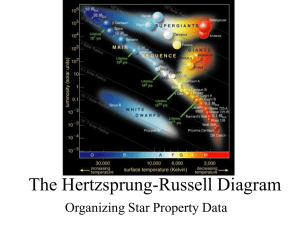
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
The H-R Diagram
... • These are even brighter than the SN II’s, which come from massive stars. • Very useful – they’re all the ~same event – 1.4 solar mass white dwarfs passing the Chandrasekhar Limit, collapsing initially, triggering carbon nuclear fusion all in a flash. So they turn out to be… • GREAT “standard candl ...
... • These are even brighter than the SN II’s, which come from massive stars. • Very useful – they’re all the ~same event – 1.4 solar mass white dwarfs passing the Chandrasekhar Limit, collapsing initially, triggering carbon nuclear fusion all in a flash. So they turn out to be… • GREAT “standard candl ...
Parallax, Event Horizon, HR diagrams equation
... "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
... "1 Light Year is the distance traveled by light in one year." 1 light year (ly) is equivalent to: 63,270 AU Closer stars could appear larger. More distant stars could be very large, but seem small. How can we tell which stars are farther away? ...
Star Show FACILITATOR NOTES
... Emphasize the temperature-color link by pointing out that an incandescent light bulb which closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filame ...
... Emphasize the temperature-color link by pointing out that an incandescent light bulb which closely matches the Sun’s spectrum must have a temperature very close to the temperature at the Sun’s visible surface—well over 5000°C. Except for specialized lights used in photography, most real light filame ...
H-R Diagrams
... Looking for patterns If we plot a graph of luminosity against temperature for lots of stars we get a graph like this… ...
... Looking for patterns If we plot a graph of luminosity against temperature for lots of stars we get a graph like this… ...
neutron star - Livonia Public Schools
... or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size, believed to be near its final stage of evolution. • The sun begins as a nebula, spends much of its life as a main-sequence star, and then becomes a red giant, a planetary nebula, a white dwarf, and, finally, a black dwarf. ...
... or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size, believed to be near its final stage of evolution. • The sun begins as a nebula, spends much of its life as a main-sequence star, and then becomes a red giant, a planetary nebula, a white dwarf, and, finally, a black dwarf. ...
xam2ans
... in the core of a main sequence star like the Sun? Answer: The rest mass energy of a neutron is larger than a proton plus electron. Consequently this reaction is endothermic, which means energetically unfavorable. (d) On the other hand, p+ + e → n + e does occur in a neutron star or a sufficiently ...
... in the core of a main sequence star like the Sun? Answer: The rest mass energy of a neutron is larger than a proton plus electron. Consequently this reaction is endothermic, which means energetically unfavorable. (d) On the other hand, p+ + e → n + e does occur in a neutron star or a sufficiently ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... A. is visible during daytime, while other stars are visible only at night. B. has a much hotter temperature than most stars, making it glow brighter. C. emits yellow light, which is several times brighter than other colors. D. is far closer than any other star, which makes it look the brightest. ...
... A. is visible during daytime, while other stars are visible only at night. B. has a much hotter temperature than most stars, making it glow brighter. C. emits yellow light, which is several times brighter than other colors. D. is far closer than any other star, which makes it look the brightest. ...
Introduction to the HR Diagram
... 2) If one were to plot height against weight for humans there would be a general relation which would define the locus of normality for humans in this diagram. 3) As humans age, their height and weight do change, so the position of an individual person in this diagram will evolve with time. 4) Over ...
... 2) If one were to plot height against weight for humans there would be a general relation which would define the locus of normality for humans in this diagram. 3) As humans age, their height and weight do change, so the position of an individual person in this diagram will evolve with time. 4) Over ...
Stars
... know that a basketball is much larger than a baseball. But what seems to happen if you friend carries the basketball to the other end of the field? The basketball looks smaller than the baseball to you. The basketball does not really get smaller. It looks smaller because it is much farther away. ...
... know that a basketball is much larger than a baseball. But what seems to happen if you friend carries the basketball to the other end of the field? The basketball looks smaller than the baseball to you. The basketball does not really get smaller. It looks smaller because it is much farther away. ...
November 2005 - Otterbein University
... • Careful study of the Sun ~ 370 years • We have studied the Sun for only 1/27 millionth of its lifetime! ...
... • Careful study of the Sun ~ 370 years • We have studied the Sun for only 1/27 millionth of its lifetime! ...
Week 11
... FUSION: small nuclei combine together IF they collide fast enough • example: hydrogen ...
... FUSION: small nuclei combine together IF they collide fast enough • example: hydrogen ...
What are yellow stars?
... • Arcturus is the brightest star in the Constellation of Boötes. • Arcturus is the 4th Brightest stars. • Arcturus is visible from both hemispheres in the sky. ...
... • Arcturus is the brightest star in the Constellation of Boötes. • Arcturus is the 4th Brightest stars. • Arcturus is visible from both hemispheres in the sky. ...
Foundations III The Stars
... Gravity dictates that such a close-in planet would keep the same side facing the star at all times, the same way the moon always shows the same face to Earth. That means the planet has a blazing-hot daytime side, a frigid nighttime side, and a band of eternal sunrise or sunset where water — and per ...
... Gravity dictates that such a close-in planet would keep the same side facing the star at all times, the same way the moon always shows the same face to Earth. That means the planet has a blazing-hot daytime side, a frigid nighttime side, and a band of eternal sunrise or sunset where water — and per ...
Lecture 13: The Stars –
... Gravity dictates that such a close-in planet would keep the same side facing the star at all times, the same way the moon always shows the same face to Earth. That means the planet has a blazing-hot daytime side, a frigid nighttime side, and a band of eternal sunrise or sunset where water — and per ...
... Gravity dictates that such a close-in planet would keep the same side facing the star at all times, the same way the moon always shows the same face to Earth. That means the planet has a blazing-hot daytime side, a frigid nighttime side, and a band of eternal sunrise or sunset where water — and per ...
Chapter 13
... • When a degenerate, low-mass star begins to fuse helium, it will not expand – The core temperature increases exponentially – Helium fusion proceeds explosively in what is called a helium flash ...
... • When a degenerate, low-mass star begins to fuse helium, it will not expand – The core temperature increases exponentially – Helium fusion proceeds explosively in what is called a helium flash ...
Chapter 29: Stars - Mr. Pelton Science
... • What is the difference between brightness and luminosity? • What are the properties used to identify stars? ...
... • What is the difference between brightness and luminosity? • What are the properties used to identify stars? ...
HR Diagram Activity - Mr. Alster`s Science Classes
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
... Purpose: In this lab we will investigate the relationship between the temperature, brightness and diameter of stars. Introduction The H-R Diagram is a tool that astronomers use to classify stars based on their luminosity, magnitude, temperature, spectral class and evolutionary stage. The H-R Diagram ...
More detailed notes - Particle Physics and Particle Astrophysics
... Hydrogen fusion converts about 0.7% of the mass of the initial hydrogen into energy via E = mc2. Helium fusion is only about a tenth as efficient, converting about 0.07% of the mass of the helium into energy. In addition, as can be seen in the diagram, stars tend to be more luminous in the helium-bu ...
... Hydrogen fusion converts about 0.7% of the mass of the initial hydrogen into energy via E = mc2. Helium fusion is only about a tenth as efficient, converting about 0.07% of the mass of the helium into energy. In addition, as can be seen in the diagram, stars tend to be more luminous in the helium-bu ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... star called a red dwarf. In this first stage of life, our sun was a dim red star. Circle an area and put a 1 on your H-R diagram to show the first stage of the sun’s formation. b. As the sun grew older and fusion continued, it became a stable star and entered the main sequence stage of its life cycl ...
... star called a red dwarf. In this first stage of life, our sun was a dim red star. Circle an area and put a 1 on your H-R diagram to show the first stage of the sun’s formation. b. As the sun grew older and fusion continued, it became a stable star and entered the main sequence stage of its life cycl ...
Star

A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names. Extensive catalogues of stars have been assembled by astronomers, which provide standardized star designations.For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Once the hydrogen in the core of a star is nearly exhausted, almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime and, for some stars, by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the principal determinant of its evolution and eventual fate. Other characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement. A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Once the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily converted into helium through nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity. Once the hydrogen fuel at the core is exhausted, a star with at least 0.4 times the mass of the Sun expands to become a red giant, in some cases fusing heavier elements at the core or in shells around the core. The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of its matter into the interstellar environment, where it will contribute to the formation of a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements. Meanwhile, the core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or (if it is sufficiently massive) a black hole.Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.























