. Though galaxy arms appear to be intact features, stars are actually constantly moving in and out of them as they orbit the centre of the Milky Way, like London commuters in a busy traff ...
... Conclusion: The stars in a spiral arm cannot always be the same since spiral structure would wind up very tightly. Though galaxy arms appear to be intact features, stars are actually constantly moving in and out of them as they orbit the centre of the Milky Way, like London commuters in a busy traff ...
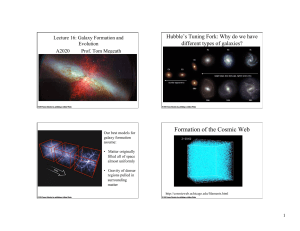
Lecture 16
... – Our best models for galaxy formation assume that gravity made galaxies out of regions of the early universe that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The gas collapsed to form galaxies. Galaxies continue to cannibalize smaller galaxies and draw in gas as the evolve. What determines the m ...
... – Our best models for galaxy formation assume that gravity made galaxies out of regions of the early universe that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The gas collapsed to form galaxies. Galaxies continue to cannibalize smaller galaxies and draw in gas as the evolve. What determines the m ...
Air Cherenkov Methods in Cosmic Rays: A Review
... Some attempts were made to observe reflected EAS signal in mountains Now the idea of a fixed balloon is realized and the project of an experiment with a high-altitude balloon is under development ...
... Some attempts were made to observe reflected EAS signal in mountains Now the idea of a fixed balloon is realized and the project of an experiment with a high-altitude balloon is under development ...
The Next 2-3 Weeks
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
Friday03
... morphologies, and emission line fraction well-known • Early-types consistent with passive evolution since z>2 • Small fraction of actively star-forming galaxies ...
... morphologies, and emission line fraction well-known • Early-types consistent with passive evolution since z>2 • Small fraction of actively star-forming galaxies ...
US - Real Science
... scattered around the arms. But astronomers simply __ not know what is compressing this gas so much ____ stars are forming at a staggering rate. Probing further into ___ 1313's interior reveals more mystery. In the midst of ___ starburst regions, two objects are emitting highly energetic X-rays. ____ ...
... scattered around the arms. But astronomers simply __ not know what is compressing this gas so much ____ stars are forming at a staggering rate. Probing further into ___ 1313's interior reveals more mystery. In the midst of ___ starburst regions, two objects are emitting highly energetic X-rays. ____ ...
Characteristics of Our Galaxy
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
... variables (useful for judging distances), pre-main sequence stars, T-Tauri stars, Herbigharo objects, and even some A stars can be found in the arms. These stars are very metal rich and have highly circular orbits, although they comprise likely less than one percent of Milky Way stars. Young thin d ...
1 Introduction - Wiley-VCH
... The contribution of these multifrequency surveys to the study of galaxy evolution is invaluable, since it simultaneously provides us with information on the different components of any extragalactic object (see Table 1.1 for a summary). The modern instrumentation now in our hands enables us to measu ...
... The contribution of these multifrequency surveys to the study of galaxy evolution is invaluable, since it simultaneously provides us with information on the different components of any extragalactic object (see Table 1.1 for a summary). The modern instrumentation now in our hands enables us to measu ...
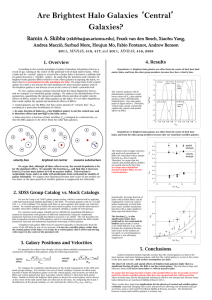
Ramin A. Skibba - Southern California Center for Galaxy Evolution
... significant fraction of halos, the BHG is not the central galaxy. This fraction is large and increases from ≈25% in low-mass halos to ≈40% in massive halos. We argue that the large fraction of halos with satellite BHGs is due to recently accreted relatively massive satellite galaxies that have not m ...
... significant fraction of halos, the BHG is not the central galaxy. This fraction is large and increases from ≈25% in low-mass halos to ≈40% in massive halos. We argue that the large fraction of halos with satellite BHGs is due to recently accreted relatively massive satellite galaxies that have not m ...
Elliptical galaxies
... •If the isophotes are not circularly symmetric, then the galaxy cannot be spherically symmetric, but it can still be axisymmetric. •In general the line of sight will be inclined at an angle with respect to the equatorial plane of an axisymmetric galaxy. •In that case, there are infinite de-projected ...
... •If the isophotes are not circularly symmetric, then the galaxy cannot be spherically symmetric, but it can still be axisymmetric. •In general the line of sight will be inclined at an angle with respect to the equatorial plane of an axisymmetric galaxy. •In that case, there are infinite de-projected ...
PH607lec11-4gal2
... Conclusion: The stars in a spiral arm cannot always be the same since spiral structure would wind up very tightly. Though galaxy arms appear to be intact features, stars are actually constantly moving in and out of them as they orbit the centre of the Milky Way, like London commuters in a busy traff ...
... Conclusion: The stars in a spiral arm cannot always be the same since spiral structure would wind up very tightly. Though galaxy arms appear to be intact features, stars are actually constantly moving in and out of them as they orbit the centre of the Milky Way, like London commuters in a busy traff ...
Estimating the mass and star formation rate in galaxies
... total quantity of dust between the observed and the emitting source. Since dust is formed during the late stages of stellar evolution regions such as nuclei of galaxies, where many generations of stars are actively forming or have formed, evolved and “died” are often enshrouded by ...
... total quantity of dust between the observed and the emitting source. Since dust is formed during the late stages of stellar evolution regions such as nuclei of galaxies, where many generations of stars are actively forming or have formed, evolved and “died” are often enshrouded by ...
V - ESO
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
... This is generally assumed to be the reason why, though star formation proceeds on a typical scale comparable to the size of a giant molecular cloud (~80 pc, Efremov 1995, AJ 100, 2757), Milky Way massive clusters tend to be much smaller. Image taken from class by James Schombert, University of Oreg ...
PHYSICS – Astrophysics Section I
... ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer, with some reaching the surface. Almost all visible light reaches the surface of the Earth, although some wavelengths are scattered more easily than others. Infra-red and microwaves are partially absorbed by the atmosphere, and most radio waves ar ...
... ultraviolet radiation is absorbed by the ozone layer, with some reaching the surface. Almost all visible light reaches the surface of the Earth, although some wavelengths are scattered more easily than others. Infra-red and microwaves are partially absorbed by the atmosphere, and most radio waves ar ...
Chapter 12 Quiz, Nov. 28, 2012, Astro 162, Section 4 12-1
... 12-31. The time for a fluctuation in brightness of a quasar allows astronomers to place an upper limit on its a) luminosity. b) size. X c) age. d) distance. Chapter 12 Thought/Writing Questions 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars for ...
... 12-31. The time for a fluctuation in brightness of a quasar allows astronomers to place an upper limit on its a) luminosity. b) size. X c) age. d) distance. Chapter 12 Thought/Writing Questions 12-32. Why are the spiral arms of our Galaxy brighter than the regions between them? The O and B stars for ...
PH607lec08
... been found to occur in very luminous, compact star clusters (up to 108 solar luminosities, dimensions of a few parsecs), which occur in bursting dwarfs, interacting galaxies, and mergers Both direct mergers and more indirect interactions can trigger star formation in galaxies Caused by gas compressi ...
... been found to occur in very luminous, compact star clusters (up to 108 solar luminosities, dimensions of a few parsecs), which occur in bursting dwarfs, interacting galaxies, and mergers Both direct mergers and more indirect interactions can trigger star formation in galaxies Caused by gas compressi ...
The Milky Way
... The angular momentum of the Milky Way. The gravitational attraction of the stars near the Galactic center. The gravitational attraction of the supermassive black hole in the Galactic center. The gravitational attraction of the stars in the halo of the Milky Way. The gravitational attraction of all m ...
... The angular momentum of the Milky Way. The gravitational attraction of the stars near the Galactic center. The gravitational attraction of the supermassive black hole in the Galactic center. The gravitational attraction of the stars in the halo of the Milky Way. The gravitational attraction of all m ...
Document
... mass density of the universe has roughly doubled since z ~ 1…Intriguingly, the integrated stellar mass of blue galaxies with young stars has not significantly changed since z ~ 1…instead, the growth of the total stellar mass density is dominated by the growth of the total mass in the largely passive ...
... mass density of the universe has roughly doubled since z ~ 1…Intriguingly, the integrated stellar mass of blue galaxies with young stars has not significantly changed since z ~ 1…instead, the growth of the total stellar mass density is dominated by the growth of the total mass in the largely passive ...
Galaxies
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
Ch17_Galaxies
... Stellar and Gas Content of Galaxies • Other items of note: – Ellipticals have a large range of sizes from globular cluster sizes to 100 times the mass of the Milky Way – Census of galaxies nearby: Most are dim dwarf E and dwarf Irr sparsely populated with stars – Census of distant galaxies: In clus ...
... Stellar and Gas Content of Galaxies • Other items of note: – Ellipticals have a large range of sizes from globular cluster sizes to 100 times the mass of the Milky Way – Census of galaxies nearby: Most are dim dwarf E and dwarf Irr sparsely populated with stars – Census of distant galaxies: In clus ...
black hole
... The core of helium ash cannot generate nuclear energy. Nevertheless, it can grow hotter—because it contracts and converts gravitational energy into thermal energy. The rising temperature heats the unprocessed hydrogen just outside the core—hydrogen that was never previously hot enough to fuse. ...
... The core of helium ash cannot generate nuclear energy. Nevertheless, it can grow hotter—because it contracts and converts gravitational energy into thermal energy. The rising temperature heats the unprocessed hydrogen just outside the core—hydrogen that was never previously hot enough to fuse. ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.