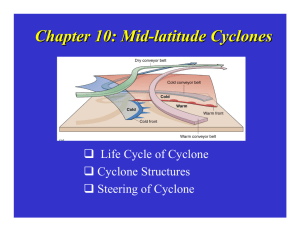
Atmospheric circulation structures associated with freezing rain in
... the surface, 850 hPa, and 500 hPa, bracket the potential interval of duration of each event. As outlined by Cheng et al. (1), duration thresholds, chosen to be 8 and 12h, are used to determine variability among the categories. The longest events are found in the EC and CP categories. Moreover, 80% o ...
... the surface, 850 hPa, and 500 hPa, bracket the potential interval of duration of each event. As outlined by Cheng et al. (1), duration thresholds, chosen to be 8 and 12h, are used to determine variability among the categories. The longest events are found in the EC and CP categories. Moreover, 80% o ...
Click here to chapter 5
... Three terms that we’ve used in this chapter are wind, airflow, and atmospheric circulation. Though their meanings may seem obvious, it is necessary before going ahead to clarify what meteorologists mean by these terms. Wind is essentially the movement of air relative to earth’s surface. As you’ll fi ...
... Three terms that we’ve used in this chapter are wind, airflow, and atmospheric circulation. Though their meanings may seem obvious, it is necessary before going ahead to clarify what meteorologists mean by these terms. Wind is essentially the movement of air relative to earth’s surface. As you’ll fi ...
the MSWord file, in format.
... Thought questions: what is the difference between weather and climate? From my all time favorite blog – www.wasatchweatherweenies by Jim Steenburgh of UofU meteorology… from what meteorologists quip: “Climate is what you expect… weather is what you get.” Content Some Terms: CLIMATE... long-term we ...
... Thought questions: what is the difference between weather and climate? From my all time favorite blog – www.wasatchweatherweenies by Jim Steenburgh of UofU meteorology… from what meteorologists quip: “Climate is what you expect… weather is what you get.” Content Some Terms: CLIMATE... long-term we ...
Earth Systems
... 9. Dew point is the temp when condensation occurs. The more water vapor in the air, the higher the relative humidity, so the higher the dew point. 10. The warm, moist air has a high R.H. and reaches the dew point when it cools around the glass, therefore forming condensation ...
... 9. Dew point is the temp when condensation occurs. The more water vapor in the air, the higher the relative humidity, so the higher the dew point. 10. The warm, moist air has a high R.H. and reaches the dew point when it cools around the glass, therefore forming condensation ...
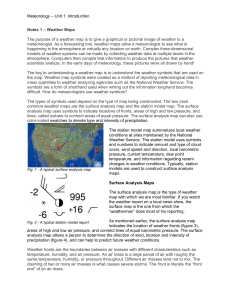
Notes 1 Weather Maps - Spearfish School District
... There are two main types of barometers – the most widely available and reliable Mercury Barometers, or the newer digital friendly Aneroid Barometer. How does a Barometer Work? The classic mercury barometer is typically a glass tube about 3 feet high with one end open and the other end sealed. The tu ...
... There are two main types of barometers – the most widely available and reliable Mercury Barometers, or the newer digital friendly Aneroid Barometer. How does a Barometer Work? The classic mercury barometer is typically a glass tube about 3 feet high with one end open and the other end sealed. The tu ...
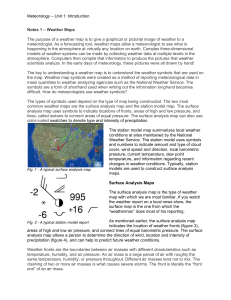
Meteorology – Unit 1: Introduction Notes 1 – Weather Maps The
... There are two main types of barometers – the most widely available and reliable Mercury Barometers, or the newer digital friendly Aneroid Barometer. How does a Barometer Work? The classic mercury barometer is typically a glass tube about 3 feet high with one end open and the other end sealed. The tu ...
... There are two main types of barometers – the most widely available and reliable Mercury Barometers, or the newer digital friendly Aneroid Barometer. How does a Barometer Work? The classic mercury barometer is typically a glass tube about 3 feet high with one end open and the other end sealed. The tu ...
Conservation of Angular Momentum
... angular velocity of the earth, is taken to 30N. Question: What happens to the object's tangential and angular velocities? Answer: As the object moves to the North the distance to the earth's axis decreases. Thus, both the angular velocity and tangential velocity must increase; the object moves to th ...
... angular velocity of the earth, is taken to 30N. Question: What happens to the object's tangential and angular velocities? Answer: As the object moves to the North the distance to the earth's axis decreases. Thus, both the angular velocity and tangential velocity must increase; the object moves to th ...
Atmospheric convection

Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference, layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes.