First Light Sources at the End of the Dark Ages: Direct
... begun. Thus, near-infrared observations of these dwarfs could reveal strong Lyman ! and He II emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will reg ...
... begun. Thus, near-infrared observations of these dwarfs could reveal strong Lyman ! and He II emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will reg ...
Summary: Modes of Star Formation
... Infrared observations of the newly formed stars embedded in molecular clouds show that most stars do indeed form in clusters. In the Orion clouds, for example, most of the newly formed stars are located in several embedded or partly obscured clusters, of which the Trapezium cluster is just the large ...
... Infrared observations of the newly formed stars embedded in molecular clouds show that most stars do indeed form in clusters. In the Orion clouds, for example, most of the newly formed stars are located in several embedded or partly obscured clusters, of which the Trapezium cluster is just the large ...
1 Introduction - High Point University
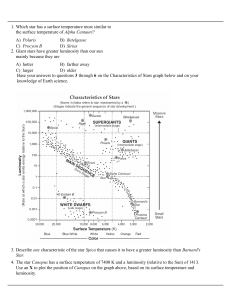
... primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius. Describe the sizes of stars along the main sequence. What are stars like near the top of the main sequence, th ...
... primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R diagram. Move the active cursor up and down the main sequence and explore the different values of stellar radius. Describe the sizes of stars along the main sequence. What are stars like near the top of the main sequence, th ...
Document
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
... • In a visual binary, you can see two stars. • However, for most binary stars, their separation is very small compared to their distance, and from Earth they appear to be a single point. • How do you observe these types of binaries? Use spectroscopy! ...
Star Formation in Our Galaxy - Wiley-VCH
... Along with their gas, molecular clouds contain an admixture of small solid particles, the interstellar dust grains. These particles efficiently absorb light with wavelengths smaller than their diameters (about 0.1 µm) and reradiate this energy into the infrared. Regions where the dust effectively bl ...
... Along with their gas, molecular clouds contain an admixture of small solid particles, the interstellar dust grains. These particles efficiently absorb light with wavelengths smaller than their diameters (about 0.1 µm) and reradiate this energy into the infrared. Regions where the dust effectively bl ...
Apparent Magnitude - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
PPS
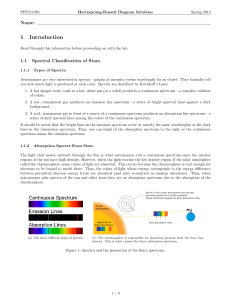
... interested in the properties of the glass in the prisms, and how in affected the light, but to his surprise he discovered that there are many dark lines in the spectrum of white light, including light from the Sun. A few of these dark lines in the solar spectrum, now known as Fraunhofer lines, had b ...
... interested in the properties of the glass in the prisms, and how in affected the light, but to his surprise he discovered that there are many dark lines in the spectrum of white light, including light from the Sun. A few of these dark lines in the solar spectrum, now known as Fraunhofer lines, had b ...
Stellar Continua
... How precisely can we measure them? What are the units? What can we learn from the continuum? ...
... How precisely can we measure them? What are the units? What can we learn from the continuum? ...
Hubble Data Processing and Archiving
... RR Lyrae-Type Variable Stars Discovered by Williamina Fleming in 1893 in Omega Centauri Change their brightness by pulsing like the air in a ...
... RR Lyrae-Type Variable Stars Discovered by Williamina Fleming in 1893 in Omega Centauri Change their brightness by pulsing like the air in a ...
Ecosystems, from life, to the Earth, to the Galaxy
... Stars form from the collapse of clouds of molecular gas under the influence of gravity. The clouds are prevented from collapsing by a number of internal support mechanisms, such as pressure, rotation, magnetic fields and turbulence. They require a triggering mechanism to overcome this, which may be ...
... Stars form from the collapse of clouds of molecular gas under the influence of gravity. The clouds are prevented from collapsing by a number of internal support mechanisms, such as pressure, rotation, magnetic fields and turbulence. They require a triggering mechanism to overcome this, which may be ...
PHYS3380_111115_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... - required some revisions to models of high mass stellar evolution, which had suggested that supernovae would result from red supergiants. Now believe star was chemically poor in elements heavier than He - contracted and heated up after phase as cool, red supergiant during which it lost much of its ...
... - required some revisions to models of high mass stellar evolution, which had suggested that supernovae would result from red supergiants. Now believe star was chemically poor in elements heavier than He - contracted and heated up after phase as cool, red supergiant during which it lost much of its ...
1 Introduction - University of Amsterdam
... compact helium core is revealed it is identified as a Wolf-Rayet star. The supernova progenitor state (at the top of the diagram) determines the characteristics of the final explosion and therefore also the nature of the compact object that is left behind. It is not only mass that governs the evolut ...
... compact helium core is revealed it is identified as a Wolf-Rayet star. The supernova progenitor state (at the top of the diagram) determines the characteristics of the final explosion and therefore also the nature of the compact object that is left behind. It is not only mass that governs the evolut ...
Chapter 15
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
... the hydrogen fuel in its core to make helium. The helium is basically just sitting there, so it's not producing any energy. Instead, the core is shrinking and getting hotter. Before long, it'll get hot enough to ignite the helium, which will begin fusing together to make heavier elements. When that ...
stellar spectra instructor notes
... etc. Provisions were also made in the original scheme for subdwarfs (= VI) and white dwarfs (= VIII), but those classes never became popular. Subdwarfs are now recognized as metalpoor stars that are difficult to classify in any case, and white dwarfs are degenerate stars (D) that have since been giv ...
... etc. Provisions were also made in the original scheme for subdwarfs (= VI) and white dwarfs (= VIII), but those classes never became popular. Subdwarfs are now recognized as metalpoor stars that are difficult to classify in any case, and white dwarfs are degenerate stars (D) that have since been giv ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
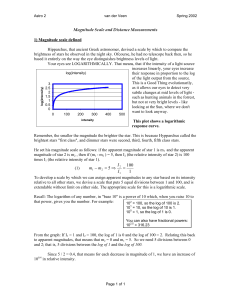
... figure you’ll see that there are horizontal marks indicating various ages from 10 7 to 1010 years! The way you determine the age of a cluster, or star, is you find where the Main Sequence stars start to move away from the well defined grouping by that name. Young stars move away higher up the H-R di ...
... figure you’ll see that there are horizontal marks indicating various ages from 10 7 to 1010 years! The way you determine the age of a cluster, or star, is you find where the Main Sequence stars start to move away from the well defined grouping by that name. Young stars move away higher up the H-R di ...
Star

A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth. Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names. Extensive catalogues of stars have been assembled by astronomers, which provide standardized star designations.For at least a portion of its life, a star shines due to thermonuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core, releasing energy that traverses the star's interior and then radiates into outer space. Once the hydrogen in the core of a star is nearly exhausted, almost all naturally occurring elements heavier than helium are created by stellar nucleosynthesis during the star's lifetime and, for some stars, by supernova nucleosynthesis when it explodes. Near the end of its life, a star can also contain degenerate matter. Astronomers can determine the mass, age, metallicity (chemical composition), and many other properties of a star by observing its motion through space, luminosity, and spectrum respectively. The total mass of a star is the principal determinant of its evolution and eventual fate. Other characteristics of a star, including diameter and temperature, change over its life, while the star's environment affects its rotation and movement. A plot of the temperature of many stars against their luminosities, known as a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (H–R diagram), allows the age and evolutionary state of a star to be determined.A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Once the stellar core is sufficiently dense, hydrogen becomes steadily converted into helium through nuclear fusion, releasing energy in the process. The remainder of the star's interior carries energy away from the core through a combination of radiative and convective processes. The star's internal pressure prevents it from collapsing further under its own gravity. Once the hydrogen fuel at the core is exhausted, a star with at least 0.4 times the mass of the Sun expands to become a red giant, in some cases fusing heavier elements at the core or in shells around the core. The star then evolves into a degenerate form, recycling a portion of its matter into the interstellar environment, where it will contribute to the formation of a new generation of stars with a higher proportion of heavy elements. Meanwhile, the core becomes a stellar remnant: a white dwarf, a neutron star, or (if it is sufficiently massive) a black hole.Binary and multi-star systems consist of two or more stars that are gravitationally bound, and generally move around each other in stable orbits. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can have a significant impact on their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster or a galaxy.