Weather Unit Foldable - Cole`s Science Pages
... - This is the layer we live in and the smallest layer – Temperature decreases as altitude increases 140 to 76 degrees F – All weather happens here – This is the ONLY layer living things can live in – 16 km above sea level ...
... - This is the layer we live in and the smallest layer – Temperature decreases as altitude increases 140 to 76 degrees F – All weather happens here – This is the ONLY layer living things can live in – 16 km above sea level ...
FOSS Weather and Water Glossary FOSS Weather and
... Glossary (10/5/04) Absorb: To take in; to transform radiant energy into a different form, resulting in a rise in temperature. Air mass: A large body of air that has uniform temperature and humidity. Air masses have distinct boundaries and can extend hundreds or thousands of kilometers over Earth’s s ...
... Glossary (10/5/04) Absorb: To take in; to transform radiant energy into a different form, resulting in a rise in temperature. Air mass: A large body of air that has uniform temperature and humidity. Air masses have distinct boundaries and can extend hundreds or thousands of kilometers over Earth’s s ...
Weather Unit Foldable
... Rain and flooding along the Pacific coast Warm water disrupts food chain of fish, birds, and sea mammals Tornadoes and thunderstorms in southern US Fewer than normal hurricanes in the Atlantic ...
... Rain and flooding along the Pacific coast Warm water disrupts food chain of fish, birds, and sea mammals Tornadoes and thunderstorms in southern US Fewer than normal hurricanes in the Atlantic ...
... 8. Check your straw regularly and keep marking its location on the paper for a few days. Add notes that tell you what the weather is like (e.g. "rainy," "windy," or "sunny,") next to the mark. 9. Examine the paper after several days. Check the markings and the weather statements you have put next to ...
chapter 4 - Maritime Safety Queensland
... system that draws in the cooler air from offshore (the sea breeze). The resultant onshore breezes may be vigorous by late afternoon, particularly in the summer months. The rising air along coastal hinterlands, particularly where the higher land reinforces the uplift of air, may produce heavy cloud b ...
... system that draws in the cooler air from offshore (the sea breeze). The resultant onshore breezes may be vigorous by late afternoon, particularly in the summer months. The rising air along coastal hinterlands, particularly where the higher land reinforces the uplift of air, may produce heavy cloud b ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6
... 31. Coriolis force is due to the _____________________________________________________. In the Northern Hemisphere, this force causes air to turn to the ___________________. 32. Geostrophic balance, a balance between ______________________________________________ and ________________________________ ...
... 31. Coriolis force is due to the _____________________________________________________. In the Northern Hemisphere, this force causes air to turn to the ___________________. 32. Geostrophic balance, a balance between ______________________________________________ and ________________________________ ...
Introduction to Meteorology Homework #3 (Chapters 5 and 6) Due
... 31. Coriolis force is due to the _____________________________________________________. In the Northern Hemisphere, this force causes air to turn to the ___________________. 32. Geostrophic balance, a balance between ______________________________________________ and ________________________________ ...
... 31. Coriolis force is due to the _____________________________________________________. In the Northern Hemisphere, this force causes air to turn to the ___________________. 32. Geostrophic balance, a balance between ______________________________________________ and ________________________________ ...
weather test study guide
... 10. What causes different types of precipitation? The temperature of the air: cold air causes sleet or snow, while hail is formed very high in the atmosphere. Rain forms in warmer air. 11. What tools do meteorologists use to make weather forecasts? Rain gauges, wind vanes, anemometers, barometers, h ...
... 10. What causes different types of precipitation? The temperature of the air: cold air causes sleet or snow, while hail is formed very high in the atmosphere. Rain forms in warmer air. 11. What tools do meteorologists use to make weather forecasts? Rain gauges, wind vanes, anemometers, barometers, h ...
Weather Lab Powerpoint Charts
... Weather vs climate Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
... Weather vs climate Atmosphere Temperature Wind Humidity Precipitation Air pressure Fronts ...
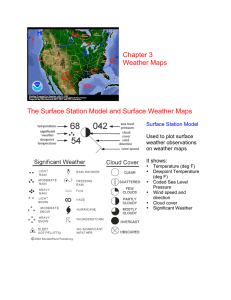
Chapter 3 Weather Maps The Surface Station Model and Surface
... Temperature gradient – change in temperature over a given distance Isodrosotherms – contour lines of constant dewpoint temperature ...
... Temperature gradient – change in temperature over a given distance Isodrosotherms – contour lines of constant dewpoint temperature ...
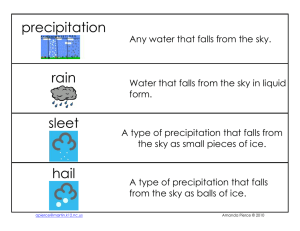
precipitation rain sleet hail
... The movement of water from Earth’s surface into the air, and back to the Earth’s surface. ...
... The movement of water from Earth’s surface into the air, and back to the Earth’s surface. ...
History of Meteorology
... Short term weather forecasts (24-48 hours) Long term weather forecasts (up to 5 days or longer) ...
... Short term weather forecasts (24-48 hours) Long term weather forecasts (up to 5 days or longer) ...
Atmosphere and Weather Study Guide
... Nitrogen makes up 78% of the earth’s atmosphere and oxygen makes up 21%. 3. Why is the atmosphere important to life on Earth? It traps energy from the sun to keep Earth’s surface warm and water in liquid form. The atmosphere protects living things from dangerous radiation from the sun. It also preve ...
... Nitrogen makes up 78% of the earth’s atmosphere and oxygen makes up 21%. 3. Why is the atmosphere important to life on Earth? It traps energy from the sun to keep Earth’s surface warm and water in liquid form. The atmosphere protects living things from dangerous radiation from the sun. It also preve ...
Air Pressure and Winds-I
... Air moves from high to low pressure in middle of column, causing surface pressure to change. Difference in pressure in ...
... Air moves from high to low pressure in middle of column, causing surface pressure to change. Difference in pressure in ...
Science Scientific Method - SOEST
... ~1450 Cardinal Nicholas de Cusa invented hygrometer. ~1590 Galileo invented thermometer. 1643 A student of Galileo, Torricelli, invented the water barometer to measure atmospheric pressure. Galileo used mercury the next year. ~1650 Pascal and Descartes demonstrated that pressure decreases with heigh ...
... ~1450 Cardinal Nicholas de Cusa invented hygrometer. ~1590 Galileo invented thermometer. 1643 A student of Galileo, Torricelli, invented the water barometer to measure atmospheric pressure. Galileo used mercury the next year. ~1650 Pascal and Descartes demonstrated that pressure decreases with heigh ...
Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
... b. are generally faster than surface winds. c. are unaffected by the Coriolis force. d. do not influence surface weather. ...
... b. are generally faster than surface winds. c. are unaffected by the Coriolis force. d. do not influence surface weather. ...
5 th 6 Weeks - Weather Vocabulary
... 5th 6 Weeks - Weather Vocabulary 1. Weather - the condition of the atmosphere at a place for a short period of time 2. Weather Forecast - a prediction of what the weather will be, based on weather data 3. Weather System - an area in the lower atmosphere where the air is moving around a high or low a ...
... 5th 6 Weeks - Weather Vocabulary 1. Weather - the condition of the atmosphere at a place for a short period of time 2. Weather Forecast - a prediction of what the weather will be, based on weather data 3. Weather System - an area in the lower atmosphere where the air is moving around a high or low a ...
WPF-Weather101
... especially with weather." An Atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the Earth that is held in place by Earth's gravity." ...
... especially with weather." An Atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the Earth that is held in place by Earth's gravity." ...
Classroom Teacher Preparation Earth Science 16: Weather
... Fronts – boundaries between warm and cold air Pressure – the weight of air pressing down on earth Rain – drops of liquid water that fall to earth’s surface Snow – water vapor frozen into ice crystals Sleet – ice pellets that form when raindrops hit a subfreezing patch of air near earth’s surface Hai ...
... Fronts – boundaries between warm and cold air Pressure – the weight of air pressing down on earth Rain – drops of liquid water that fall to earth’s surface Snow – water vapor frozen into ice crystals Sleet – ice pellets that form when raindrops hit a subfreezing patch of air near earth’s surface Hai ...
Lecture Packet#1
... height. Climbing to an altitude of only 5.5 km where the pressure is 500 mb, would put you above one-half of the atmosphere’s molecules. ...
... height. Climbing to an altitude of only 5.5 km where the pressure is 500 mb, would put you above one-half of the atmosphere’s molecules. ...
The Earth`s Atmosphere
... toward earth's surface, and the whole column of gases weighs 14.7 psi at sea level, a pressure of 1013.25 mb or 29.92 in.Hg. The amount of force exerted Over an area of surface is called Air pressure! Air Density is The number of air Molecules in a given Space (volume) ...
... toward earth's surface, and the whole column of gases weighs 14.7 psi at sea level, a pressure of 1013.25 mb or 29.92 in.Hg. The amount of force exerted Over an area of surface is called Air pressure! Air Density is The number of air Molecules in a given Space (volume) ...
File
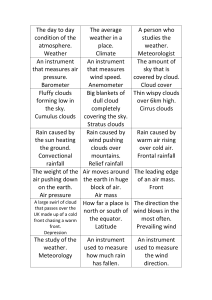
... A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that passes over the north or south of UK made up of a cold the equator. front chasing a warm front. Latitude ...
... A large swirl of cloud How far a place is that passes over the north or south of UK made up of a cold the equator. front chasing a warm front. Latitude ...
4th Grade Weather Read and answer each question carefully. 1
... pressure. You notice the pressure is dropping. What do you predict will happen to the weather? A) It will be sunny. B) It will be hotter. C) It will not change. D) It will rain. ...
... pressure. You notice the pressure is dropping. What do you predict will happen to the weather? A) It will be sunny. B) It will be hotter. C) It will not change. D) It will rain. ...
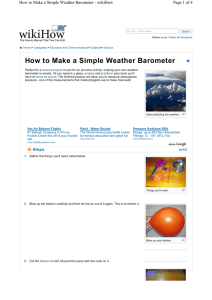
Barometer

A barometer is a scientific instrument used in meteorology to measure atmospheric pressure. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Numerous measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, high pressure systems and frontal boundaries.Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be transported from place to place matching the atmospheric pressure to the corresponding altitude, while a barometer is kept stationary and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather. The main exception to this is ships at sea, which can use a barometer because their elevation does not change. Due to the presence of weather systems, aircraft altimeters may need to be adjusted as they fly between regions of varying normalized atmospheric pressure.