General Astrophysical Concepts: Astronomical length scales
... to the black hole’s mass The event horizon or Schwarzschild radius of a black hole, the region over which it is capable of trapping light (radiation), is proportional to the black hole’s mass “A black hole has no hair” is a statement that describes the loss of identity of matter when it is swallowed ...
... to the black hole’s mass The event horizon or Schwarzschild radius of a black hole, the region over which it is capable of trapping light (radiation), is proportional to the black hole’s mass “A black hole has no hair” is a statement that describes the loss of identity of matter when it is swallowed ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble Space Telescope Apparent Magnitude: brightness as it appears from Earth Absolute Magnitude: brightness as it appears 32.6 ly away ...
... 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble Space Telescope Apparent Magnitude: brightness as it appears from Earth Absolute Magnitude: brightness as it appears 32.6 ly away ...
Review 1
... Let us remind ourselves: 1. Photosphere produces the continuum spectrum peaking in yellow. This tells us that its temperature is 5800 K 2. Upper levels of Photosphere are cooler, making an absorption line spectrum. 3. Dark edges in Solar granules imply lower temperature. 4. The Chromosphere has an e ...
... Let us remind ourselves: 1. Photosphere produces the continuum spectrum peaking in yellow. This tells us that its temperature is 5800 K 2. Upper levels of Photosphere are cooler, making an absorption line spectrum. 3. Dark edges in Solar granules imply lower temperature. 4. The Chromosphere has an e ...
Nebular Theory worksheet 2017
... further proposed that our solar system was once a star surrounded by a dust cloud. It is currently theorized that our solar system (and others like it) formed from a collapsing nebula. A nebula is a swirling collection of gases (mostly hydrogen and helium) and dust particles (solid matter in the for ...
... further proposed that our solar system was once a star surrounded by a dust cloud. It is currently theorized that our solar system (and others like it) formed from a collapsing nebula. A nebula is a swirling collection of gases (mostly hydrogen and helium) and dust particles (solid matter in the for ...
What can Spectroscopy tell us
... This is a spectrum of the Sun. The dark bands are called absorption lines and indicate different atoms present in the outer cooler layers of the Sun. The pattern of the absorption lines allows astronomers to determine the types of atoms and molecules that make up the star. Click on the links below ...
... This is a spectrum of the Sun. The dark bands are called absorption lines and indicate different atoms present in the outer cooler layers of the Sun. The pattern of the absorption lines allows astronomers to determine the types of atoms and molecules that make up the star. Click on the links below ...
Astronomy
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
... Ursa Major and Ursa Minor • Artemis, the moon goddess and goddess of the hunt, always had hunting companions with her when she went on the hunt. One such companion was Callisto, a beautiful young maiden. One day Zeus passed by a woodland cove and spied the sleeping Callisto. Zeus disguised himself ...
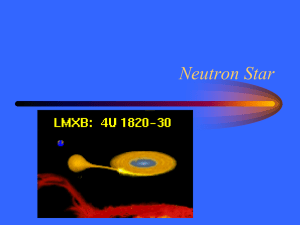
Neutron Star
... • When the mass of the core is greater than 1.4 M, electrons cannot support the gravitational force. • This is the Chandrasekar limit: beyond that it’s supernova. ...
... • When the mass of the core is greater than 1.4 M, electrons cannot support the gravitational force. • This is the Chandrasekar limit: beyond that it’s supernova. ...
PowerPoint - Earth Science with Mrs. Wilson
... When a star forms it begins its “life.” When a star runs out of fuel, it dies. So a star has a life similar to a battery that cannot be recharged. When the battery runs out of energy, it is finished. Our sun will run out of energy and it will be finished too. But this will not happen for another 5 ...
... When a star forms it begins its “life.” When a star runs out of fuel, it dies. So a star has a life similar to a battery that cannot be recharged. When the battery runs out of energy, it is finished. Our sun will run out of energy and it will be finished too. But this will not happen for another 5 ...
Astro 1 & 100 Levine Homework Stars Name:____________________________
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
... You may want to do the lecture-tutorial on pg 33, Apparent and Absolute Magnitude of Stars, prior to doing this portion of the homework, if you need a refresher on m and M. Ranking questions are 2 points each. Consider the following table of stars: ...
WEST ORANGE PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... The mass of the objects and the distance (squared) between them (measured from the centers of the objects). As mass increases, gravity increases. As distance increases, gravity decreases (by a factor of 4). 12.Which of Newton’s Laws best describes a sled sliding on a flat, icy surface with a ...
... The mass of the objects and the distance (squared) between them (measured from the centers of the objects). As mass increases, gravity increases. As distance increases, gravity decreases (by a factor of 4). 12.Which of Newton’s Laws best describes a sled sliding on a flat, icy surface with a ...
Constellation
... mass of gas held together by its own gravity in which the energy generated by nuclear reactions in the interior is balanced by the outflow of energy to the surface, and the inwarddirected gravitational forces are balanced by the outwarddirected gas and radiation pressures. An Binary Star is a stella ...
... mass of gas held together by its own gravity in which the energy generated by nuclear reactions in the interior is balanced by the outflow of energy to the surface, and the inwarddirected gravitational forces are balanced by the outwarddirected gas and radiation pressures. An Binary Star is a stella ...
Monday, December 8 - Otterbein University
... constellation Scorpius as shown in Figure 1. At 4 PM that afternoon, where will the Sun be with respect to the stars shown in this diagram? ...
... constellation Scorpius as shown in Figure 1. At 4 PM that afternoon, where will the Sun be with respect to the stars shown in this diagram? ...
the Study Guide
... form of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light as well as gamma rays, X-rays, radio waves, and microwaves. Star: A giant ball of gas, mainly hydrogen, undergoing constant nuclear reaction, thereby generating immense amounts of heat, light, and other kinds of radiation. There are many different kin ...
... form of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light as well as gamma rays, X-rays, radio waves, and microwaves. Star: A giant ball of gas, mainly hydrogen, undergoing constant nuclear reaction, thereby generating immense amounts of heat, light, and other kinds of radiation. There are many different kin ...
00
... eclipses the larger because the higher temperature exists on the inner faces. Since both the effect of ellipticity and the reflection effect result from the closeness of two stars it is difficult to separate one effect from the other. The proximity gives rise to other effects, too, for not only does ...
... eclipses the larger because the higher temperature exists on the inner faces. Since both the effect of ellipticity and the reflection effect result from the closeness of two stars it is difficult to separate one effect from the other. The proximity gives rise to other effects, too, for not only does ...
The illustration shows the Sun just after it has made the transition to
... star produces more energy. Now, your first instinct is probably to wonder why the gas doesn’t getter hotter if that is the case, rather than cooler – and that instinct would be sound if the gas could be held in place somehow, perhaps by an imaginary glass globe surrounding the star. If it weren’t al ...
... star produces more energy. Now, your first instinct is probably to wonder why the gas doesn’t getter hotter if that is the case, rather than cooler – and that instinct would be sound if the gas could be held in place somehow, perhaps by an imaginary glass globe surrounding the star. If it weren’t al ...
Habitibility of Earth, in our Solar System, and Beyond
... liquid hydrocarbons, like methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6). ...
... liquid hydrocarbons, like methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6). ...
the sun - WordPress.com
... The mass of the Sun is approximately 330,000 times greater than that of Earth. It is almost three quarters Hydrogen, whilst most of the remaining mass is Helium. ...
... The mass of the Sun is approximately 330,000 times greater than that of Earth. It is almost three quarters Hydrogen, whilst most of the remaining mass is Helium. ...
Observing the Universe 1
... 8. When the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth the eclipse formed is called a ...
... 8. When the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth the eclipse formed is called a ...
Star Characteristics
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
... Color + Temperature = Length of life Blue and white are the brightest Yellow stars last 10 billion years Red stars last longer It then turns into a super giant or red giant. ...
IK Pegasi

IK Pegasi (or HR 8210) is a binary star system in the constellation Pegasus. It is just luminous enough to be seen with the unaided eye, at a distance of about 150 light years from the Solar System.The primary (IK Pegasi A) is an A-type main-sequence star that displays minor pulsations in luminosity. It is categorized as a Delta Scuti variable star and it has a periodic cycle of luminosity variation that repeats itself about 22.9 times per day. Its companion (IK Pegasi B) is a massive white dwarf—a star that has evolved past the main sequence and is no longer generating energy through nuclear fusion. They orbit each other every 21.7 days with an average separation of about 31 million kilometres, or 19 million miles, or 0.21 astronomical units (AU). This is smaller than the orbit of Mercury around the Sun.IK Pegasi B is the nearest known supernova progenitor candidate. When the primary begins to evolve into a red giant, it is expected to grow to a radius where the white dwarf can accrete matter from the expanded gaseous envelope. When the white dwarf approaches the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.44 solar masses (M☉), it may explode as a Type Ia supernova.