Atmosphere. Clouds.
... The vapor condenses to a liquid when air is cooled past the saturation point. Dew forms due to the ground temperature drop at night. Fog forms when large areas of cool land or water come in contact with air. Clouds form due to air cooling by expansion as it rises. A normal cooling rate of air is 0.6 ...
... The vapor condenses to a liquid when air is cooled past the saturation point. Dew forms due to the ground temperature drop at night. Fog forms when large areas of cool land or water come in contact with air. Clouds form due to air cooling by expansion as it rises. A normal cooling rate of air is 0.6 ...
Weather
... • In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right. • In the Southern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the left. ...
... • In the Northern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the right. • In the Southern Hemisphere, the deflection is to the left. ...
Chapter 1 - Weather Underground
... waves, thus these waves don’t travel very far But, at night, the D region dissipates, allowing for AM waves to bounce off the E and F regions ...
... waves, thus these waves don’t travel very far But, at night, the D region dissipates, allowing for AM waves to bounce off the E and F regions ...
Chapter 19 Test Review Notes
... balancing the weight of the air column that stretches from your head to the top of the atmosphere. Air exerts pressure in all directions. A barograph records and measures air pressure on a chart. ...
... balancing the weight of the air column that stretches from your head to the top of the atmosphere. Air exerts pressure in all directions. A barograph records and measures air pressure on a chart. ...
Synoptic Map
... Tropical cyclone, also called hurricane and typhoon, is the names given to an intense low pressure region that forms and migrates in the tropical ocean regions and is associated with intense winds and a very strong convection activity which brings thunderstorms and large amounts of rainfall ...
... Tropical cyclone, also called hurricane and typhoon, is the names given to an intense low pressure region that forms and migrates in the tropical ocean regions and is associated with intense winds and a very strong convection activity which brings thunderstorms and large amounts of rainfall ...
Eyewitness
... 7. What is the word for a strong Japanese wind? 8. How fast can debris travel in a tornado? 9. Weather forecasting is good for how many hours ahead? 10. How long has it been for some parts of the South American desert since it has gotten rain? 11. Does cold or warm air hold more water? 12. How many ...
... 7. What is the word for a strong Japanese wind? 8. How fast can debris travel in a tornado? 9. Weather forecasting is good for how many hours ahead? 10. How long has it been for some parts of the South American desert since it has gotten rain? 11. Does cold or warm air hold more water? 12. How many ...
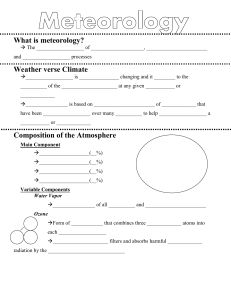
What is meteorology? The ________________ of ___________
... Precipitation: is any ______ of _________ that _______ from a ____________. When it comes to ______________________ atmospheric processes, _____________________ is the most ______________________ ______________ in the __________________ ...
... Precipitation: is any ______ of _________ that _______ from a ____________. When it comes to ______________________ atmospheric processes, _____________________ is the most ______________________ ______________ in the __________________ ...
Weather Lab Powerpoint Charts
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
... Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
Climate and Weather
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
... As this air cools down, it falls as rain or snow. The windward sides of a mountain tend to be wetter than the leeward sides (the sides sheltered from the wind). Rain Shadow – the area on the leeward side of a mountain that receives little precipitation. ...
“Meteorology”? - U. S. Naval Sea Cadet Corps Resources Page
... The sun’s energy is more concentrated when the sun is directly overhead (a) than when it is at an angle (b). ...
... The sun’s energy is more concentrated when the sun is directly overhead (a) than when it is at an angle (b). ...
weather reviewScienc.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... c) also known as atmospheric pressure d) happens mostly when the temperature is very low 7. Dewpoint is NOT: a) measured in ºC b) a measure of atmospheric moisture c) used by pilots d) the temperature at which air must be cooled to form water droplets 8. We always give speed and direction with wind, ...
... c) also known as atmospheric pressure d) happens mostly when the temperature is very low 7. Dewpoint is NOT: a) measured in ºC b) a measure of atmospheric moisture c) used by pilots d) the temperature at which air must be cooled to form water droplets 8. We always give speed and direction with wind, ...
1. The atmosphere is a layer of gases that surround the earth_
... 6. Why is air pressure greatest at the Earth’s surface? Because ...
... 6. Why is air pressure greatest at the Earth’s surface? Because ...
Weather and Water Cycle Study Guide
... 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temperature at which water freezes (32 degrees Fahrenheit ). 8.clouds: form when water vapor cools and condensation dust particu ...
... 4.climate: pattern of weather in an area over time. 5.current: stream of water that flows like a river in the ocean. 6.meteorology: study of weather. 7.freezing point: the temperature at which water freezes (32 degrees Fahrenheit ). 8.clouds: form when water vapor cools and condensation dust particu ...
Weather Tools
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
... • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. ...
A Short Note on Pineapple Express
... the Pacific coast of North America (see Fig. 1). Such an “atmospheric river” is usually marked by a quasi-stationary surface front along which mobile cyclones develop and track toward the coast. Periods of heavy precipitation occur when the warm moist air is forced over the coastal mountain ranges. ...
... the Pacific coast of North America (see Fig. 1). Such an “atmospheric river” is usually marked by a quasi-stationary surface front along which mobile cyclones develop and track toward the coast. Periods of heavy precipitation occur when the warm moist air is forced over the coastal mountain ranges. ...
Weather Unit 2
... weather patterns not only for that present time but also for the weather of the next several days. ...
... weather patterns not only for that present time but also for the weather of the next several days. ...
5 th 6 Weeks - Weather Vocabulary
... 27. Occluded front - forms when a cold front overtakes a warm front, capturing the warm air mass between two cold air masses-generally produces light rain or other precipitation ...
... 27. Occluded front - forms when a cold front overtakes a warm front, capturing the warm air mass between two cold air masses-generally produces light rain or other precipitation ...
Earth Science SOL Review Power Point (Oceanography and
... Stratus 21. What does water vapor condense on? _______________________________ 22. Winds blow from _____________ pressure to ___________ pressure. 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ___ ...
... Stratus 21. What does water vapor condense on? _______________________________ 22. Winds blow from _____________ pressure to ___________ pressure. 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ___ ...
Section 6.2
... spark of light that occurs within a storm cloud, between a cloud and Earth’s surface, or between two storm clouds. ...
... spark of light that occurs within a storm cloud, between a cloud and Earth’s surface, or between two storm clouds. ...
6.2 Cloud formation
... spark of light that occurs within a storm cloud, between a cloud and Earth’s surface, or between two storm clouds. ...
... spark of light that occurs within a storm cloud, between a cloud and Earth’s surface, or between two storm clouds. ...
what to know about meteorology list
... cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds occurs. **Making air rise will almost always make clouds; air rises along fronts, in a low pressure system, up a mountain or just because it is heated so ALL these things are associated with prec ...
... cools as it rises; temperature falls to the dew point; condensation (onto condensation nuclei) of clouds occurs. **Making air rise will almost always make clouds; air rises along fronts, in a low pressure system, up a mountain or just because it is heated so ALL these things are associated with prec ...
170131_PR_KISTERS_HydroMaster_en_final
... Situational awareness Severe weather events pose a direct threat to life, health, infrastructure, production and assets. Such threats are becoming increasingly severe due to increased urbanisation, population growth and climate change. Extreme and highly localised weather events are appearing more ...
... Situational awareness Severe weather events pose a direct threat to life, health, infrastructure, production and assets. Such threats are becoming increasingly severe due to increased urbanisation, population growth and climate change. Extreme and highly localised weather events are appearing more ...
Severe weather

Severe weather refers to any dangerous meteorological phenomena with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. Types of severe weather phenomena vary, depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High winds, hail, excessive precipitation, and wildfires are forms and effects of severe weather, as are thunderstorms, downbursts, lightning, tornadoes, waterspouts, tropical cyclones, and extratropical cyclones. Regional and seasonal severe weather phenomena include blizzards, snowstorms, ice storms, and duststorms.