electricity - Montgomery College
... chemical energy table saw converts into mechanical energy Kitchen appliances converts to thermal energy ...
... chemical energy table saw converts into mechanical energy Kitchen appliances converts to thermal energy ...
Document
... = conductivity = 1/ For charge transport to occur - must have: - something the carry the charge - the ability to move ...
... = conductivity = 1/ For charge transport to occur - must have: - something the carry the charge - the ability to move ...
EME4-1
... charged electrons, but also by positively charged holes and (iii) electrical conductivity is sensitive to temperature, illumination, and magnetic fields; these properties result from the fact that, due to the nature of interatomic bonds (mostly covalent), in semiconductors, in contrast to metals but ...
... charged electrons, but also by positively charged holes and (iii) electrical conductivity is sensitive to temperature, illumination, and magnetic fields; these properties result from the fact that, due to the nature of interatomic bonds (mostly covalent), in semiconductors, in contrast to metals but ...
Resistance & Resistors
... of cross section A1 is 0.400 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the current density across A1? (b) If the current density across A2 is one-fourth the value across A1, what is the radius of the conductor at A2? ...
... of cross section A1 is 0.400 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the current density across A1? (b) If the current density across A2 is one-fourth the value across A1, what is the radius of the conductor at A2? ...
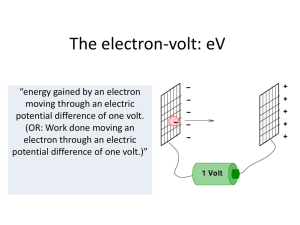
The electron-volt - Hockerill Students
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
... moving through an electric potential difference of one volt. (OR: Work done moving an electron through an electric potential difference of one volt.)” ...
FREE ELECTRON THEORY
... In a perfect crystal; the collisions of electrons are with thermally excited lattice vibrations (scattering of an electron by a phonon). This electron-phonon scattering gives a temperature dependent ph (T ) collision time which tends to infinity as T 0. In real metal, the electrons also collide wi ...
... In a perfect crystal; the collisions of electrons are with thermally excited lattice vibrations (scattering of an electron by a phonon). This electron-phonon scattering gives a temperature dependent ph (T ) collision time which tends to infinity as T 0. In real metal, the electrons also collide wi ...
The Electrical Conductivity of a Partially Ionized Argon
... with the potassium atoms and the COULOMB interaction are taken into account as well the conductivity in the magnetic field varies by about 20%. ...
... with the potassium atoms and the COULOMB interaction are taken into account as well the conductivity in the magnetic field varies by about 20%. ...
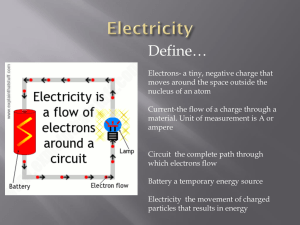
Lesson 6.1 What is Electricity? - d
... Identify an element based on the atomic number. Identify metals, metalloids, and non-metals on the periodic table. Judge whether a material is a conductor, insulator, or semiconductor based upon its number of valance electrons and its position on the periodic table. Explain how the Law of Charges ho ...
... Identify an element based on the atomic number. Identify metals, metalloids, and non-metals on the periodic table. Judge whether a material is a conductor, insulator, or semiconductor based upon its number of valance electrons and its position on the periodic table. Explain how the Law of Charges ho ...
Chap 19 Learn Obj
... Describe the formation of electron energy bands as a large number of atoms, initially widely separated and isolated from one another, are gradually brought together, and allowed to bond to one another such that a crystalline solid is formed. ...
... Describe the formation of electron energy bands as a large number of atoms, initially widely separated and isolated from one another, are gradually brought together, and allowed to bond to one another such that a crystalline solid is formed. ...
Proposed Final Questions
... 12) What is the voltage difference across a 5.00 resistor that carries a current of 5.00 A? a) 100 V b) 25 V c) 4.0 V d) 1.0 V 13) Rubbing two objects such as plastic and wool together creates a static charge because a) atoms are transferred from one object to another b) the electrons in one objec ...
... 12) What is the voltage difference across a 5.00 resistor that carries a current of 5.00 A? a) 100 V b) 25 V c) 4.0 V d) 1.0 V 13) Rubbing two objects such as plastic and wool together creates a static charge because a) atoms are transferred from one object to another b) the electrons in one objec ...
Unit G495 - Field and particle pictures - Insert
... It was known in ancient Greece that rubbed amber attracted small objects, like hair and dust. The phenomenon was given a name by the Englishman Francis Gilbert in 1600, who called it amberisation, and then electrification from electron, the Greek word for amber. Further investigations by the French ...
... It was known in ancient Greece that rubbed amber attracted small objects, like hair and dust. The phenomenon was given a name by the Englishman Francis Gilbert in 1600, who called it amberisation, and then electrification from electron, the Greek word for amber. Further investigations by the French ...
Atoms and Energies
... slightly (the size of the shift is very small compared with the energy difference between different levels) Atoms in solids form bands of closely-spaced energy levels Electrons fill the lowest-energy bands first The highest energy band with electrons in it is called the valence band If the valence b ...
... slightly (the size of the shift is very small compared with the energy difference between different levels) Atoms in solids form bands of closely-spaced energy levels Electrons fill the lowest-energy bands first The highest energy band with electrons in it is called the valence band If the valence b ...
Electricity 2015
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. Electromagnets are wide ...
... An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. Electromagnets are wide ...
Semester exam chapter 7. PHYS4315
... Assume that both loops have their normal parallel to the z-axis. What is the mutual inductance between the loops if the distance r is sufficiently large that the dipole approximation may be used? ...
... Assume that both loops have their normal parallel to the z-axis. What is the mutual inductance between the loops if the distance r is sufficiently large that the dipole approximation may be used? ...
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY
... electrons in a completely filled band cannot move, since all states occupied (Pauli principle); only way to move would be to “jump” into next higher band needs energy; electrons in partly filled band can move, since there are free states to move to. Classification of solids into three types, acc ...
... electrons in a completely filled band cannot move, since all states occupied (Pauli principle); only way to move would be to “jump” into next higher band needs energy; electrons in partly filled band can move, since there are free states to move to. Classification of solids into three types, acc ...