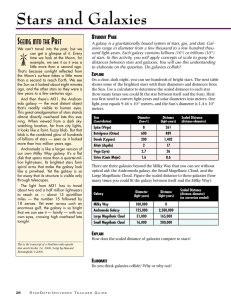
Origins of the Universe
... typically containing millions to hundreds of billions of member stars – A star is a large hot ball of gas which generates energy in its core by nuclear reactions Around 100 billion in the universe Held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another Formed around 200 ...
... typically containing millions to hundreds of billions of member stars – A star is a large hot ball of gas which generates energy in its core by nuclear reactions Around 100 billion in the universe Held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another Formed around 200 ...
Ch. 21 notes-1
... They contain billions of stars but have little gas and dust. So they cannot form new star. They contain old stars. Irregular Galaxies Some galaxies do not have regular shapes. The Large Magellanic Cloud is an irregular galaxy about 160,000 light-years away from our galaxy. It is one of our clos ...
... They contain billions of stars but have little gas and dust. So they cannot form new star. They contain old stars. Irregular Galaxies Some galaxies do not have regular shapes. The Large Magellanic Cloud is an irregular galaxy about 160,000 light-years away from our galaxy. It is one of our clos ...
Stars and Galaxies
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
Galaxies and Stars
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
Unit 1: The Big Picture
... – Thought Milky Way made up entire universe until 1920s – Small fuzzy patches in telescopes appeared as nebulae, Latin for clouds – Edwin Hubble measured approximate distance to nearby Andromeda…no way Milky Way was that large – 3 Types: spiral, elliptical, irregular ...
... – Thought Milky Way made up entire universe until 1920s – Small fuzzy patches in telescopes appeared as nebulae, Latin for clouds – Edwin Hubble measured approximate distance to nearby Andromeda…no way Milky Way was that large – 3 Types: spiral, elliptical, irregular ...
General Astrophysical Concepts: Astronomical length scales
... The gravitational field of a black hole extends out to an infinite distance ...
... The gravitational field of a black hole extends out to an infinite distance ...
Universe and Galaxy Short Study Guide
... instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s birth, but instead evolve with the galaxy by trapping an amazingly exact percentage (0.2) of the mass ...
... instead grew on a diet of gas and stars controlled by their host galaxies in the beginning years of the universe. An initial look at 30 galaxies indicates that black holes do not precede a galaxy’s birth, but instead evolve with the galaxy by trapping an amazingly exact percentage (0.2) of the mass ...
ppt
... with ~ same speed • But this creates a winding dilemma • So density waves must sweep around galaxy, which move more slowly around the galaxy than the matter inside • This crowding promotes stellar birth and recycling of ISM ...
... with ~ same speed • But this creates a winding dilemma • So density waves must sweep around galaxy, which move more slowly around the galaxy than the matter inside • This crowding promotes stellar birth and recycling of ISM ...
combined astro show 2013
... • Will the Universe expand forever or collapse in a Big Crunch? • Oscillating Universe? • The expansion of the Universe is speeding up! • Dark Energy? • Dark Matter? • Big Freeze? ...
... • Will the Universe expand forever or collapse in a Big Crunch? • Oscillating Universe? • The expansion of the Universe is speeding up! • Dark Energy? • Dark Matter? • Big Freeze? ...
Study Guide
... Period: ___________________ Date: ___________________ Study Guide Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe ...
... Period: ___________________ Date: ___________________ Study Guide Chapter 12 Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe ...
Unit 1
... • In the 1700’s, Charles Messier was observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is ...
... • In the 1700’s, Charles Messier was observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • also known as M45 or the Seven Sisters • located in the constellation of Taurus • dominated by hot, blue stars, which have formed within the last 100 million years. • Of all clusters close to the Earth it is the best known and most striking to the naked eye ...
... • also known as M45 or the Seven Sisters • located in the constellation of Taurus • dominated by hot, blue stars, which have formed within the last 100 million years. • Of all clusters close to the Earth it is the best known and most striking to the naked eye ...
doc - IAC
... same way as planetary masses are measured. The most massive ones are 100 to 150 times heavier than the Sun. The most massive stars evolve more rapidly than those of low mass. Does this in any way affect the galaxies in which they are found? Indeed it does. Massive stars have very short lifetimes, at ...
... same way as planetary masses are measured. The most massive ones are 100 to 150 times heavier than the Sun. The most massive stars evolve more rapidly than those of low mass. Does this in any way affect the galaxies in which they are found? Indeed it does. Massive stars have very short lifetimes, at ...
Great Astronomers of the 20th Century
... galaxy clusters • Faber-Jackson relation to determine distances to galaxies – Picks up where Period-Luminosity relationship runs out of steam – Luminosity of galaxy is correlated to the width of its spectral absorption lines – Velocity dispersion of the inner few kiloparsecs of a galaxy ...
... galaxy clusters • Faber-Jackson relation to determine distances to galaxies – Picks up where Period-Luminosity relationship runs out of steam – Luminosity of galaxy is correlated to the width of its spectral absorption lines – Velocity dispersion of the inner few kiloparsecs of a galaxy ...
WK10revisedoneweek
... •Giant Ellipticals are the size of our galaxy but are rare •Dwarf Ellipticals are more common (6000 light yrs across) ...
... •Giant Ellipticals are the size of our galaxy but are rare •Dwarf Ellipticals are more common (6000 light yrs across) ...
The Sun and Beyond - Valhalla High School
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
... The Milky Way- our home galaxy Milky Way Local GroupThe Milky Way is not an island universe, but a member of a small cluster of galaxies called the Local Group. The Local Group contains about 3 dozen known galaxies, clumped in two subgroups around two massive spiral galaxies -the Milky Way, a ...
The Universe and Galaxies - West Jefferson Local Schools
... - ________ is required for light to travel through space - light travels a little over 8 minutes from the sun to earth - the farther away an object/star is, the ________ it takes for light to get to us, and the older the light is when it gets to us = “Light is OLD” - we see the ________of other star ...
... - ________ is required for light to travel through space - light travels a little over 8 minutes from the sun to earth - the farther away an object/star is, the ________ it takes for light to get to us, and the older the light is when it gets to us = “Light is OLD” - we see the ________of other star ...
The Universe and Galaxies - West Jefferson Local Schools
... - ________ is required for light to travel through space - light travels a little over 8 minutes from the sun to earth - the farther away an object/star is, the ________ it takes for light to get to us, and the older the light is when it gets to us = “Light is OLD” - we see the ________of other star ...
... - ________ is required for light to travel through space - light travels a little over 8 minutes from the sun to earth - the farther away an object/star is, the ________ it takes for light to get to us, and the older the light is when it gets to us = “Light is OLD” - we see the ________of other star ...
Name____________________________________________
... S6E1 Where do we live in the Universe, Milky Way, and our Solar System? 1. Between 15-20 billion years ago the Universe began expanding out of an enormous explosion scientist called the Big Bang theory. 2. From largest to smallest, order the following (1 is largest -4 is smallest): __4___ The Sun __ ...
... S6E1 Where do we live in the Universe, Milky Way, and our Solar System? 1. Between 15-20 billion years ago the Universe began expanding out of an enormous explosion scientist called the Big Bang theory. 2. From largest to smallest, order the following (1 is largest -4 is smallest): __4___ The Sun __ ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe
... • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence stars. ...
... • A white dwarf is is a star that has used up all of its hydrogen and is the leftover center of an older star. • Class F stars are yellow-white • The majority of stars in our galaxy are main sequence stars. ...
File
... 22) What is a galaxy? 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is wh ...
... 22) What is a galaxy? 23) What are the three classifications of galaxies? What do each look like? Which is most common? 24) What shape is the Milky Way? 25) What is the local group? 26) How many stars are in the Milky Way? 27) Approximately how big is the Milky Way 28) The largest known galaxy is wh ...
Groups of Stars
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas and dust, and dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally ""milky"", a reference to the Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand (103) stars to giants with one hundred trillion (1014) stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology, including elliptical, spiral, and irregular. Many galaxies are thought to have black holes at their active centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than our own Sun. As of July 2015, EGSY8p7 is the oldest and most distant galaxy with a light travel distance of 13.2 billion light-years from Earth, and observed as it existed 570 million years after the Big Bang. Previously, as of May 2015, EGS-zs8-1 was the most distant known galaxy, estimated to have a light travel distance of 13.1 billion light-years away and to have 15% of the mass of the Milky Way.Approximately 170 billion (1.7 × 1011) to 200 billion (2.0 × 1011) galaxies exist in the observable universe. Most of the galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter and usually separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs). The space between galaxies is filled with a tenuous gas with an average density less than one atom per cubic meter. The majority of galaxies are gravitationally organized into associations known as galaxy groups, clusters, and superclusters. At the largest scale, these associations are generally arranged into sheets and filaments that are surrounded by immense voids.