Galaxy formation in the Planck cosmology - II. Star
... to that described in this paper, i.e. the distribution of formation times of all the stars that make up the galaxy.2 Measures of the SFH of the main galactic component can only be inferred statistically by observing populations of galaxies at different redshifts and making some assumptions about mer ...
... to that described in this paper, i.e. the distribution of formation times of all the stars that make up the galaxy.2 Measures of the SFH of the main galactic component can only be inferred statistically by observing populations of galaxies at different redshifts and making some assumptions about mer ...
Spectroscopic variability of two Oe stars
... which include a ratio LLbol ∼ 10−6 , i.e. a factor 10 higher than for normal OB stars but at least an order of magnitude lower than for Be high-mass X-ray binaries, variations on timescales from minutes to months, and an X-ray spectrum that is dominated by a very hot plasma with kT ≥ 10 keV. The ori ...
... which include a ratio LLbol ∼ 10−6 , i.e. a factor 10 higher than for normal OB stars but at least an order of magnitude lower than for Be high-mass X-ray binaries, variations on timescales from minutes to months, and an X-ray spectrum that is dominated by a very hot plasma with kT ≥ 10 keV. The ori ...
Summary of Talks at Growing Black Holes 2004 in Garching
... to estimates of quasar lifetimes. At z < 2.5, SDSS clustering scale is about 7 Mpc. There is now preliminary, tentative evidence for correlation length to increase with redshift. Spectra of emission lines in high z quasars & Continuum shape consistent with lower z objects -> implication : rapid ch ...
... to estimates of quasar lifetimes. At z < 2.5, SDSS clustering scale is about 7 Mpc. There is now preliminary, tentative evidence for correlation length to increase with redshift. Spectra of emission lines in high z quasars & Continuum shape consistent with lower z objects -> implication : rapid ch ...
Striated AKR Emission: A Remote Tracer of Ion Solitary Structures R.L. Mutel,
... less than 1% of all WBD spectra observed when the spacecraft was above 30◦ magnetic latitude (Note that below this latitude, there is often shadowing by the Earth’s plasmasphere.) The occurrence probabilities were computed by dividing the number of dynamic spectra (length 52 sec) for which SAKR emis ...
... less than 1% of all WBD spectra observed when the spacecraft was above 30◦ magnetic latitude (Note that below this latitude, there is often shadowing by the Earth’s plasmasphere.) The occurrence probabilities were computed by dividing the number of dynamic spectra (length 52 sec) for which SAKR emis ...
sections 23-25 powerpoint
... Elliptical galaxy (E). A spheroidal galaxy containing millions to billions of old low-mass stars and no gas or dust. Spiral Galaxy (S). A galaxy with a spheroidal bulge of several million old low-mass stars and a flattened pancake-like disk of billions of old low-mass and young high-mass stars, alon ...
... Elliptical galaxy (E). A spheroidal galaxy containing millions to billions of old low-mass stars and no gas or dust. Spiral Galaxy (S). A galaxy with a spheroidal bulge of several million old low-mass stars and a flattened pancake-like disk of billions of old low-mass and young high-mass stars, alon ...
Baryons at Low Densities: The Stellar Halos around Galaxies
... galaxies. On account of their low surface brightness, detailed study of their physical properties has been difficult and, until recently, confined largely to the Milky Way (MW) and Andromeda (M31). Since the advent of large cameras and surveys, both from ground and space, our knowledge of stellar ha ...
... galaxies. On account of their low surface brightness, detailed study of their physical properties has been difficult and, until recently, confined largely to the Milky Way (MW) and Andromeda (M31). Since the advent of large cameras and surveys, both from ground and space, our knowledge of stellar ha ...
Galaxy Sorting
... 1. Discuss with the students briefly what a galaxy is, mentioning that it contains billions of stars bound together by their mutual gravity. Our Sun is just one of more than one hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. Note that other galaxies are very far away from us. Because of ...
... 1. Discuss with the students briefly what a galaxy is, mentioning that it contains billions of stars bound together by their mutual gravity. Our Sun is just one of more than one hundred billion stars that make up the Milky Way Galaxy. Note that other galaxies are very far away from us. Because of ...
The Telescope - Salt Lake Astronomical Society
... order to obtain a pure signal from the source. This is even more important when you consider that sources of cosmic gamma-rays are extremely weak and require long observations, sometimes several weeks, to get a significant detection or accurate measurement of a source. ...
... order to obtain a pure signal from the source. This is even more important when you consider that sources of cosmic gamma-rays are extremely weak and require long observations, sometimes several weeks, to get a significant detection or accurate measurement of a source. ...
instructor notes: weeks 9/10
... Lenticular galaxies get their name because they are “lenslike,” but are more like spiral and barred spiral galaxies in possessing a flattened disk, rather than like elliptical galaxies which mostly possess an ellipsoidal symmetry. The distinguishing feature of lenticulars relative to spiral galaxie ...
... Lenticular galaxies get their name because they are “lenslike,” but are more like spiral and barred spiral galaxies in possessing a flattened disk, rather than like elliptical galaxies which mostly possess an ellipsoidal symmetry. The distinguishing feature of lenticulars relative to spiral galaxie ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... The Milky Way, the galaxy in which we live, is but one of many galaxies. As a matter of fact, the Milky Way, also called the Galaxy, is a fairly average representative of the class of spiral galaxies. Two other examples of spiral galaxies are shown in Figs. 1.1 and 1.2, one of which we are viewing f ...
... The Milky Way, the galaxy in which we live, is but one of many galaxies. As a matter of fact, the Milky Way, also called the Galaxy, is a fairly average representative of the class of spiral galaxies. Two other examples of spiral galaxies are shown in Figs. 1.1 and 1.2, one of which we are viewing f ...
powerpoint - Physics @ IUPUI
... • The only real difference is the distribution of galaxy types. ...
... • The only real difference is the distribution of galaxy types. ...
Estimating the Age of Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... What is the rate of expansion of Cas A? The average amount of energy released in a core collapse supernova event is ~1044 Joules, and approximately one quarter of the energy drives the expansion of the remnant. Although the initial collapse and rebound of the core ejects the outer layers of the star ...
... What is the rate of expansion of Cas A? The average amount of energy released in a core collapse supernova event is ~1044 Joules, and approximately one quarter of the energy drives the expansion of the remnant. Although the initial collapse and rebound of the core ejects the outer layers of the star ...
Module 4.1 - The Scale of the Universe [slide 1] We now turn to
... therefore, luminosity must change. If we observe stars spectroscopically, we can observe the velocity of the photo sphere. Come towards us and go away from us. So we can measure stellar temperatures using colors or spectroscopy. We can measure velocity of the pulsating photosphere using spectroscopy ...
... therefore, luminosity must change. If we observe stars spectroscopically, we can observe the velocity of the photo sphere. Come towards us and go away from us. So we can measure stellar temperatures using colors or spectroscopy. We can measure velocity of the pulsating photosphere using spectroscopy ...
Deep Chandra Observations of the Arches and Quintuplet Clusters at... Hui Dong Q. Daniel Wang ( &
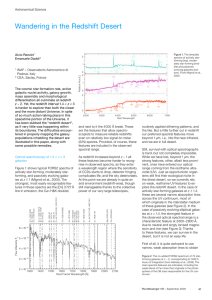
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
... The diffuse emission has a spectrum that is substantially harder than that of the point-like sources. In the core region (e.g. ≤ 15”, for Arches). The potential contamination of faint undetected point-like sources could be upto ∼ 65%, but mostly at energies ≤ 4 keV. The remaining diffuse emission ca ...
Wandering in the Redshift Desert
... relief may be offered by Ly-α, if the specSQNFQ@OG HR DEjBHDMS DMNTFG HM SGD 45 Indeed, even if not in emission, Ly-α is such a strong feature that it helps a lot in getting redshifts. However, in a spectrograph such as e.g., VIMOS, Ly-α does not enter before z ~ 1.8, hence the range 1.4 < z < 1.8 i ...
... relief may be offered by Ly-α, if the specSQNFQ@OG HR DEjBHDMS DMNTFG HM SGD 45 Indeed, even if not in emission, Ly-α is such a strong feature that it helps a lot in getting redshifts. However, in a spectrograph such as e.g., VIMOS, Ly-α does not enter before z ~ 1.8, hence the range 1.4 < z < 1.8 i ...
Is Draco II one of the faintest dwarf galaxies? First study from Keck
... For a cold stellar system like Dra II, it is particularly important to assess the level of systematics on the measured velocity uncertainties. DEIMOS is known to yield a small level of systematics that cannot be entirely explained from properly tracking the sources of noise in the spectra. These sys ...
... For a cold stellar system like Dra II, it is particularly important to assess the level of systematics on the measured velocity uncertainties. DEIMOS is known to yield a small level of systematics that cannot be entirely explained from properly tracking the sources of noise in the spectra. These sys ...
Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Chapter 24
... away—roughly 100 million times farther than the Moon. To appreciate how far this is, imagine that the Earth and Moon are dots on a sheet of paper one millimeter apart. On this scale, the Sun is 390 millimeters (about 15 inches) away, and Proxima Centauri is about 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles) aw ...
... away—roughly 100 million times farther than the Moon. To appreciate how far this is, imagine that the Earth and Moon are dots on a sheet of paper one millimeter apart. On this scale, the Sun is 390 millimeters (about 15 inches) away, and Proxima Centauri is about 100,000 kilometers (62,000 miles) aw ...
Chapter 15 Stars, Galaxies, and Universe
... Structure of the Milky Way Our solar system is located in a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way. From the side, the Milky Way appears to be a narrow disk with a bulge in the middle. The galaxy’s spiral structure is visible only from above or below. Center is 25,000 light years away from Earth ...
... Structure of the Milky Way Our solar system is located in a spiral galaxy called the Milky Way. From the side, the Milky Way appears to be a narrow disk with a bulge in the middle. The galaxy’s spiral structure is visible only from above or below. Center is 25,000 light years away from Earth ...
Hidden57_rf
... Nonetheless, until the mid-20th century our knowledge of the Universe was limited almost entirely to the narrow band of light that could penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere and was visible to our eyes or to sensitive photographic plates loaded at the focus of increasingly large telescopes. With these r ...
... Nonetheless, until the mid-20th century our knowledge of the Universe was limited almost entirely to the narrow band of light that could penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere and was visible to our eyes or to sensitive photographic plates loaded at the focus of increasingly large telescopes. With these r ...
PDF Full-text
... detectability of various molecules in optical and infrared spectra (e.g., [3,5,9]), and to test the effect of different UV flux illumination on the mixing ratios of many molecules (e.g., [3,5,10]). The assumed UV spectral-energy distributions for these models range from the minimal UV flux associate ...
... detectability of various molecules in optical and infrared spectra (e.g., [3,5,9]), and to test the effect of different UV flux illumination on the mixing ratios of many molecules (e.g., [3,5,10]). The assumed UV spectral-energy distributions for these models range from the minimal UV flux associate ...
THREE INTRIGUER NEBULAE IN CONSTELLATION CARINA
... Richtler, researchers of Universities in Argentina and Chile, confirm the existence of two compact elliptical (cE) galaxies in the central region of the Antlia cluster. Thus, Antlia becomes the nearest galaxy cluster harboring more than one cE galaxy among its galaxy population. Compact elliptical ( ...
... Richtler, researchers of Universities in Argentina and Chile, confirm the existence of two compact elliptical (cE) galaxies in the central region of the Antlia cluster. Thus, Antlia becomes the nearest galaxy cluster harboring more than one cE galaxy among its galaxy population. Compact elliptical ( ...
The Formation and Evolution of Massive Black Holes - Ira-Inaf
... time of more than 12 billion years, with the record holder, ULAS J1120+0641, at 12.9 billion years (21). Given that the universe is 13.7 billion years old, this particular quasar existed just 800 million years after the Big Bang. From the luminosity of this quasar, we can infer that the MBH powering ...
... time of more than 12 billion years, with the record holder, ULAS J1120+0641, at 12.9 billion years (21). Given that the universe is 13.7 billion years old, this particular quasar existed just 800 million years after the Big Bang. From the luminosity of this quasar, we can infer that the MBH powering ...
Magnificent Cosmos - Academic Program Pages at Evergreen
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
mg_colloq - University of Massachusetts Amherst
... Are they telling us about a different formation mechanism for massive galaxies (e.g. Dekel et al. 2009; Wuyts et al. 2011; Sales et al. 2012)? ...
... Are they telling us about a different formation mechanism for massive galaxies (e.g. Dekel et al. 2009; Wuyts et al. 2011; Sales et al. 2012)? ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.











![Module 4.1 - The Scale of the Universe [slide 1] We now turn to](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002846843_1-9e0ec9d1a2abbbab3c0d406694bfc4e2-300x300.png)