Ch 3 PPT - Blountstown Middle School
... The universe is made up of stars, gas, and dust, as well as invisible dark matter. Material in the universe is pulled by gravity into galaxies, including our own Milky Way galaxy. ...
... The universe is made up of stars, gas, and dust, as well as invisible dark matter. Material in the universe is pulled by gravity into galaxies, including our own Milky Way galaxy. ...
Star Formation
... • Supernova blast waves near clouds can initiate star formation (happened for our own sun, from SNe produced radioactive daughter products in meteorites) • Collapse raises density, core cannot radiate away heat gravitational collapse heat fast enough, and temp rises, until H fusion begins at 10 mill ...
... • Supernova blast waves near clouds can initiate star formation (happened for our own sun, from SNe produced radioactive daughter products in meteorites) • Collapse raises density, core cannot radiate away heat gravitational collapse heat fast enough, and temp rises, until H fusion begins at 10 mill ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... a 3AU (400AU) 3 m A mB 2 4 Solar masses Pyr (4,000 yr) 2 The combined mass of the binary star system is between 4 and 16 solar masses 6. Two stars are orbiting each other, both 4.2 arcsec from their center of mass. Their orbital period is 420.3 years and their distance from the Earth is 104 ...
... a 3AU (400AU) 3 m A mB 2 4 Solar masses Pyr (4,000 yr) 2 The combined mass of the binary star system is between 4 and 16 solar masses 6. Two stars are orbiting each other, both 4.2 arcsec from their center of mass. Their orbital period is 420.3 years and their distance from the Earth is 104 ...
stars-notes
... Composition of Stars, continued • A continuous spectrum shows all of the colors, while an absorption spectrum shows which wavelengths of light are absorbed. • The spectrum of a star is an absorption spectrum because the atmosphere of the star absorbs certain portions of the light produced by the sta ...
... Composition of Stars, continued • A continuous spectrum shows all of the colors, while an absorption spectrum shows which wavelengths of light are absorbed. • The spectrum of a star is an absorption spectrum because the atmosphere of the star absorbs certain portions of the light produced by the sta ...
Star Formation
... Until it is in equilibrium The star has reached the Main Sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse Astronomy 1-2 ...
... Until it is in equilibrium The star has reached the Main Sequence and will remain there as long as it has hydrogen to fuse Astronomy 1-2 ...
Diapositiva 1
... Stellar activity does not depend on age or rotation Very slow angular momentum loss. Braking time ~ 109yr. Rotational velocity distribution must be imposed the pre-main sequence evolution ...
... Stellar activity does not depend on age or rotation Very slow angular momentum loss. Braking time ~ 109yr. Rotational velocity distribution must be imposed the pre-main sequence evolution ...
Earth in Space and Time (SC.5.E.5.1)
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
... actually larger than the Sun. If this is true, why do these stars appear like points of light in the sky? A. These stars are hotter than the Sun. B. These stars have less mass than the Sun. C. These stars are farther away from Earth than the Sun is. D. These stars are made of different chemicals tha ...
How Stars Work: Ay 122 - Fall 2004 - Lecture 7
... For an isolated, static, spherically symmetric star, four basic laws / equations needed to describe structure: • Conservation of mass • Conservation of energy (at each radius, the change in the energy flux equals the local rate of energy release) • Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium (at each radius ...
... For an isolated, static, spherically symmetric star, four basic laws / equations needed to describe structure: • Conservation of mass • Conservation of energy (at each radius, the change in the energy flux equals the local rate of energy release) • Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium (at each radius ...
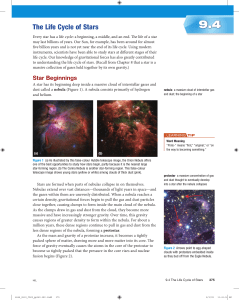
The Life Cycle of Stars
... These main sequence stars vary in surface temperature, as you can see from the shape of the band in the H–R diagram in Figure 4. The hotter these stars are, the more luminous they are. Astronomers have determined that hotter, more luminous main sequence stars are more massive, while cooler, less lum ...
... These main sequence stars vary in surface temperature, as you can see from the shape of the band in the H–R diagram in Figure 4. The hotter these stars are, the more luminous they are. Astronomers have determined that hotter, more luminous main sequence stars are more massive, while cooler, less lum ...
Letot STELLAR EVOLUTION By Kyle Letot Grade Level: 6
... Protostar: A protostar is what you have before a star forms. It is a cloud of gas that over time pressure and gravity push down to make it collapse into a star. ...
... Protostar: A protostar is what you have before a star forms. It is a cloud of gas that over time pressure and gravity push down to make it collapse into a star. ...
Stellar Magnitudes and Distances
... • the direction and speed a star is moving • its mass • its brightness or luminosity • its chemical composition • its size • its age • its temperature ...
... • the direction and speed a star is moving • its mass • its brightness or luminosity • its chemical composition • its size • its age • its temperature ...
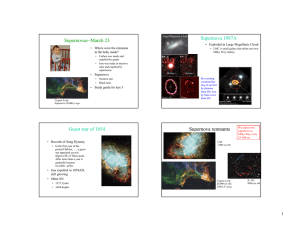
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... Guest star of 1054 • Records of Sung Dynasty • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
... Guest star of 1054 • Records of Sung Dynasty • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
nebula - Harding University
... In these pictures you will see evidence of stellar formation and of the presence of disk-like structures surrounding these new stars. The four massive stars that dominate this region are emitting radiation and gasses which are interacting with the smaller young stars being formed. These stellar ...
... In these pictures you will see evidence of stellar formation and of the presence of disk-like structures surrounding these new stars. The four massive stars that dominate this region are emitting radiation and gasses which are interacting with the smaller young stars being formed. These stellar ...
P10263v1.2 Lab 5 Text
... easily visible to the naked eye. There are many theories about what happened to the 7th one. Celaeno has often been called the “Lost Pleiad” because she was hit by lightning according to Greek mythology. In reality, the star we call Celaeno is just at the limit of human vision in terms of brightness ...
... easily visible to the naked eye. There are many theories about what happened to the 7th one. Celaeno has often been called the “Lost Pleiad” because she was hit by lightning according to Greek mythology. In reality, the star we call Celaeno is just at the limit of human vision in terms of brightness ...
Document
... Red Dwarfs : Stars with a core mass of .08 to 0.4 solar mass Coolest and dimmest of all MS stars. They remain on MS hundreds of billions of years. When all the H is converted to He fusion ceases, they cool down, moving down and to the right in the H-R diagram. ...
... Red Dwarfs : Stars with a core mass of .08 to 0.4 solar mass Coolest and dimmest of all MS stars. They remain on MS hundreds of billions of years. When all the H is converted to He fusion ceases, they cool down, moving down and to the right in the H-R diagram. ...
The Lifecycle of the Stars
... The leftover core of a star is so dense that it causes the gravitational collapse. Lifecycle of a star notes. >Once a star (or anything for that matter) falls into the black hole it will never be able to excape its gravitational ...
... The leftover core of a star is so dense that it causes the gravitational collapse. Lifecycle of a star notes. >Once a star (or anything for that matter) falls into the black hole it will never be able to excape its gravitational ...
Star

A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names. Extensive catalogues of stars have been assembled by astronomers, which provide standardized star designations.For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Once the hydrogen in the core of a star is nearly exhausted, almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime and, for some stars, by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the principal determinant of its evolution and eventual fate. Other characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement. A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Once the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily converted into helium through nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity. Once the hydrogen fuel at the core is exhausted, a star with at least 0.4 times the mass of the Sun expands to become a red giant, in some cases fusing heavier elements at the core or in shells around the core. The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of its matter into the interstellar environment, where it will contribute to the formation of a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements. Meanwhile, the core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or (if it is sufficiently massive) a black hole.Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.