Our Galaxy, The Milky Way
... • Velocity dispersion of stars increases with their mean age: the evidence for a stochastic acceleration due to GMC and spiral arm encounters in a differentially rotating Galaxy • The shape of the velocity ellipsoid also changes: older stars rotate more slowly; the thick disk rotates with a speed of ...
... • Velocity dispersion of stars increases with their mean age: the evidence for a stochastic acceleration due to GMC and spiral arm encounters in a differentially rotating Galaxy • The shape of the velocity ellipsoid also changes: older stars rotate more slowly; the thick disk rotates with a speed of ...
Section 4
... Which type of galaxy does not have a regular shape? (Irregular) Which type of galaxy is the Milky Way? (Spiral) Apply Tell students that just as Earth revolves around the sun, so the sun revolves around the Milky Way. It takes about 220 million years for our solar system to complete one revolution. ...
... Which type of galaxy does not have a regular shape? (Irregular) Which type of galaxy is the Milky Way? (Spiral) Apply Tell students that just as Earth revolves around the sun, so the sun revolves around the Milky Way. It takes about 220 million years for our solar system to complete one revolution. ...
TRANSIT
... groups - together with other young people – on astronomical projects. The projects vary from night-time observations to theoretical problems, depending on your own interests. The working groups will be led by young scientists from the IAYC team. The IAYC 2009 will offer a wide range of working grou ...
... groups - together with other young people – on astronomical projects. The projects vary from night-time observations to theoretical problems, depending on your own interests. The working groups will be led by young scientists from the IAYC team. The IAYC 2009 will offer a wide range of working grou ...
The Reflector: January 2010 - Peterborough Astronomical Association
... star birthing area in Sagittarius to two double stars in Cygnus, a million stars in a ball in Hercules, and finally to the final stages of star life in M57 and M27, all in one night. It’s quite a story and you’ll meet a red giant star—Antares—along the way. Planet buffs will also be able to take in ...
... star birthing area in Sagittarius to two double stars in Cygnus, a million stars in a ball in Hercules, and finally to the final stages of star life in M57 and M27, all in one night. It’s quite a story and you’ll meet a red giant star—Antares—along the way. Planet buffs will also be able to take in ...
File
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
... Visible nebulae that you placed yellow labels are located nearby the Solar System and invisible nebulae (but seen in radio wavelength) that you placed silver labels are located far from our Solar System. Visible light emitted from far nebulae are absorbed by foreground gas and dust in the space and ...
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field Project Overview
... The velocity you calculated for this star is much less than the speed of light, so we could have found a decent approximation to the answer using z = v/c. But, if you use the approximation equation to calculate the recession velocity based on the spectral shift from the spectrum of a distant galaxy ...
... The velocity you calculated for this star is much less than the speed of light, so we could have found a decent approximation to the answer using z = v/c. But, if you use the approximation equation to calculate the recession velocity based on the spectral shift from the spectrum of a distant galaxy ...
Cosmology Handouts
... 7. Figure 1 shows the seven similarly bright stars of the Big Dipper. They look equally close but they are not. For example, star A is two times farther away from us than star B. How would you arrange seven students with different flashlights to form something that looks like the Big Dipper? ...
... 7. Figure 1 shows the seven similarly bright stars of the Big Dipper. They look equally close but they are not. For example, star A is two times farther away from us than star B. How would you arrange seven students with different flashlights to form something that looks like the Big Dipper? ...
Lecture 18, Gravitational Waves, Future Missions and
... Gravitational waves are often described as ripples in space-time. In general relativity, mass leads to a curvature of space-time. Gravity waves are produced by accelerating masses (if the motion is not perfectly symmetric). Gravity waves have not yet been detected, though we do have indirect evidenc ...
... Gravitational waves are often described as ripples in space-time. In general relativity, mass leads to a curvature of space-time. Gravity waves are produced by accelerating masses (if the motion is not perfectly symmetric). Gravity waves have not yet been detected, though we do have indirect evidenc ...
Activity 1 - Galaxies
... Telescopes can be designed to detect any type of electromagnetic wave. This advance in technology has allowed astronomers to generate images of objects in space from the visible light, infra-red, radio waves, X-rays and any other electromagnetic waves they emit. Astronomers have learnt a great deal ...
... Telescopes can be designed to detect any type of electromagnetic wave. This advance in technology has allowed astronomers to generate images of objects in space from the visible light, infra-red, radio waves, X-rays and any other electromagnetic waves they emit. Astronomers have learnt a great deal ...
Lecture 2: ppt, 5 MB
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
... Supernovae: Massive stars end in glorious explosions. Hubble found three mysterious rings of material encircling a doomed star that exploded as a supernova in 1987. During the years since the eruption, Hubble spied brightened spots on the ...
hubble_refurb
... The wispy, glowing, magenta structures in this image are the remains of a star 10 to 15 times the mass of the Sun that we would have seen exploding as a supernova 3,000 years ago. The remnant’s fast-moving gas is plowing into the surrounding gas of the galaxy, creating a supersonic shock wave in th ...
... The wispy, glowing, magenta structures in this image are the remains of a star 10 to 15 times the mass of the Sun that we would have seen exploding as a supernova 3,000 years ago. The remnant’s fast-moving gas is plowing into the surrounding gas of the galaxy, creating a supersonic shock wave in th ...
Determination of spiral orbits with constant tangential velocity
... Near to the center, the measured velocity agrees really well with the calculation. However, for greater distances from the center a surprising discrepancy appears. The measured velocities are nearly independent from the distance to the center. The red curve shows the measurement four our own Milky W ...
... Near to the center, the measured velocity agrees really well with the calculation. However, for greater distances from the center a surprising discrepancy appears. The measured velocities are nearly independent from the distance to the center. The red curve shows the measurement four our own Milky W ...
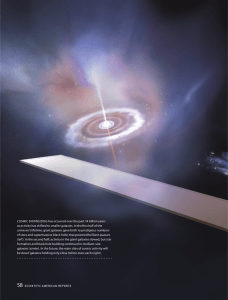
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... t o p i e c e t o g e t h e r the history of the cosmos, astronomers must first make sense of the astounding multitude of objects they observe. Our most sensitive optical views of the universe come from the Hubble Space Telescope. In the Hubble Deep Field studies — 10day exposures of two tiny region ...
... t o p i e c e t o g e t h e r the history of the cosmos, astronomers must first make sense of the astounding multitude of objects they observe. Our most sensitive optical views of the universe come from the Hubble Space Telescope. In the Hubble Deep Field studies — 10day exposures of two tiny region ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. April 2006. 1
... NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4656 (10.4) pc. are a fine example of a pair of interacting galaxies, both edge-on to our view, located mid-way between Cor Coroli and the Coma star cluster. One end of NGC4656 has a distinct hook which may be glimpsed in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M9 ...
... NGC4631 (9.7) sg and NG4656 (10.4) pc. are a fine example of a pair of interacting galaxies, both edge-on to our view, located mid-way between Cor Coroli and the Coma star cluster. One end of NGC4656 has a distinct hook which may be glimpsed in 8" telescopes under good seeing conditions. NGC4736 (M9 ...
The Extragalactic Distance Database: Color–Magnitude Diagrams
... footprint of the observations used in our analysis is highlighted in yellow. The red boxes represent the footprint of another ACS observation of the galaxy. Footprints of observations other than those used for the production of the galaxy’s CMD often appear in these images, but those that are used a ...
... footprint of the observations used in our analysis is highlighted in yellow. The red boxes represent the footprint of another ACS observation of the galaxy. Footprints of observations other than those used for the production of the galaxy’s CMD often appear in these images, but those that are used a ...
file - University of California San Diego
... The forest, Burbidge notes, may represent light not from the quasar itself but from diffuse gas clouds that lie along our line of sight to the quasar and absorb some of its spectrum. "These gas clouds may be in a primordial region, perhaps evolving into a cluster of galaxies around the quasar," Burb ...
... The forest, Burbidge notes, may represent light not from the quasar itself but from diffuse gas clouds that lie along our line of sight to the quasar and absorb some of its spectrum. "These gas clouds may be in a primordial region, perhaps evolving into a cluster of galaxies around the quasar," Burb ...
Dark Matter -24-------------------------------~-----------R-E-S-O-N-A-N-C
... (i) It doesn't exist; the law of gravitation must be modified so that the stars are all there is to a galaxy. (ii) Dark matter exists, but consists entirely of ord~nary matter - Jupiter-like objects called broum dwarfs that are not massive enough to start the stellar energy-generating process of nuc ...
... (i) It doesn't exist; the law of gravitation must be modified so that the stars are all there is to a galaxy. (ii) Dark matter exists, but consists entirely of ord~nary matter - Jupiter-like objects called broum dwarfs that are not massive enough to start the stellar energy-generating process of nuc ...
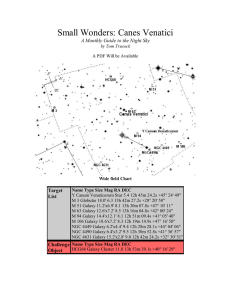
Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... normal ratio, and we have no reason to believe otherwise, then the planets can only explain a tiny part of the invisible matter. Brown dwarf stars (more about these in later lectures) are stars which had too little mass to start nuclear reactions. They emit thermal radiation, but their temperature i ...
... normal ratio, and we have no reason to believe otherwise, then the planets can only explain a tiny part of the invisible matter. Brown dwarf stars (more about these in later lectures) are stars which had too little mass to start nuclear reactions. They emit thermal radiation, but their temperature i ...
Star formation, feedback and the role of SNe II and SNe Ia in the
... of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out the “tidal dwarf” hypothesis and find that Draco is a cosmological ...
... of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out the “tidal dwarf” hypothesis and find that Draco is a cosmological ...
ASTR 340 - TerpConnect
... simply way to produce the objects we see and feel. A strong force of attraction, nuclear force, binds neutrons and protons together to form a compact body, the nucleus, with size about 10-15 m. The protons are positively charged while the neutron has not charged. Thus, the nucleus is positively char ...
... simply way to produce the objects we see and feel. A strong force of attraction, nuclear force, binds neutrons and protons together to form a compact body, the nucleus, with size about 10-15 m. The protons are positively charged while the neutron has not charged. Thus, the nucleus is positively char ...
Galaxy
.jpg?width=300)
A galaxy is a gravitationally bound system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas and dust, and dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias (γαλαξίας), literally ""milky"", a reference to the Milky Way. Galaxies range in size from dwarfs with just a few thousand (103) stars to giants with one hundred trillion (1014) stars, each orbiting their galaxy's own center of mass. Galaxies are categorized according to their visual morphology, including elliptical, spiral, and irregular. Many galaxies are thought to have black holes at their active centers. The Milky Way's central black hole, known as Sagittarius A*, has a mass four million times greater than our own Sun. As of July 2015, EGSY8p7 is the oldest and most distant galaxy with a light travel distance of 13.2 billion light-years from Earth, and observed as it existed 570 million years after the Big Bang. Previously, as of May 2015, EGS-zs8-1 was the most distant known galaxy, estimated to have a light travel distance of 13.1 billion light-years away and to have 15% of the mass of the Milky Way.Approximately 170 billion (1.7 × 1011) to 200 billion (2.0 × 1011) galaxies exist in the observable universe. Most of the galaxies are 1,000 to 100,000 parsecs in diameter and usually separated by distances on the order of millions of parsecs (or megaparsecs). The space between galaxies is filled with a tenuous gas with an average density less than one atom per cubic meter. The majority of galaxies are gravitationally organized into associations known as galaxy groups, clusters, and superclusters. At the largest scale, these associations are generally arranged into sheets and filaments that are surrounded by immense voids.