Chapter 1: The World of Energy, Introduction to Physics 104
... positive charge (+) and negative charge (–). Objects with equal numbers of positive and negative charge have a total net charge of zero and are electrically neutral. Objects with more positive than negative charge have a net positive charge, and objects with more negative than positive charge have a ...
... positive charge (+) and negative charge (–). Objects with equal numbers of positive and negative charge have a total net charge of zero and are electrically neutral. Objects with more positive than negative charge have a net positive charge, and objects with more negative than positive charge have a ...
Electron-Cloud Energy and Angular Distributions
... revealing the peak at very low energies. Bottom: enlarged scale illustrating details of the spectrum at higher energies. The energy spectra indicate that there is a maximum electron energy. Such limit is most clearly seen in the SPS spectrum of Fig. 3 It is not unexpected since the momentum transfer ...
... revealing the peak at very low energies. Bottom: enlarged scale illustrating details of the spectrum at higher energies. The energy spectra indicate that there is a maximum electron energy. Such limit is most clearly seen in the SPS spectrum of Fig. 3 It is not unexpected since the momentum transfer ...
Energy Stored by Radiating Systems
... The total energy of a dynamic system, see Box 1, represents a well-known and fundamental characteristic describing the energy stored in all of its degrees of freedom. By contrast, the observable part of total energy is a more subtle quantity typically defined in such a way that its value has a direc ...
... The total energy of a dynamic system, see Box 1, represents a well-known and fundamental characteristic describing the energy stored in all of its degrees of freedom. By contrast, the observable part of total energy is a more subtle quantity typically defined in such a way that its value has a direc ...
Preparing - broward.k12.fl.us
... •applying the domain theory to the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials •determining the orientation and magnitude of a magnetic field •determining the magnitude and direction of the force on a charge or charges moving in a magnetic field •analyzing the behavior of a current-carrying wire in a m ...
... •applying the domain theory to the magnetization of ferromagnetic materials •determining the orientation and magnitude of a magnetic field •determining the magnitude and direction of the force on a charge or charges moving in a magnetic field •analyzing the behavior of a current-carrying wire in a m ...
Chapter 2 ENERGY, ENERGY TRANSFER, AND
... 2-15C Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in two forms: heat and work. 2-16C The form of energy that crosses the boundary of a closed system because of a temperature difference is heat; all other forms are work. 2-17C An adiabatic process is a process during which there is no heat tra ...
... 2-15C Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in two forms: heat and work. 2-16C The form of energy that crosses the boundary of a closed system because of a temperature difference is heat; all other forms are work. 2-17C An adiabatic process is a process during which there is no heat tra ...
Introduction to quantum and solid state physics for
... computers/mobile phones; this is a partial list of technologies which rely on quantum mechanics to work. As an engineer you should have an understanding of how they work. If you don’t, you’ll be left behind. It’s true that engineering software often calculates the quantum effects ...
... computers/mobile phones; this is a partial list of technologies which rely on quantum mechanics to work. As an engineer you should have an understanding of how they work. If you don’t, you’ll be left behind. It’s true that engineering software often calculates the quantum effects ...
1 - Henry County Schools
... A solid metal ball and a hollow plastic ball of the same external radius are released from rest in a large vacuum chamber. When each has fallen 1m, they both have the same (A) inertia (B) speed (C) momentum (D) kinetic energy (E) change in potential energy ...
... A solid metal ball and a hollow plastic ball of the same external radius are released from rest in a large vacuum chamber. When each has fallen 1m, they both have the same (A) inertia (B) speed (C) momentum (D) kinetic energy (E) change in potential energy ...
9646 Physics H2 syllabus for 2016
... (a) recall the following base quantities and their units: mass (kg), length (m), time (s), current (A), temperature (K), amount of substance (mol) (b) express derived units as products or quotients of the base units and use the named units listed in ‘Summary of Key Quantities, Symbols and Units’ as ...
... (a) recall the following base quantities and their units: mass (kg), length (m), time (s), current (A), temperature (K), amount of substance (mol) (b) express derived units as products or quotients of the base units and use the named units listed in ‘Summary of Key Quantities, Symbols and Units’ as ...
HEAT - Weebly
... Latent Heat: Latent heat describes the amount of energy in the form of heat that is required for a material to undergo a change of phase. A solid consists of molecules that are tightly bound to each other by forces acting between them. Energy must be supplied in the form of heat to overcome these f ...
... Latent Heat: Latent heat describes the amount of energy in the form of heat that is required for a material to undergo a change of phase. A solid consists of molecules that are tightly bound to each other by forces acting between them. Energy must be supplied in the form of heat to overcome these f ...
Assemblage: Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases
... (b) Evaluate the contribution of defects to the entropy and to the specific heat to first order in exp (−ω/2T ). A14. N atoms of mass m of an ideal classical gas are in a cylinder with insulating walls, closed at one end by a piston. The initial volume and temperature are V0 and T0 , respectively. ( ...
... (b) Evaluate the contribution of defects to the entropy and to the specific heat to first order in exp (−ω/2T ). A14. N atoms of mass m of an ideal classical gas are in a cylinder with insulating walls, closed at one end by a piston. The initial volume and temperature are V0 and T0 , respectively. ( ...
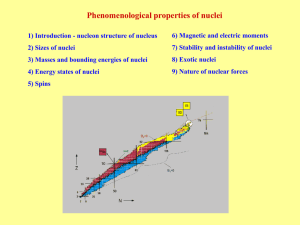
Snímek 1
... Neutron scattering (mass distribution) larger r0. Larger volume of neutron matter is done by larger number of neutrons at nuclei (in the other case the volume of protons should be larger because Coulomb repulsion). Distribution of mass density connected with charge ρ = f(r) measured by electron sc ...
... Neutron scattering (mass distribution) larger r0. Larger volume of neutron matter is done by larger number of neutrons at nuclei (in the other case the volume of protons should be larger because Coulomb repulsion). Distribution of mass density connected with charge ρ = f(r) measured by electron sc ...
motion in straight line
... When you listen to someone describing how to get to a place they sometimes talk about how _____ to walk or drive, but they _____ describe which direction to travel in. They may do this by simply _____, or saying keep going straight, or go left, then right, or go west then north. If you live 20 km fr ...
... When you listen to someone describing how to get to a place they sometimes talk about how _____ to walk or drive, but they _____ describe which direction to travel in. They may do this by simply _____, or saying keep going straight, or go left, then right, or go west then north. If you live 20 km fr ...
heat and temperature
... What differences can you observe between the two ways of heating up? A2: Choose fire as the source of heat. Click on play until the temperature (average energy) is equal to 5 units. Write down the time taken. Click on init and double the number of particles. What can you observe regarding the new te ...
... What differences can you observe between the two ways of heating up? A2: Choose fire as the source of heat. Click on play until the temperature (average energy) is equal to 5 units. Write down the time taken. Click on init and double the number of particles. What can you observe regarding the new te ...
R eduction(12).pdf
... modeling is likely to use of Bayes theorem (because it is a theorem of probability), but not all probabilistic modeling is Bayesian. In fact, the use of ensembles obviates the need for priors probabilities, which is the hallmark of Bayesianism. The ensemble approach, coupled with the optimization of ...
... modeling is likely to use of Bayes theorem (because it is a theorem of probability), but not all probabilistic modeling is Bayesian. In fact, the use of ensembles obviates the need for priors probabilities, which is the hallmark of Bayesianism. The ensemble approach, coupled with the optimization of ...
Electric fields are
... Electric Potential Energy can be considered unrealized kinetic energy for a particle in a fixed location. It takes work to move a particle from a position of lower potential energy to a position of higher potential energy. This increase in potential energy at rest may be converted to (or “realized a ...
... Electric Potential Energy can be considered unrealized kinetic energy for a particle in a fixed location. It takes work to move a particle from a position of lower potential energy to a position of higher potential energy. This increase in potential energy at rest may be converted to (or “realized a ...
ITER_en - Site officiel de l`Association Savoir sans
... system does not allow the minimal temperature of 100 million degrees, necessary to provoke the establishment of auto-maintained fusion reactions, to be obtained. Additional methods of heating are therefore used: hyperfrequencies and neutral particles injection. Fusion reactions were obtained during ...
... system does not allow the minimal temperature of 100 million degrees, necessary to provoke the establishment of auto-maintained fusion reactions, to be obtained. Additional methods of heating are therefore used: hyperfrequencies and neutral particles injection. Fusion reactions were obtained during ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.










![Assemblage: Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930189_1-a7a37d9ca413714c6a603f524253db38-300x300.png)