stars_space
... Explain the additional stages undergone by the most massive stars. Your account should include what is meant by (a) supernova, (b) neutron star, and (c) black hole. (a) How does a star produce energy? (b) Explain why the Sun is neither expanding or contracting at the present time. Copy and answer qu ...
... Explain the additional stages undergone by the most massive stars. Your account should include what is meant by (a) supernova, (b) neutron star, and (c) black hole. (a) How does a star produce energy? (b) Explain why the Sun is neither expanding or contracting at the present time. Copy and answer qu ...
3A8d
... of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in the traditional formation/evolution model, which proposed that the formation of galaxies was largely completed in single rapid collapse events more than 10 ...
... of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in the traditional formation/evolution model, which proposed that the formation of galaxies was largely completed in single rapid collapse events more than 10 ...
Week 11 Concept Summary
... (a) Disk: The disk is very thin compared to its size, like a CD (but even thinner in proportion!). It contains a lot of gas and dust, as well as many stars both young and old. Open clusters are also found here. Most stars in the disk have conentrations of heavy elements similar to the Sun’s. They al ...
... (a) Disk: The disk is very thin compared to its size, like a CD (but even thinner in proportion!). It contains a lot of gas and dust, as well as many stars both young and old. Open clusters are also found here. Most stars in the disk have conentrations of heavy elements similar to the Sun’s. They al ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... By plotting the distances of globular clusters (estimated using regular variable stars) we can determine the sun’s location relative to the stellar halo of the Galaxy. We conclude that our Sun lies within the galactic disk, some 8000 pc (26,000 ly) from the Galactic centre. ...
... By plotting the distances of globular clusters (estimated using regular variable stars) we can determine the sun’s location relative to the stellar halo of the Galaxy. We conclude that our Sun lies within the galactic disk, some 8000 pc (26,000 ly) from the Galactic centre. ...
Our Galactic Archipelago
... million stars in the Milky Way. Wilman I was the first ultrafaint discovered in SDSS data (discovered in 2004, promoted to a galaxy in 2007). It has a diameter of 100 pc (less than the thickness of the MW disk) and consists of only 2,000 stars. ...
... million stars in the Milky Way. Wilman I was the first ultrafaint discovered in SDSS data (discovered in 2004, promoted to a galaxy in 2007). It has a diameter of 100 pc (less than the thickness of the MW disk) and consists of only 2,000 stars. ...
Document
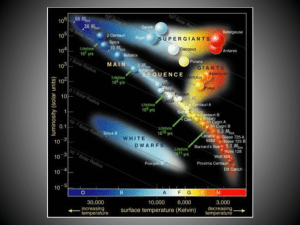
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: ...
Descriptions For Posters
... the consellation Cassiopeia. The original star, about 15 to 20 times more massive than our sun, died in a cataclysmic "supernova" explosion relatively recently in our own Milky Way galaxy. Pandora’s Cluster The giant galaxy cluster appears to be the result of a simultaneous pile-up of at least four ...
... the consellation Cassiopeia. The original star, about 15 to 20 times more massive than our sun, died in a cataclysmic "supernova" explosion relatively recently in our own Milky Way galaxy. Pandora’s Cluster The giant galaxy cluster appears to be the result of a simultaneous pile-up of at least four ...
Messier 87

Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, and generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it is notable for its large population of globular clusters—M87 contains about 12,000 compared to the 150-200 orbiting the Milky Way—and its jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends outward at least 1,500 parsecs (4,900 light-years), travelling at relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and is a popular target for both amateur astronomy observations and professional astronomy study.French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, cataloguing it as a nebulous feature while searching for objects that would confuse comet hunters. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, M87 is located about 16.4 million parsecs (53.5 million light-years) from Earth. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical galaxies, diminishing in luminosity with distance from the centre. Forming around one sixth of M87's mass, the stars in this galaxy have a nearly spherically symmetric distribution, their density decreasing with increasing distance from the core. At the core is a supermassive black hole, which forms the primary component of an active galactic nucleus. This object is a strong source of multiwavelength radiation, particularly radio waves. M87's galactic envelope extends out to a radius of about 150 kiloparsecs (490,000 light-years), where it has been truncated—possibly by an encounter with another galaxy. Between the stars is a diffuse interstellar medium of gas that has been chemically enriched by elements emitted from evolved stars.