The Missing Mass
... where P and a are the period and semi-major axis of the orbit, and the atom of gas is much less massive than the galaxy. If the atom’s orbit is circular, then a is the radius of the circle (r), and, according to Kepler’s 2nd law, the atom’s speed is constant. So ...
... where P and a are the period and semi-major axis of the orbit, and the atom of gas is much less massive than the galaxy. If the atom’s orbit is circular, then a is the radius of the circle (r), and, according to Kepler’s 2nd law, the atom’s speed is constant. So ...
Document
... The observation that there are few spiral galaxies in areas of high galaxy density. ...
... The observation that there are few spiral galaxies in areas of high galaxy density. ...
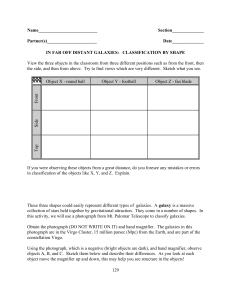
In Far Off Distant Galaxies: Classification by Shape
... Object A is a star in the fore ground (located between observer and Virgo Cluster). They are bright Milky Way Galaxy stars showing diffraction spikes (an artifact of the telescope). Object B is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It is disk shaped with arms. The two or more arms are visible due to ...
... Object A is a star in the fore ground (located between observer and Virgo Cluster). They are bright Milky Way Galaxy stars showing diffraction spikes (an artifact of the telescope). Object B is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It is disk shaped with arms. The two or more arms are visible due to ...
ASTRO 1050 The Structure of the Milky Way Galaxy
... around the center of the Galaxy evenly in a spherical cloud in the halo. You can find a picture of a globular cluster below. Harlow Shapley realized that depending on where you are in the Galaxy, the pattern of globular clusters will look different. In reality, globular clusters are spread out in a ...
... around the center of the Galaxy evenly in a spherical cloud in the halo. You can find a picture of a globular cluster below. Harlow Shapley realized that depending on where you are in the Galaxy, the pattern of globular clusters will look different. In reality, globular clusters are spread out in a ...
Planets and Moons - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... and billions of stars held together by gravity. One galaxy can have hundreds of billions of stars and be as large as 200,000 light years across. • Galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias meaning "milky", a reference to the Milky Way. • Many galaxies are believed to have black holes at their active ...
... and billions of stars held together by gravity. One galaxy can have hundreds of billions of stars and be as large as 200,000 light years across. • Galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias meaning "milky", a reference to the Milky Way. • Many galaxies are believed to have black holes at their active ...
Document
... – Light-years (about 8,000 miles per second, or 6 trillion miles in 1 year) – The closest star to our sun is Proxima Centauri at 4.3 light years away (25.8 trillion miles) ...
... – Light-years (about 8,000 miles per second, or 6 trillion miles in 1 year) – The closest star to our sun is Proxima Centauri at 4.3 light years away (25.8 trillion miles) ...
Diapositiva 1
... The “halo” is really the “stellar halo” – turns out there’s actually a larger halo we can’t even see! ...
... The “halo” is really the “stellar halo” – turns out there’s actually a larger halo we can’t even see! ...
Aug 2015 supplement - Hermanus Astronomy
... relatively ordinary mass of the galaxy that contained it. Most galaxies host black holes with masses less than 1 percent of the galaxy. In CID-947, the black hole mass is 10 percent that of its host galaxy. Because of this remarkable disparity, the team deduced this black hole grew so quickly that t ...
... relatively ordinary mass of the galaxy that contained it. Most galaxies host black holes with masses less than 1 percent of the galaxy. In CID-947, the black hole mass is 10 percent that of its host galaxy. Because of this remarkable disparity, the team deduced this black hole grew so quickly that t ...
Messier 87

Messier 87 (also known as Virgo A or NGC 4486, and generally abbreviated to M87) is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it is notable for its large population of globular clusters—M87 contains about 12,000 compared to the 150-200 orbiting the Milky Way—and its jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends outward at least 1,500 parsecs (4,900 light-years), travelling at relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky, and is a popular target for both amateur astronomy observations and professional astronomy study.French astronomer Charles Messier discovered M87 in 1781, cataloguing it as a nebulous feature while searching for objects that would confuse comet hunters. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, M87 is located about 16.4 million parsecs (53.5 million light-years) from Earth. Unlike a disk-shaped spiral galaxy, M87 has no distinctive dust lanes. Instead, it has an almost featureless, ellipsoidal shape typical of most giant elliptical galaxies, diminishing in luminosity with distance from the centre. Forming around one sixth of M87's mass, the stars in this galaxy have a nearly spherically symmetric distribution, their density decreasing with increasing distance from the core. At the core is a supermassive black hole, which forms the primary component of an active galactic nucleus. This object is a strong source of multiwavelength radiation, particularly radio waves. M87's galactic envelope extends out to a radius of about 150 kiloparsecs (490,000 light-years), where it has been truncated—possibly by an encounter with another galaxy. Between the stars is a diffuse interstellar medium of gas that has been chemically enriched by elements emitted from evolved stars.