Full band - Institute of Materials Science
... • At room temperature, the first Si piece has a lot of free electrons, and the second one has free holes • When an electric field is applied, the two types of charge carriers move in opposite directions, as they are oppositely charged n-type Si ...
... • At room temperature, the first Si piece has a lot of free electrons, and the second one has free holes • When an electric field is applied, the two types of charge carriers move in opposite directions, as they are oppositely charged n-type Si ...
List of important topics: Electricity • Charge • Coulomb Force
... overall rotating charge that can be considered as a loop. The combined movement of all the electrons in an atom does not always create such a pattern but if it does then the atom possesses ...
... overall rotating charge that can be considered as a loop. The combined movement of all the electrons in an atom does not always create such a pattern but if it does then the atom possesses ...
INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS II FORMULA
... units: 1 A = 1 C/s . J~ current density, I = J~ · dA Electric current: I = dQ dt Conductor, cross-sectional area A, charge carriers of charge q, density n, drift velocity ~vd , the current is I = nqvd A, so that the current density is J~ = nq~vd . ...
... units: 1 A = 1 C/s . J~ current density, I = J~ · dA Electric current: I = dQ dt Conductor, cross-sectional area A, charge carriers of charge q, density n, drift velocity ~vd , the current is I = nqvd A, so that the current density is J~ = nq~vd . ...
Ionic Bonding - petersonORHS
... representing the name given) CaClO3 Step 2 Label charges Ca+2 ClO3-1 Step 3 Write subscripts that balance the charges Ca(ClO3)2 Step 4: Erase charges from your formula ...
... representing the name given) CaClO3 Step 2 Label charges Ca+2 ClO3-1 Step 3 Write subscripts that balance the charges Ca(ClO3)2 Step 4: Erase charges from your formula ...
Nanomaterials
... Optical dispersion in a crystal made by non spherical atoms. A 3D bandgap appear when structures are designed to have zero intensity in directions of allowed Bragg reflections. Repeat period is on the order of 30μm (3D optical bandgap in the far IR, limit of today technology). ...
... Optical dispersion in a crystal made by non spherical atoms. A 3D bandgap appear when structures are designed to have zero intensity in directions of allowed Bragg reflections. Repeat period is on the order of 30μm (3D optical bandgap in the far IR, limit of today technology). ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
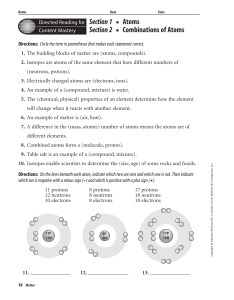
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
Sample Midterm 1 - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... (c) Qualitatively draw the electric field in the semiconductor as a function of x. Hint use dε/dx = qN/ε. ...
... (c) Qualitatively draw the electric field in the semiconductor as a function of x. Hint use dε/dx = qN/ε. ...
Lawson criterion / plasma physics
... Potential in vacuum The length scale for shielding is the Debye length which depends on both Temperature as well as density. It is around 10-5 m for a fusion plasma ...
... Potential in vacuum The length scale for shielding is the Debye length which depends on both Temperature as well as density. It is around 10-5 m for a fusion plasma ...
SOLID-STATE PHYSICS II 2008 O. Entin-Wohlman
... • The pn junction diode. Free electrons on the n-side and free holes on the p-side can initially wander across the junction. When a free electron meets a free hole it can ’drop into it’. So far as charge movements are concerned this means the hole and electron cancel each other and vanish. As a resu ...
... • The pn junction diode. Free electrons on the n-side and free holes on the p-side can initially wander across the junction. When a free electron meets a free hole it can ’drop into it’. So far as charge movements are concerned this means the hole and electron cancel each other and vanish. As a resu ...
CHEM1405 2012-J-2 June 2012 • What is the ground state electron
... Japanese Fukushima nuclear reactor. They have half lives of 8 days and 30 years, respectively. What is the definition of half-life? Half-life is the amount of time required for the amount (or activity) of a sample to decrease to half its initial value. What percentage of both isotopes will still be ...
... Japanese Fukushima nuclear reactor. They have half lives of 8 days and 30 years, respectively. What is the definition of half-life? Half-life is the amount of time required for the amount (or activity) of a sample to decrease to half its initial value. What percentage of both isotopes will still be ...
Electrostatics The Nature of Electric Charge
... Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Properties of charge Like charges repel, unlike charges attract. Charge is conserved: it cannot be created or destroyed. Charges aren’t “used up”, but their energy can be “harnessed”. Electrons a ...
... Charges are arbitrarily called positive and negative. In most cases, only the negative charge is mobile. Properties of charge Like charges repel, unlike charges attract. Charge is conserved: it cannot be created or destroyed. Charges aren’t “used up”, but their energy can be “harnessed”. Electrons a ...
periodic trends
... • Z* increases across a period owing to incomplete shielding by inner electrons. • Estimate Z* by --> [ Z - (no. inner electrons) ] • Charge felt by 2s e- in Li Z* = 3 - 2 = 1 • Be Z* = 4 - 2 = 2 • B Z* = 5 - 2 = 3 and so on! ...
... • Z* increases across a period owing to incomplete shielding by inner electrons. • Estimate Z* by --> [ Z - (no. inner electrons) ] • Charge felt by 2s e- in Li Z* = 3 - 2 = 1 • Be Z* = 4 - 2 = 2 • B Z* = 5 - 2 = 3 and so on! ...
Atomic number
... element. Everything is made of atoms Proton: positive particle in the nucleus Neutron: neutral particle in the nucleus Electron: tiny negative charge outside the nucleus Atoms are mostly…. … empty space! Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated ...
... element. Everything is made of atoms Proton: positive particle in the nucleus Neutron: neutral particle in the nucleus Electron: tiny negative charge outside the nucleus Atoms are mostly…. … empty space! Element: a substance made of only one kind of atom, cannot be chemically or physically separated ...